|
一、I/O类型及与其相关概念: 1.1同步和异步:synchronous, asynchronous 【关注的是消息通知机制】 同步:调用发出不会立即返回,但一旦返回就可以返回最终结果; 异步:调用发出之后,被调用方立即返回消息,但返回的非最终结果;被调用者通过状态、通知机制来通知调者,或通过回调函数来处理结果; 1.2阻塞和非阻塞:block, nonblock【关注的是调用等等调用结果(消息、返回值)时的状态】 阻塞:调用结果返回之前,调用者(调用线程)会被挂起;调用者只有在得到结果之后才会返回; 阻塞:调用结果返回之前,调用不会阻塞当前线程; 1.3五种I/O模型; 阻塞型IO [blocking IO] 非阻塞型IO [nonblocking IO] 复用型IO [IO multiplexing]【slect,poll复用器】pefork,worker 信号驱动型IO [signal driven IO]【epoll】 event 异步IO [asyncrhonous IO] 其工作流程如下:
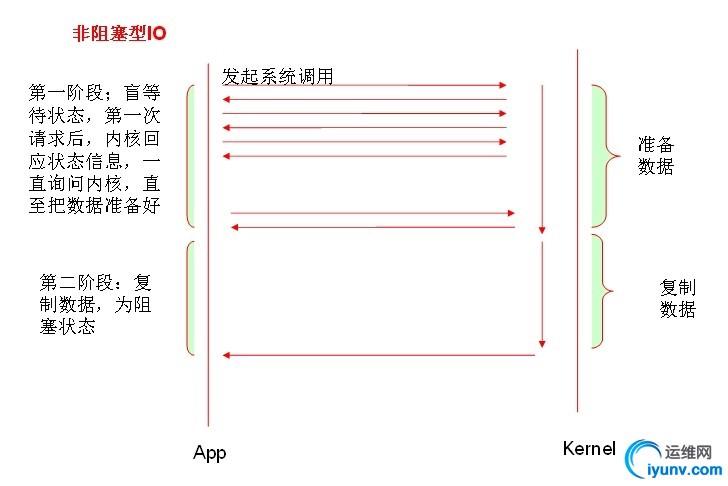
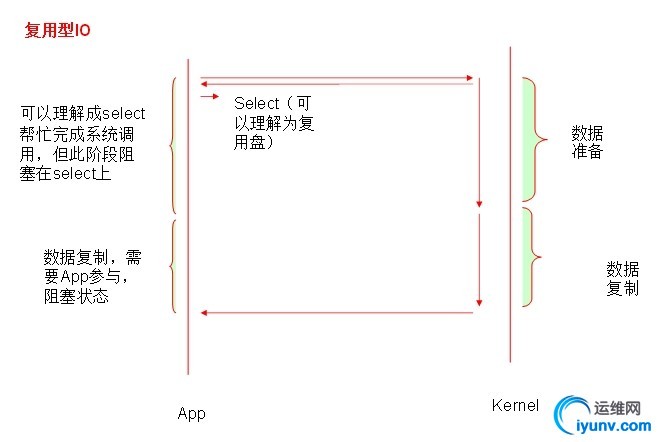
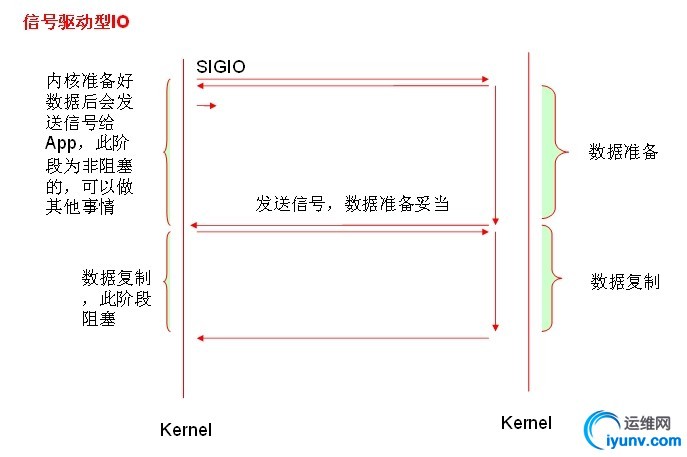
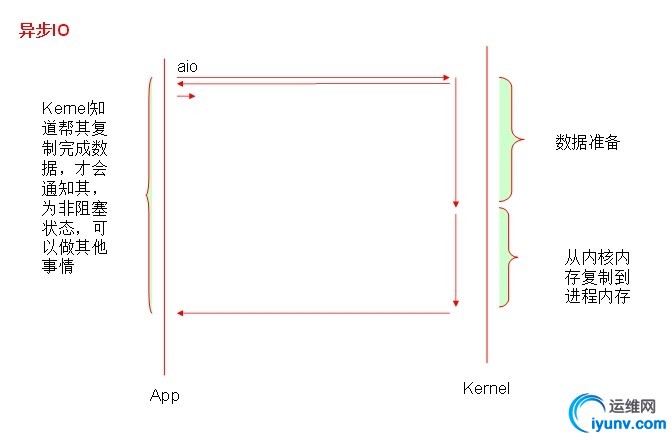
1.4一个read操作:(1) 等待数据准备好;(2) 从内核向进程复制数据;
1.5 轮询与触发 (1)轮询:用一个进程,但是使用非阻塞的I/O读取数据,当一个I/O不可读的时候立刻返回,检查下一个是否可读,这种形式的循环为轮询(polling),这种方法比较浪费CPU时间,因为大多数时间是不可读,但是仍花费时间不断反复执行read系统调用 (2)水平触发:当条件满足后会一直响应;信号驱动IO为例;此处理解为,当数据准备好后,内核会一直发送消息通知进程,直到进程响应为止 (3)边缘触发:当条件满足的瞬间才会响应; 1.5Select、Poll、Epoll 1.5.1 Select (1)最大并发数限制,因为一个进程所打开的 FD (文件描述符)是有限制的,由 FD_SETSIZE 设置,默认值是 1024/2048 ,因此 Select 模型的最大并发数就被相应限制了。文件描述符数FD_SETSIZE 此处无法更改 (2)效率问题,select 每次调用都会线性扫描全部的 FD 集合,这样效率就会呈现线性下降,把 FD_SETSIZE 改大的后果就是,大家都慢慢来,什么?都超时了。 (3)内核 / 用户空间内存拷贝问题,如何让内核把 FD 消息通知给用户空间呢?在这个问题上select 采取了内存拷贝方法。 总结为:1.连接数受限 2.查找配对速度慢 3.数据由内核拷贝到用户态 1.5.2 Poll 基本上效率和 select 是相同的, select 缺点的 (2) 和 (3)它都没有改掉。 1.5.3 Epoll (1) Epoll 没有最大并发连接的限制,上限是最大可以打开文件的数目,这个数字一般远大于 2048, 一般来说这个数目和系统内存关系很大 ,具体数目可以 cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 察看。 (2)效率提升,Epoll 最大的优点就在于它只管你“活跃”的连接 ,而跟连接总数无关,因此在实际的网络环境中,Epoll 的效率就会远远高于 select 和 poll 。 (3)内存拷贝,Epoll 在这点上使用了“共享内存 ”,这个内存拷贝也省略了 1.6 prefork、worker、event prefork:多进程模型,每个进程响应一个请求;稳定性好,但并发能力有限;预先生成多个空闲进程;select系统调用,最多1024个; worker:多进程模型,每个进程可生成多个线程,每个线程响应一个请求;预先生成多个空闲线程;(select) event:一个进程直接响应n个请求;可同时启动多个进程
1.7 nginx支持的IO类型: 异步IO(aio)、信号驱动型(边缘触发)、内存映射、事件驱动 libevent:epoll
二、Nginx概念及特点简介: 2.1 概念; Nginx (读作"engine X") 由IgorSysoev(俄罗斯)于2005年编写,是一个免费、开源、高性能的HTTP服务器和反向代理,也可以作为一个IMAP/POP3代理服务器。Nginx因为稳定,丰富的功能集,配置简单,资源占用低而闻名世界。 2.2 Nginx的特性: (1)模块化设计、较好扩展性 (2)高可靠性:每个worker进程相对独立,master进程在1个worker进程出错时可以快速“拉起”新的worker子进程提供服务 (3)低内存消耗:10000个keep-alive连接在Nginx仅消耗2.5MB (4)支持热部署:master管理进程与worker工作进程的分离设计,使得Nginx能够提供热部署功能,即可以在7×24小时不间断服务的前提下,升级Nginx的可执行文件。当然,它也支持不停止服务就更新配置项、更换日志文件等功能。 2.3 基本功能: (1)静态资源的web服务器,能缓存打开的文件 描述符 (2)http, smtp, pop3协议的反向代理服务器,缓存、负载均衡; (3)支持FastCGI (fpm) (4)模块化,非DSO机制,过滤器zip,SSI及图像大小调整; (5)支持SSL 2.4 扩展功能: 基于名称和IP的虚拟主机访问控制 支持keepalive 支持平滑升级 定制访问日志 ,支持使用日志缓冲区提高日志存储性能 支持url rewrite(路径重写) 支持路径别名 支持基于IP及用户的访问控制 支持速率限制,支持并发数限制 2.5 Nginx的基本架构:(非阻塞、事件驱动、一个master生成一个或多个worker, 每个worker响应n个请求) 一个master进程,生成一个或多个worker 事件驱动: epoll, kqueue,/dev/poll (event ports) 消息通知:select, poll, rtsignals 支持sendfile, sendfile64 支持AIO(异步IO) 支持mmap(内存映射) 2.6 模块类型: 核心模块:core modules 标准HTTP模块:Standard HTTP modules 可选HTTP模块:Optional HTTP modules 邮件模块:Mail modules(作为邮件反向代理服务器时用) 第三方模块:3rd party modules
三、安装方法 3.1 RPM包安装:http://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html#stable 3.2 源码安装; (1)下载源码包 mget http://nginx.org/en/download.html Stable version(2)编译环境准备 # yum groupinstall "Development Tools""Server Platform Development" # yum install pcre-devel openssl-devel -y (3)解压安装 # tar xf nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz # cd nginx-1.6.2 # ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --user=nginx --group=nginx--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --with-http_ssl_module--with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_flv_module--with-http_mp4_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fastcgi # make && make install # mkdir /var//tmp/nginx/{client,proxy,fastcgi} -pv (4)启动与关闭 # /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #检查语法 # /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #启动nginx, # ss -tnlp #查看80端口,在浏览器上查看nginx成功启动 [ps -elFH,查看nginx启动的进程] #killall nginx (5)配置启动服务脚本【脚本添加具体内容见附件Nginx服务启动脚本】 # vim /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx # chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx # chkconfig --add nginx # chkconfig --list nginx # service nginx restart
四、核心模块相关配置文件(ngx_http_core_module); 4.1 语法着色【扩展插件】
(1)下载nginx.vim (2)安装nginx.vim 将nginx.vim放置于~/.vim/syntax/目录, # mkdir .vim/syntax/ -pv # cp nginx.vim .vim/syntax/ (3)配置 nginx.vim 而后在~/.vim/filetype.vim中添加如下行: au BufRead,BufNewFile/etc/nginx/*,/usr/local/nginx/conf/* if &ft == '' | setfiletype nginx |endif 其中“/etc/nginx”为nginx配置文件的目录
4.2核心配置段:Main 配置段 对应协议配置段:如http{...} 主体架构。如下图所示
4.3 配置指令要以分号结尾,语法格式: directivevalue1 [value2...]; 4.4 支持使用变量: 模块内置变量 自定义变量 setvar_name value 4.5 主配置段的指令的类别: 用于调试、定位问题 正常运行必备的配置 优化性能的配置 事件相关的配置 4.6 正常运行的必备配置: (1) user USERNAME [GROUPNAME]; 指定运行worker进程的用户 和组,例如:user nginx nginx;s (2)pid /path/to/pid_file; 指定nginx的pid文件; (3) worker_rlimit_nofile #; 指定一个worker进程所能够打开的最大文件句柄数(进程数); (4)worker_rlimit_sigpending #; 指定每个用户能够发往worker的信号的数量; 4.7 优化性能相关的配置: (1)worker_processes #: worker线程的个数;通常应该为物理CPU核心个数减1; (2)worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...; 绑定worker进程至指定的CPU上; CPUMASK (假如有四颗cpu,表示法) 0001 0010 0100 1000 例如:worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100; (3)timer_resolution t;时间解析度:每隔多久更新一次缓存;在x86_64系统上不用配置 gettimeofday(); (4)worker_priority nice;范围【-20, 19】
4.8 事件相关的配置: (1)accept_mutex [on|off] 【做压力测试时候用】 内部调用用户 请求至各worker时用的负载均衡锁;打开时表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地与响应新请求; (2)lock_file /path/to/lock_file; 锁文件 (3)accept_mutex_delay #ms; 每个worker进程拿到互斥锁可以相应请求,而此为等待拿到互斥锁的时间 (4)use [epoll|rgsig|select|poll]; 定义使用的事件模型;建议让Nginx自动选择; (5)worker_connections #; 每个worker进程所能够响应的最大并发请求数;
4.9 用于调试、定位问题: (1)daemon [off|on] 是否以守护进程方式启动nginx; (2)master_process on|off; 是否以master/worker模型来运行nginx; (3)error_log /path/to/error_log level; 错误日志文件及其级别;出于调试的目的,可以使用debug级别,但此级别只有在编译nginx时使用了--with-debug选项才有效;
4.10 虚拟主机相关的配置:【虚拟机及其他练习及演示信息参照附件Nginx配置练习】 (1) 定义一个虚拟主机;写在server {}配置段 (2)listen 监听的端口 完整格式 :listenaddress[:port] [default_server] [ssl] [spdy] [proxy_protocol] [setfib=number][fastopen=number] [backlog=number] [rcvbuf=size] [sndbuf=size][accept_filter=filter] [deferred] [bind] [ipv6only=on|off][so_keepalive=on|off|[keepidle]:[keepintvl]:[keepcnt]]; 常用格式:listenaddress[:port] [default_server] ssl 解析: backlog=number:指明TCP协议backlog队列的大小。默认为-1,表示不设置; rcvbuf=size:设定监听句柄的SO_RCVBUF参数;【接收缓冲大小】 [sndbuf=size]【发送缓冲大小】 [bind] 【表示一个端口绑定监听多个地址】 [ssl] 表示当前监听的端口需要支持ssl功能 Sets the address and port for IP, or the path for a UNIX-domain socket on which the server will accept requests. Both address and port, or only address or only port can be specified. An address may also be a hostname, for example: listen 127.0.0.1:8000; listen 127.0.0.1; listen 8000; listen *:8000; listen localhost:8000; (3)server_name name [...];【服务器名称或主机名】 后可跟多个主机名;名称还可以使用通配符和正则表达式(~);如果被匹配到,则可以响应 匹配规则: (b) 左侧通配符匹配,例如:*. iyunv.com; (c) 右侧通配符匹配,例如:www.*; (d) 正则表达式匹配,例如: ~^.*.magedu.com$ (e)default_server;如果都没有被匹配到,则显示默认主机 (4) location【多个优先级相同,靠前的locationn匹配】 (a)[=|~|~*|^~] /uri {...} 功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location块中的配置所处理; =: 精确匹配检查; ~: 正则表达式模式匹配,区分字符大小写; ~*:正则表达式模式 匹配,不区分字符大小写; ^~:URI的前半部分匹配,不检查正则表达式; 匹配优先级:精确匹配(=)、^~、~和~*、由不带符号的URL进行左侧匹配; Let’sillustrate the above by an example: location = / { [ configuration A] } location / { #以/为起始的所有路径 [ configuration B] } location /documents/ { [ configuration C] } location ^~ /images/ { [ configuration D] } location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ { [ configuration E] } The“/” request will match configuration A, the“/index.html” request will match configuration B, the“/documents/document.html”request will match configuration C, the“/images/1.gif” request will match configuration D, and the “/documents/1.jpg”request will match configuration E.
(b)location @name 前缀“@”定义了命名[指定]路径。这种路径不在一般的请求处理中使用,而是用在请求重定向中。这些路径不能嵌套,也不能包含嵌套路径。
(5)root 设置web资源路径映射;用于指明请求的URL所对应的文档的根目录路径; location /images/ { #【locations中也可省略】 root "/web/imgs/"; #【images的访问路径为/web/imgs/images;images目录必须存在,index.html在images目录下】 } (6)alias path 用于location配置段,定义路径别名 location /images/ { alias /www/pictures/; #【images的访问路径为/www/pictures/index.html】 } 注意:root表示指明路径为对应location的“ /” URL;alias表示路径映射,即location中的URL是相对于alias所指明的路径而言; (7)index file 【默认主页面】 indexindex.html; 放置位置:http,server,location 都可以,放在http,对所有server有效;放在server中,对所有location生效;放置location,则只对location有效 (8)error_page code [...] [=code]URI | @name【有名称的location,反向代理时会用到】 根据http状态码重定向错误页面 error_page 404 /404.html =[code]: 以指定的响应码进行响应;省略code表示以新资源的响应码为响应码; (9)try_files try_filespath1[,path2,...] URI 用在location中,定义多个路径,当用户访问一个路径时;如果第一个path找不到第一个,找第二个,…,如果都找不到,则重定向至最后一个参数的URI-path(了解即可)
4.11 网络连接相关的配置: (1)keepalive_timeout time; 保持连接的超时时长,默认为75s; (2)keepalive_requests #; 在一次保持连接上允许承载最大资源请求数; (3)keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none] 为指定类型的浏览器禁用长连接; (4)tcp_nodelay on|off 对长连接是否使用TCP_NODELAY选项;【当客户请求的资源少而小的时候,启用,客户体验好】 (5)client_header_timeout time; 读取http请求报文首部的超时时长;【对于较慢的网络连接,不怎么去响应】 (6)client_body_timeout time; 读取http请求报文body部分的超时时长;【一般不会超时;对于上传网速慢的不利,可能上传不成功,所以建议设置时长稍长一点】 (7)send_timeout time; 发送响应报文的超时时长;
4.12 对客户端请求进行限制:【通常用于http、server、location中】 (1)limit_except METHOD {...} 【在方法上做安全限制】 指定对范围之外的其它方法的访问控制; limit_exceptGET { #【指定范围之外的其他方法访问控制】 allow172.16.0.0/16; deny all; } 【只允许172.16网段的主机使用除GET以外的其他方法请求】 2、client_body_max_size SIZE; 【对用户上传文件的限制】 限制请求报文中body部分的上限;通过检测请求报文首部中的"Content_Length"来判定; 3、limit_rate speed; 限制客户端每秒种传输的字节数,默认为0,表示无限制;
4.13 对内存或磁盘资源进行分配【一般情况下,都不需要调整】 (1)client_body_in_file_only on|clean|off; 请求报文的body部分是否可暂存于磁盘【对于body较大者】;on表示允许,并且即使请求结束,也不会删除暂存的内容;clean表示会删除;off不允许暂存; (2)client_body_in_single_buffer on|off 请求报文的body部分是否可暂存在内存【内核内存】的buffer中,默认off;允许会提高性能 (3)client_body_buffer_size size; 如果(2)为on时,定义暂存空间大小 (4)client_body_temp_path DIR [level1 [level2[level3 [level4]]]] 如果(2)为on时【Client_body的】暂存文件存储路径 例如:client_body_temp_path/var/tmp/nginx/client 1 2 【一级子目录中,用2个字符定义路径,如ab,ac,ad…】 (5)client_header_buffer_size size: 接收用户请求报文的首部部分指定【分配】的内存空间的大小
4.14 MIME类型相关的配置: 1、types {} 定义MIME types至文件的扩展名; 例如:types { text/html.html; 【如果本地加载的资源为text/html类型的,都当作为.html的子类型】 image/jpeg .jpg; } 2、default_type MIME-TYPE; 指定默认MINE类型
4.15 文件操作优化相关的配置: (1)sendfile on|off; 【由内核代为完成系统调用;对于文件大小有限制,所以sendfile64可支持更大文件系统调用】【更详细概念参考博客sendfile】 (2)aio on|off; 是否启用内核级别的异步IO功能 (3)directio size|off; 【直接IO】 是否使用O_DIRECT选项去请求读取文件;与sendfile功能互斥;【数据不经过内核,直接加载至内核,与sentfile互斥;一般关闭;开启影响性能,但数据安全】 (4)open_file_cache max=N[inactive=time] |off;【是否打开缓存大小,在交互式模式下;】 nginx可以缓存以下三种信息: (a) 文件句柄、文件大小和最近一次修改时间; (b) 打开目录的目录结构; (c) 没有找到的或者没有权限操作的文件的相关信息; max=N表示可缓存的最大条目上限;一旦到达上限,则会使用LRU从缓存中删除最近最少使用的条目; inactive=time:在inactive指定的时长内没有被访问过的缓存条目就会淘汰【删除】inactive 默认时间60s;; 如果内存空间足够用,打开会提高nginx性能 (5)open_file_cache_errors on|off; 是否缓存在文件缓存中缓存打开文件时出现找不到路径,没有权限等的错误信息; (6)open_file_cache_min_uses time; 每隔多久检查一次缓存中缓存条目的有效性;默认60s; 重点关注:server{},location{}, listen, server_name, root, alias, keepalive_timeout,keepalive_requests, error_page
五、其他模块相关配置【编译时若默认没有,想启用,则编译进nginx】 5.1 基于IP的访问控制:【ngx_http_access_module】【编译时默认有此模块】 指令:Derectives:allow, deny 指令适用控制段:Context: http,server, location, limit_except ExampleConfigurationlocation / {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
deny all;
}The rulesare checked in sequence until the first match is found. In this example, accessis allowed only for IPv4 networks 10.1.1.0/16 and 192.168.1.0/24 excluding the address 192.168.1.1
5.2基于用户的basic认证配置: 【ngx_http_auth_basic_module】 ExampleConfigurationlocation / {
auth_basic "closed site";【禁止访问的区域】
auth_basic_user_file conf/htpasswd;【用户账号文件】
}
htpasswd命令创建用户账号文件;
5.3 基于gzip实现响应报文压缩:【ngx_http_gzip_module】 The ngx_http_gzip_module module is a filter that compressesresponses using the “gzip” method. This often helps to reduce thesize of transmitted data by half or even more. Directives:gzip,gzip_proxied,gzip_types,etc.
Context:http,server,locaion
ExampleConfiguration
gzip on; #功能开启
gzip_min_length 1024; #起始压缩为1K
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth; #对于私人认证信息不使用缓存压缩
gzip_types text/plain application/xml; 对text/plainapplication/xml 类型文件压缩
5.4 定制响应首部【ngx_http_headers_module】The ngx_http_headers_module module allows adding the “Expires” and “Cache-Control” header fields, and arbitrary fields, to a response header.
Example Configuration
expires 24h; 定义respose headers 缓存有效期
expires modified +24h; 修改时间向后延长24h
expires @24h; 指定缓存有效期到当天几点几分
add_header Cache-Control private;
Syntax:add_header name value [always];
Default:—Context:http, server, location, if in location
5.5 定制访问日志
ExampleConfiguration log_format compression '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] ' 【远程/客户端地址;远程用户;本地时间】
'"$request" $status $bytes_sent ' 【请求的URL及相关信息;状态码;发送字节】
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" "$gzip_ratio"'; 【上一级的页面是从哪里跳转过来的;浏览器类型;压缩比】
access_log /spool/logs/nginx-access.log compression buffer=32k;
5.6 定义合法引用:【ngx_http_referer_module】【防盗链】Context: server,location
Example Configuration
valid_referers none blocked server_names
*.example.com example.* www.example.org/galleries/
~.google.; 【以上定义的都为合法引用】
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
Parameters can be as follows:
None: ”the “Referer” field is missing in the request header;
Blocked:the “Referer” field is present in the request header, but its value has been deleted by a firewall or proxy server; such values are strings that do not start with “http://” or “https://”;
Server_names :the “Referer” request header field contains one of the server names;
5.7 URL rewrite:【ngx_http_rewrite_module】【网站某模块迁移了;做镜像站点;多个域名,但一个站点】(1)Syntax:rewrite regex replacement [flag]; Context: server, location, if Flag: last、break、redirect、permanent Example:
server {
...
rewrite ^(/download/.*)/media/(.*)..*$ $1/mp3/$2.mp3 last;
rewrite ^(/download/.*)/audio/(.*)..*$ $1/mp3/$2.ra last;
return 403;
...}
解析:【以/download开头的的,后面跟任意文件,中间有media,后面跟任意文件,以任意文件结尾;替换为$1不变,还是download,之后跟把.*替换为mp3;其他同理】
(2)Syntax: if (condition) {...} Context: server, location 比较表达式: = :等值比较 != :不等值比较 ~ :模式匹配区分大小写 ~* :不区分大小写 !~ :是否不匹配,不匹配为真,匹配则为假(不区分大小写) !~* :是否不匹配(区分大小写) -f, !-f :判断文件是否存在与不存在 -d, !-d :判断是否为目录与不为目录 -e, !-e :判断文件、目录、符号链接是否存在与不存在 -x, !-x :判断文件是否能执行与不能执行 Examples
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}(3)Syntax: return code [text]; return code URL ; return URL Context: server, location, if (4)Syntax: set $variable value Context: server, location, if
5.8 Status 【Sngx_http_stub_status_module】The ngx_http_stub_status_module module provides access to basic statusinformation. This moduleis not built by default, it should be enabled with the --with-http_stub_status_moduleconfigurationparameter. ExampleConfiguration location/basic_status { stub_status; } Thisconfiguration creates a simple web page with basic status data which may looklike as follows: Activeconnections: 291 serveraccepts handled requests 16630948 16630948 31070465 Reading:6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106
5.9 SSL 【ngx_http_ssl_module】Syntax: ssl on | off; ssl_certificate file; ssl_certificate_key file; ssl_ciphers ciphers; ssl_session_cache off | none | [builtin[:size]] [shared:name:size]; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on | off; ssl_protocols [SSLv2] [SSLv3] [TLSv1][TLSv1.1] [TLSv1.2];
ssl_session_timeout time; Context:http, server ExampleConfiguration To reducethe processor load it is recommended to set thenumber of worker processes equal to the number of processors, enablekeep-alive connections, enable theshared session cache, disable thebuilt-in session cache, andpossibly increase the session lifetime (by default, 5 minutes): worker_processesauto;
http { ... server { listen 443 ssl; keepalive_timeout 70;
ssl_protocols SSLv3 TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; ssl_ciphers AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:RC4-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:RC4-MD5; ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/conf/cert.pem; ssl_certificate_key/usr/local/nginx/conf/cert.key; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; ... }
更多资料请参考以下网站
|