|
|
lz程序猿一枚,在大数据的道路上一骑绝尘,最近对源码分析饶有兴趣,so写下此文共享给给位码农们,实力有限如有错误的地方希望大家予以指正。话不多说上文章。
RPC 实现一共有3个最重要的类,Client 客户端、Server 服务端、RPC 三类,RPC实现主要是通过java NIO 、java 动态代理、java 反射的方式实现。
本文只分析client 和RPC当前这两部分,后续会加入Server端的部分。
RPC
RPC是在Client和Server的基础上实现了Hadoop的IPC,共分两部分功能
与客户端相关的RPCInvoker,与服务端相关的Server(是RPC的内部类而不是上面的Server服务端类)。RPC中还有一个跟RPC引擎相关的类,RPCKind 枚举类,内容如下:
public enum RpcKind {
RPC_BUILTIN ((
short) 1), // 测试用
RPC_WRITABLE ((short) 2), // Use WritableRpcEngine
RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER ((short) 3); // Use ProtobufRpcEngine
final static short MAX_INDEX = RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER.value; // used for array>
public final short value; //TODO make it private
RpcKind(short val) {
this.value = val;
}
}
可以看出 Hadoop自从yarn的引入,Hadoop的序列化引擎已经不单单是writable了,新引入了google的protocol方式,因此引入了RPCEngine接口和对应的实现类ProtoBufRPCEngine和WritableRPCEngine。RPCEngine 是客户端和服务端统一获取IPC连接的地方(RPC类中也包含相关部分,最终通过RPCKind类选择适当的引擎的实现类),客户端通过getProxy获取客户端连接,服务端通过getServer获取连接。
先从getProxy开始分析,这也是客户端的IPC入口。
getProxy采用java动态代理的方式,每次对协议接口方法的调用都会被拦截下来,通过invoke方法将客户端的请求交给Client类处理。
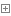
RPCEngine中的getProxy
<T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProxy(Class<T> protocol,
long clientVersion, InetSocketAddress addr,
UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout,
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException
View Code 分析一下各个参数的含义(只分析重要参数,安全相关略过)
Class<T> protocol Hadoop各个角色之间的协议(2.0之后Hadoop协议接口都已经protocol化,不在采用writable方式)如客户端和namenode之间的协议,namenode和datanode之间的协议都要接口化,各个接口中都相关的可用方法,IPC远程调用其实就是调用这些接口的实现类中的方法。下面是客户端和datanode之间的协议接口(下面的是为了说明协议接口的应用,有一定了解的可以略过):
--------------------------------------------------------协议接口-------------------------------------------------------
public interface ClientDatanodeProtocol {public static final long versionID = 9L;
/**返回一个副本的可见长度. */ long getReplicaVisibleLength(ExtendedBlock b) throws IOException;
/**
* 刷新联合namenode名单,由于configuration中的namenode节点的增加和停止已经
*删除的namenode节点(2.x开始引入了联合namenode的方式,namenode不再是单一
*节点,分布在多个节点上,每个节点管理不同的目录,如namenode1管理*/application1 ,namenode2管理/application2,每个目录互不干扰,其中某个namenode挂
*掉了,只是其管理的目录下的*应用不可用,不会影响其他的节点,datanode不变,任*何一个namenode都可以控制所有的*datanode )
*
* @throws IOException on error
**/
void refreshNamenodes() throws IOException;
/**
*删除块池目录。如果“force”是false只有块池目录为空时删除,否则块池与它的内容
*一并删除。(此方法和新hdfs datanode数据管理相关,下章会讲解)
*
* @param bpid Blockpool> * @param force If false blockpool directory is deleted only if it is empty
* i.e. if it doesn't contain any block files, otherwise it is
* deleted along with its contents.
* @throws IOException
*/
void deleteBlockPool(String bpid, boolean force) throws IOException;
/**
* 检索存储在本地文件系统上的块文件和元数据文件的路径名。
* 为了使此方法有效,下列情况之一应满足
* 客户端用户必须在数据节点被配置成能够使用这一方法
*
* 当启用安全,Kerberos身份验证必须能够连接到这个Datanode
*
* @param block
* the specified block on the local datanode
* @param token
* the block access token.
* @return the BlockLocalPathInfo of a block
* @throws IOException
* on error
*/
BlockLocalPathInfo getBlockLocalPathInfo(ExtendedBlock block,
Token<BlockTokenIdentifier> token) throws IOException;
/**
*检索Datanode上有关一个list块上卷位置信息。
*这是在一个不透明的形式{@link org.apache.hadoop.fs.VolumeId}
*为配置的每个数据目录,这是不能保证横跨DN重新启动一样的。 *
* @param blockPoolId the pool to query
* @param blockIds
* list of blocks on the local datanode
* @param tokens
* block access tokens corresponding to the requested blocks
* @return an HdfsBlocksMetadata that associates {@link ExtendedBlock}s with
* data directories
* @throws IOException
* if datanode is unreachable, or replica is not found on datanode
*/
HdfsBlocksMetadata getHdfsBlocksMetadata(String blockPoolId,
long []blockIds, List<Token<BlockTokenIdentifier>> tokens) throws IOException;
/**
* 关闭一个datanode节点.
*
* @param forUpgrade If true, data node does extra prep work before shutting
* down. The work includes advising clients to wait and saving
* certain states for quick restart. This should only be used when
* the stored data will remain the same during upgrade/restart.
* @throws IOException
*/
void shutdownDatanode(boolean forUpgrade) throws IOException;
/**
* 获取datanode元数据信息
*
* @return software/config version and uptime of the datanode
*/
DatanodeLocalInfo getDatanodeInfo() throws IOException;
/**
* Asynchronously> */
void startReconfiguration() throws IOException;
/**
*获取之前发出的重新配置任务的状态.
* @see {@link org.apache.hadoop.conf.ReconfigurationTaskStatus}.
*/
ReconfigurationTaskStatus getReconfigurationStatus() throws IOException;
/**
* 触发一个新block report
*/
void triggerBlockReport(BlockReportOptions options)
throws IOException;
}
View Code ---------------------------------------------协议接口---------------------------------------------------
long clientVersion client标识
InetSocketAddress addr 访问的服务端地址
UserGroupInformation ticket 用户组信息
Configuration conf configuration配置信息
SocketFactory factory socket工厂用来生成socket连接(IPC通信采用socket的TCP方式)
int rpcTimeout 超时时间
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy 连接重试策略(直接失败,重试和切换到另一台机器重试详细见RetryPolicy类)
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth 是否退到一般用户
此方法最终会调用相关子类的对应的方法,以ProtoBuRPCEngine为例,
public <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProxy(Class<T> protocol, long clientVersion, InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout, RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {
//Invoker 类实现了InvocationHandler
final Invoker invoker = new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory,
rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy, fallbackToSimpleAuth);
//生成代理对象(此部分不熟悉看一下java的动态代理)
return new ProtocolProxy<T>(protocol, (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
protocol.getClassLoader(), new> }
View Code Invoker
Invoker类图如
isClosed 与连接关闭有关
remoteId Client端到Server端的连接id,Client会继续分析
client Client对象
clientProtocolVersion 不同Hadoop版本之间的协议版本是不一致的,所以不能用2.1的版本与2.5的通信
protocolName 协议名
returnTypes 缓存每个协议接口中方法的返回类型(Message封装Message是google protocolBuffer的消息序列化类)
invoker构造方法
private Invoker(Class<?> protocol, Client.ConnectionId connId, Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory) {
this.remoteId = connId;
// CLIENTS 是ClientCache类型的对象,其中缓存着所有访问过的客户端对象信息,如果是新的客户端则构造新的client对象并将其缓存。 this.client = CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory, RpcResponseWrapper.class);
this.protocolName = RPC.getProtocolName(protocol);
this.clientProtocolVersion = RPC
.getProtocolVersion(protocol);
}
View Code Invoke
下面看看关键的invoke方法,当调用协议接口中的某个方法时,就会触发此方法。
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws ServiceException {long startTime = 0;if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { startTime
= Time.now();//当前时间毫秒数
}
if (args.length != 2) { // 参数必须是2个RpcController + Message
throw new ServiceException("Too many parameters for request. Method: ["
+ method.getName() + "]" + ", Expected: 2, Actual: "
+ args.length);
}
if (args[1] == null) {
throw new ServiceException("null param while calling Method: ["
+ method.getName() + "]");
}
//追述信息相关,
TraceScope traceScope = null;
// if Tracing is on then start a new span for this rpc.
// guard it in the if statement to make sure there isn't
// any extra string manipulation.
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
traceScope = Trace.startSpan(RpcClientUtil.methodToTraceString(method));
}
//RPC请求头信息,类似http中的请求头一样,客户端和服务端都要先发送头信息,然后在发送内容。注意,构造头信息是将method放入了请求中,在服务端接受时就会知道调用哪个方法。
RequestHeaderProto rpcRequestHeader = constructRpcRequestHeader(method);
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
LOG.trace(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ": Call -> " +
remoteId + ": " + method.getName() +
" {" + TextFormat.shortDebugString((Message) args[1]) + "}");
}
//method的参数信息,method反射是用到。
Message theRequest = (Message) args[1];
// server端返回的结果
final RpcResponseWrapper val;
try {
// 调用client(client已经在构造方法里生成了对应的对象)类中的call方法(client类中会具体分析该方法)返回server端的返回结果
val = (RpcResponseWrapper) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
new RpcRequestWrapper(rpcRequestHeader, theRequest), remoteId,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
LOG.trace(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ": Exception <- " +
remoteId + ": " + method.getName() +
" {" + e + "}");
}
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
traceScope.getSpan().addTimelineAnnotation(
"Call got exception: " + e.getMessage());
}
throw new ServiceException(e);
} finally {
if (traceScope != null) traceScope.close();
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
long callTime = Time.now() - startTime;
LOG.debug("Call: " + method.getName() + " took " + callTime + "ms");
}
Message prototype = null;
try {
//获取method的返回类型
prototype = getReturnProtoType(method);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServiceException(e);
}
Message returnMessage;
try {
//将返回值message序列化
returnMessage = prototype.newBuilderForType()
.mergeFrom(val.theResponseRead).build();
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
LOG.trace(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ": Response <- " +
remoteId + ": " + method.getName() +
" {" + TextFormat.shortDebugString(returnMessage) + "}");
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServiceException(e);
}
return returnMessage;
}
获取方法的返回类型(message序列化后的结果)
private Message getReturnProtoType(Method method) throws Exception {
if (returnTypes.containsKey(method.getName())) {
return returnTypes.get(method.getName());
}
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
Method newInstMethod = returnType.getMethod("getDefaultInstance");
newInstMethod.setAccessible(true);
Message prototype = (Message) newInstMethod.invoke(null, (Object[]) null);
returnTypes.put(method.getName(), prototype);
return prototype;
}
关闭客户端的IPC连接
public void close() throws IOException {
if (!isClosed) {
isClosed = true;
CLIENTS.stopClient(client);
}
}
View Code 总之,invoker 类通过client call方法拦截了协议接口方法的调用,并将处理方式发送到Client.call方法中,由call方法处理如何将调用信息发送到服务端并获取返回结果,封装成message返回最终的调用的结果。
RPCInvoker接口
此接口与上面的Invoker没有任何关系,此类只有一个call方法由server端调用,用于处理最终请求处理的地方,就是调用协议接口实现类对应方法的地方。主要采用反射的方式实现。在WritableRPCEngine和ProtoBufRPCEngine中都有对应的实现类。之所以会多出这一步骤,而不是直接在Server里直接实现call方法,是因为当前Hadoop版本序列化的方式存在两种,Hadoop实现者将这两个序列化的解析处理方法分开实现,供其他类调用,怎加了代码的重用性。
ProtoBufRpcInvoker.Call
下面以ProtoBufRPCEngine. ProtoBufRpcInvoker为例讲解call方法的具体处理步骤。
public Writable call(RPC.Server server, String protocol, Writable writableRequest,
long receiveTime) throws Exception { RpcRequestWrapper request
= (RpcRequestWrapper) writableRequest; RequestHeaderProto rpcRequest
= request.requestHeader;//获取调用的方法名 String methodName = rpcRequest.getMethodName();
//获取协议接口名
String protoName = rpcRequest.getDeclaringClassProtocolName();
//获取客户端版本
long clientVersion = rpcRequest.getClientProtocolVersion();
if (server.verbose)
LOG.info("Call: protocol=" + protocol + ", method=" + methodName);
//获取接口实现类
ProtoClassProtoImpl protocolImpl = getProtocolImpl(server, protoName,
clientVersion);
BlockingService service = (BlockingService) protocolImpl.protocolImpl;
//根据方法名获取方法描述信息
MethodDescriptor methodDescriptor = service.getDescriptorForType()
.findMethodByName(methodName);
if (methodDescriptor == null) {
String msg = "Unknown method " + methodName + " called on " + protocol
+ " protocol.";
LOG.warn(msg);
throw new RpcNoSuchMethodException(msg);
}
//根据方法描述信息获取客户端发送的message信息(protocol方式采用message类序列化信息)。
Message prototype = service.getRequestPrototype(methodDescriptor);
//获取方法参数
Message param = prototype.newBuilderForType()
.mergeFrom(request.theRequestRead).build();
Message result;
long startTime = Time.now();
int qTime = (int) (startTime - receiveTime);
Exception exception = null;
try {
server.rpcDetailedMetrics.init(protocolImpl.protocolClass);
//调用方法返回结果,内部是protocol方式实现调用协议接口中的方法。
result = service.callBlockingMethod(methodDescriptor, null, param);
} catch (ServiceException e) {
exception = (Exception) e.getCause();
throw (Exception) e.getCause();
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
throw e;
} finally {
int processingTime = (int) (Time.now() - startTime);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
String msg = "Served: " + methodName + " queueTime= " + qTime +
" procesingTime= " + processingTime;
if (exception != null) {
msg += " exception= " + exception.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
LOG.debug(msg);
}
String detailedMetricsName = (exception == null) ?
methodName :
exception.getClass().getSimpleName();
server.rpcMetrics.addRpcQueueTime(qTime);
server.rpcMetrics.addRpcProcessingTime(processingTime);
server.rpcDetailedMetrics.addProcessingTime(detailedMetricsName,
processingTime);
}
//返回最终的结果
return new RpcResponseWrapper(result);
}
Client
Client中包含很多内部类,大致可归纳为两部分,一部分是与IPC连接相关的类 connection、connectionId等,另一部分与远程接口调用相关的 Call、ParallelCall等
Client大致类图如下(不包含内部类,最终总结会包含所有类)
callIDCounter 一个生成Client.Call 类中唯一id的一个生成器。
callId 当前线程对应的call对象的id
retryCount 重试次数,连接失败或者返回结果错误或者超时
connections 当前client所有的正在处理的连接
running client是否处于运行状态
conf configuration配置类
socketFactory 创建socket的工厂
clientId 当前client的唯一id
CONNECTION_CONTEXT_CALL_ID 特殊的一种callId 用于传递connection上下文信息的callId
valueClass :Class<? extends Writable> Call服务端返回结果类型
sendParamsExecutor 多线程方式处理connection
Client构造方法
先看Client构造方法,上面Invoker调用过
public Client(Class<? extends Writable> valueClass, Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory) {
this.valueClass = valueClass;this.conf = conf;
this.socketFactory = factory;
//获取超时时间 this.connectionTimeout = conf.getInt(CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT_KEY,
CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT_DEFAULT);
this.fallbackAllowed = conf.getBoolean(CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_FALLBACK_TO_SIMPLE_AUTH_ALLOWED_KEY,
CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_FALLBACK_TO_SIMPLE_AUTH_ALLOWED_DEFAULT);
//通过uuid方式生成clientId
this.clientId = ClientId.getClientId();
//生成一个cache类型的executorService 稍后分析
this.sendParamsExecutor = clientExcecutorFactory.refAndGetInstance();
}
call
下面就看一下,Invoker类中的invoke方法调用的call方法是怎么把方法发送到服务端的。
public Writable call(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest, ConnectionId remoteId,
int serviceClass, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {//生成一个Call类型的对象,上面曾说过,client中包含很多内部类,Call就是其中之一,负责远程接口调用。下面会细化此类
final Call call = createCall(rpcKind, rpcRequest);
//生成一个connection对象,Hadoop在此处进行了一些优化措施,如果当前连接在过去的曾经应用过,并且当前仍然是活跃的,那么就复用此连接。这会减少内存的开销和远程socket通信的开销,后面会细化此类
Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call, serviceClass,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
try {
//call对象已经把调用信息进行了封装,然后通过connection对象将call封装的信息发送到server端。
connection.sendRpcRequest(call); // send the rpc request
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
throw new IOException("connection has been closed", e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
LOG.warn("interrupted waiting to send rpc request to server", e);
throw new IOException(e);
}
boolean interrupted = false;
synchronized (call) {
while (!call.done) {
try {
//在此处会堵塞当前线程,直道call有返回结果。由notify唤醒。
call.wait(); // wait for the result
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// save the fact that we were interrupted
interrupted = true;
}
}
//线程中断异常处理
if (interrupted) {
// set the interrupt flag now that we are done waiting
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
//call 返回错误处理
if (call.error != null) {
if (call.error instanceof RemoteException) {
call.error.fillInStackTrace();
throw call.error;
} else { // local exception
InetSocketAddress address = connection.getRemoteAddress();
throw NetUtils.wrapException(address.getHostName(),
address.getPort(),
NetUtils.getHostname(),
0,
call.error);
}
} else {
//将正确信息返回到invoker中。
return call.getRpcResponse();
}
}
}
此方法主要步骤,先创建call远程调用对象将调用信息封装,在生成远程连接对象connection,然后将call通过connection发送到服务端等待返回结果,期间可能出现各种错误信息(超时、连接错误,线程中断等等),最后将正确的结果返回到invoker中。
getConnection
获取连接connection方法getConnection
private Connection getConnection(ConnectionId remoteId, Call call,
int serviceClass, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)throws IOException {
//确保当前client处于运行状态 if (!running.get()) {
// the client is stopped
throw new IOException("The client is stopped");
}
Connection connection;
/* we could avoid this allocation for each RPC by having a
* connectionsId object and with set() method. We need to manage the
* refs for keys in HashMap properly. For now its ok.
*/
do {
//加上同步锁会有多个线程同时获取连接,避免相同连接生成多次
synchronized (connections) {
connection = connections.get(remoteId);
//如果连接池中不包含想要的连接则创建新连接
if (connection == null) {
connection = new Connection(remoteId, serviceClass);
connections.put(remoteId, connection);
}
}
} while (!connection.addCall(call));//将刚刚创建的call添加到次connection中,一个connection可以处理多个调用。
//connection初始IOstream,其中包含创建请求头消息并发送信息。
//此段代码并没有放到同步代码块中,原因是如果服务端很慢的话,它会花费很长的时间创建一个连接,这会使整个系统宕掉(同步代码使得每次只能处理一个线程,其他的connection都要等待,这会使系统处于死等状态)。
connection.setupIOstreams(fallbackToSimpleAuth);
return connection;
}
createCall
创建Call 方法很简单直接调用call的构造方法。
Call createCall(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest) {return new Call(rpcKind, rpcRequest);
}
Connection
下面讲一下Client的内部类:
在说connection之前,说一下Hadoop IPC消息传递的方式,其实是采用变长消息格式,所以每次发送消息之前要发送消息的总长度包含消息头信息,一般用dataLength表示消息长度,Hadoop用4个字节的来存储消息的大小。
Hadoop在connection初始建立连接的时候,会发送connection消息头和消息上下文(后面会有两个方法处理这两段信息),那么Hadoop是如何判断发送过来的信息是connection过来的,
类似java,Hadoop也有一个魔数 ‘hrpc’ 这个魔数存储在connection发送的消息头中,正好占的是dataLength的4个字节,这是Hadoop精心设置的一种方式。如果dataLength字段是hrpc则说明是集群中某个client发送过来的信息,而头信息并不需要数据内容,只包含头信息,这使得在处理头信息时,不用关心信息长度。因为他的长度就是头信息那么大。
Connection类图大致如下(只包含重要信息,安全和权限相关去掉)
Server 对应服务端的地址和端口
remoteId connectionId 是connection的唯一id属性
socket 与服务端的socket连接
in 输入,从连接中获取服务端返回的结果用
out 输出,发送数据到服务端用
lastActivity 最近一次进行I/O的时间用于判断超时
rpcTimeout 超时时间范围
calls 当前connection处理的所有call
maxIdleTime 最大空闲时间,如果超过这个时间,connection将会从client对象中的connections map对象中剔除掉,将剩余的空间留给比较忙的connection。
connectionRetryPolicy 连接失败的重试策略。
maxRetriesOnSocketTimeouts 在socket中最大的重试超时时间范围。
shouldCloseConnection 是否应该关闭当前connection,true关闭
sendRpcRequestLock 同步锁用对象。
TcpNoDelay 是否采用Nagle算法(与tcp数据包相关)
closeException 关闭connection可能是因为某种错误,记录错误信息
doping 每隔一段时间发送的ping信息,防止服务端误认为客户端死掉。
pingInterval ping的时间间隔
pingRequest ping发送的内容
在上面的getConnection中,如果当前没有对应的Connection对象,那么就生成新的
//Connection中的很多属性在ConnectionId类中都已经存在了。构造方法主要是初始化上面的属性
public Connection(ConnectionId remoteId, int serviceClass) throws IOException {this.remoteId = remoteId;this.server = remoteId.getAddress();if (server.isUnresolved()) {throw NetUtils.wrapException(server.getHostName(), server.getPort(),
null,0,new UnknownHostException()); }
this.rpcTimeout = remoteId.getRpcTimeout();this.maxIdleTime = remoteId.getMaxIdleTime();this.connectionRetryPolicy = remoteId.connectionRetryPolicy;this.maxRetriesOnSasl = remoteId.getMaxRetriesOnSasl();this.maxRetriesOnSocketTimeouts = remoteId.getMaxRetriesOnSocketTimeouts();this.tcpNoDelay = remoteId.getTcpNoDelay();this.doPing = remoteId.getDoPing();if (doPing) {// construct a RPC header with the callId as the ping callId pingRequest = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
RpcRequestHeaderProto pingHeader = ProtoUtil
.makeRpcRequestHeader(RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
OperationProto.RPC_FINAL_PACKET, PING_CALL_ID,
RpcConstants.INVALID_RETRY_COUNT, clientId);
pingHeader.writeDelimitedTo(pingRequest);
}
this.pingInterval = remoteId.getPingInterval();
this.serviceClass = serviceClass;
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("The ping interval is " + this.pingInterval + " ms.");
}
UserGroupInformation ticket = remoteId.getTicket();
// try SASL if security is enabled or if the ugi contains tokens.
// this causes a SIMPLE client with tokens to attempt SASL
boolean trySasl = UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled() ||
(ticket != null && !ticket.getTokens().isEmpty());
this.authProtocol = trySasl ? AuthProtocol.SASL : AuthProtocol.NONE;
this.setName("IPC Client (" + socketFactory.hashCode() +") connection to " +
server.toString() +
" from " + ((ticket==null)?"an unknown user":ticket.getUserName()));
this.setDaemon(true);
}
setupIOstreams
下面分析一下在getConnection中的setupIOstreams,这是Connection初始IO和发送头信息的方法 ,注意此处的同步锁synchronized和上面的getConnection 的同步代码块意义不一样,代码块锁住了所有的Connection,而这里的同步锁只是在Connection重用的时候同步锁。
private synchronized void setupIOstreams( AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) {
//如果是已经存在的连接,或者这个连接应该关闭了,直接返回。两种情况都已不需要初始化Connection了。 if (socket != null || shouldCloseConnection.get()) {
return;
}
try {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Connecting to "+server);
}
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
Trace.addTimelineAnnotation("IPC client connecting to " + server);
}
short numRetries = 0;
Random rand = null;
while (true) {
//connection初始化
setupConnection();
//生成socket的IO
InputStream inStream = NetUtils.getInputStream(socket);
OutputStream outStream = NetUtils.getOutputStream(socket);
//发送请求头信息
writeConnectionHeader(outStream);
----------------------------------------安全、权限相关---------------------------------------------
if (authProtocol == AuthProtocol.SASL) {
final InputStream in2 = inStream;
final OutputStream out2 = outStream;
UserGroupInformation ticket = remoteId.getTicket();
if (ticket.getRealUser() != null) {
ticket = ticket.getRealUser();
}
try {
authMethod = ticket
.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<AuthMethod>() {
@Override
public AuthMethod run()
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return setupSaslConnection(in2, out2);
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
authMethod = saslRpcClient.getAuthMethod();
if (rand == null) {
rand = new Random();
}
handleSaslConnectionFailure(numRetries++, maxRetriesOnSasl, ex,
rand, ticket);
continue;
}
if (authMethod != AuthMethod.SIMPLE) {
// Sasl connect is successful. Let's set up Sasl i/o streams.
inStream = saslRpcClient.getInputStream(inStream);
outStream = saslRpcClient.getOutputStream(outStream);
// for testing
remoteId.saslQop =
(String)saslRpcClient.getNegotiatedProperty(Sasl.QOP);
LOG.debug("Negotiated QOP is :" + remoteId.saslQop);
if (fallbackToSimpleAuth != null) {
fallbackToSimpleAuth.set(false);
}
} else if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {
if (!fallbackAllowed) {
throw new IOException("Server asks us to fall back to SIMPLE " +
"auth, but this client is configured to only allow secure " +
"connections.");
}
if (fallbackToSimpleAuth != null) {
fallbackToSimpleAuth.set(true);
}
}
}
----------------------------------------安全、权限相关---------------------------------------------
//是否到了发送ping的时间
if (doPing) {
//将ping内容读入
inStream = new PingInputStream(inStream);
}
this.in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(inStream));
// SASL may have already buffered the stream
if (!(outStream instanceof BufferedOutputStream)) {
outStream = new BufferedOutputStream(outStream);
}
this.out = new DataOutputStream(outStream);
//发送Connection上下文
writeConnectionContext(remoteId, authMethod);
// 更新活跃时间
touch();
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
Trace.addTimelineAnnotation("IPC client connected to " + server);
}
// 开启run方法,其中包含接受server返回信息。
start();
return;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
//异常关闭连接
if (t instanceof IOException) {
//此方法会是shouldCloseConnection 变为true,
markClosed((IOException)t);
} else {
markClosed(new IOException("Couldn't set up IO streams", t));
}
close();
}
}
此方法主要是初始化Connection,建立连接头信息,并发送请求头和请求上下文,更新活跃时间。代码最后开启线程开始接受server端返回的结果。markClosed方法会使shouldCloseConnection变为true,标记表示Connection应该关闭了,其他方法遇到这个属性时将会直接跳过不处理任何事情,最终到run(Connection继承自Thread)方法时,通过waitForWork判断关闭连接,调用Connection的close方法。
markClosed
private synchronized void markClosed(IOException e) {//通过cas方式设置为true if (shouldCloseConnection.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
closeException = e;
//唤醒所有阻塞在此连接的线程。
notifyAll();
}
}
setupConnection
下面看一下如何初始化Connection
private synchronized void setupConnection() throws IOException {//io错误次数
short ioFailures = 0;
//超时次数
short timeoutFailures = 0;
//循环直道成功创建socket连接
while (true) {
try {
//创建socket
this.socket = socketFactory.createSocket();
this.socket.setTcpNoDelay(tcpNoDelay);
this.socket.setKeepAlive(true);
---------------------------权限、安全相关---------------------------------------
/*
* Bind the socket to the host specified in the principal name of the
* client, to ensure Server matching address of the client connection
* to host name in principal passed.
*/
UserGroupInformation ticket = remoteId.getTicket();
if (ticket != null && ticket.hasKerberosCredentials()) {
KerberosInfo krbInfo =
remoteId.getProtocol().getAnnotation(KerberosInfo.class);
if (krbInfo != null && krbInfo.clientPrincipal() != null) {
String host =
SecurityUtil.getHostFromPrincipal(remoteId.getTicket().getUserName());
// If host name is a valid local address then bind socket to it
InetAddress localAddr = NetUtils.getLocalInetAddress(host);
if (localAddr != null) {
this.socket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(localAddr, 0));
}
}
}
---------------------------权限、安全相关---------------------------------------
//将socket绑定到server端
NetUtils.connect(this.socket, server, connectionTimeout);
//超时时间和ping间隔相同。
if (rpcTimeout > 0) {
pingInterval = rpcTimeout; // rpcTimeout overwrites pingInterval
}
//设置socket超时
this.socket.setSoTimeout(pingInterval);
return;
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException toe) {
/* 连接超时可能是连接地址发生了改变,调用updateAdress方法,如果返回true
*说明连接地址确实改变了,重新建立连接。
*/
if (updateAddress()) {
//更新超时次数和io错误次数为0
timeoutFailures = ioFailures = 0;
}
//此方法会关闭socket连接,
handleConnectionTimeout(timeoutFailures++,
maxRetriesOnSocketTimeouts, toe);
} catch (IOException ie) {
if (updateAddress()) {
timeoutFailures = ioFailures = 0;
}
handleConnectionFailure(ioFailures++, ie);
}
}
}
updateAddress
更新server端
private synchronized boolean updateAddress() throws IOException {// Do a fresh lookup with the old host name. InetSocketAddress currentAddr = NetUtils.createSocketAddrForHost(
server.getHostName(), server.getPort());
//如果地址与以前的不同则更新
if (!server.equals(currentAddr)) {
LOG.warn("Address change detected. Old: " + server.toString() +
" New: " + currentAddr.toString());
//更新为新的地址
server = currentAddr;
return true;
}
return false;
}
writeConnectionHeader
发送请求头,相对简单,不解释
/** * Write the connection header - this is sent when connection is established
* +----------------------------------+
* | "hrpc" 4 bytes |
* +----------------------------------+
* | Version (1 byte) |
* +----------------------------------+
* | Service> * +----------------------------------+
* | AuthProtocol (1 byte) |
* +----------------------------------+
*/ private void writeConnectionHeader(OutputStream outStream)
throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(outStream));
// Write out the header, version and authentication method
out.write(RpcConstants.HEADER.array());
out.write(RpcConstants.CURRENT_VERSION);
out.write(serviceClass);
out.write(authProtocol.callId);
out.flush();
}
writeConnectionContext
发送请求上下文
/* 此方法和上面的方法都不是同步的,原因是他们只在初始化的时候调用一次。
*/
private void writeConnectionContext(ConnectionId remoteId, AuthMethod authMethod)
throws IOException {// Write out the ConnectionHeader IpcConnectionContextProto message = ProtoUtil.makeIpcConnectionContext(
RPC.getProtocolName(remoteId.getProtocol()),
remoteId.getTicket(),
authMethod);
//构造上下文信息,只有上下文内容,没有信系,
RpcRequestHeaderProto connectionContextHeader = ProtoUtil
//rpc引擎类型,rpc打包方式,context的callId默认-3,重试次数-1表示一直重试,客户端id
.makeRpcRequestHeader(RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
OperationProto.RPC_FINAL_PACKET, CONNECTION_CONTEXT_CALL_ID,
RpcConstants.INVALID_RETRY_COUNT, clientId);
RpcRequestMessageWrapper request =
new RpcRequestMessageWrapper(connectionContextHeader, message);
// Write out the packet length
out.writeInt(request.getLength());
request.write(out);
}
sendRpcRequest
下面是client call方法中通过Connection sendRPCRequest发送远程调用
/** Initiates a rpc call by sending the rpc request to the remote server.
*/ public void sendRpcRequest(final Call call)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
//如果应该关闭连接,返回
if (shouldCloseConnection.get()) {
return;
}
// 序列化的call将会被发送到服务端,这是在call线程中处理
// 而不是sendParamsExecutor 线程
// 因此如果序列化出现了问题,也能准确的报告
// 这也是一种并发序列化的方式.
//
// Format of a call on the wire:
// 0) Length of rest below (1 + 2)
// 1) RpcRequestHeader - is serialized Delimited hence contains length
// 2) RpcRequest
//
// Items '1' and '2' are prepared here.
final DataOutputBuffer d = new DataOutputBuffer();
//构造请求头信息,与连接刚建立时候类似。
RpcRequestHeaderProto header = ProtoUtil.makeRpcRequestHeader(
call.rpcKind, OperationProto.RPC_FINAL_PACKET, call.id, call.retry,
clientId);
//将请求信息和头信息写到一个输入流的buffer中
header.writeDelimitedTo(d);
call.rpcRequest.write(d);
//
synchronized (sendRpcRequestLock) {
//多线程方式发送请求
Future<?> senderFuture = sendParamsExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//out加同步锁,以免多个消息写乱输出流
synchronized (Connection.this.out) {
if (shouldCloseConnection.get()) {
return;
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled())
LOG.debug(getName() + " sending #" + call.id);
//通过Connection的out输出流将请求信息发送到服务端
byte[] data = d.getData();
//计算信息总长度
int totalLength = d.getLength();
//写出长度信息
out.writeInt(totalLength); // Total Length
//写出内容信息
out.write(data, 0, totalLength);// RpcRequestHeader + RpcRequest
out.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// exception at this point would leave the connection in an
// unrecoverable state (eg half a call left on the wire).
// So, close the connection, killing any outstanding calls
markClosed(e);
} finally {
//the buffer is just an in-memory buffer, but it is still polite to
// close early
IOUtils.closeStream(d);
}
}
});
try {
//阻塞等待结果,真正的返回结果是在call 中。
senderFuture.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
// cause should only be a RuntimeException as the Runnable above
// catches IOException
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("unexpected checked exception", cause);
}
}
}
}
Connection.run
Connection是thread的子类,每个Connection都会有一个自己的线程,这样能够加快请求的处理速度。在setupIOStream方法中最后的地方调用的Connection开启线程的方法,start,这样Connection就能够等待返回的结果。
public void run() {if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) LOG.debug(getName()
+ ": starting, having connections " + connections.size());
try {
//等待是否有可用的call,直到Connection可关闭时,结束循环
while (waitForWork()) {//wait here for work - read or close connection
//接受返回结果
receiveRpcResponse();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// This truly is unexpected, since we catch IOException in receiveResponse
// -- this is only to be really sure that we don't leave a client hanging
// forever.
LOG.warn("Unexpected error reading responses on connection " + this, t);
markClosed(new IOException("Error reading responses", t));
}
//while循环判断shouldCloseConnection为true,关闭Connection
close();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled())
LOG.debug(getName() + ": stopped, remaining connections "
+ connections.size());
}
此方法中如果有待处理的call并且当前Connection可用,client客户端尚在运行中,则停留在while循环中处理call。直到shouldCloseConnection为true,关闭连接。下面是waitForWork方法
waitForWork
private synchronized boolean waitForWork() {
//在连接可用,尚未有可处理的call时,挂起当前线程直到达到最大空闲时间。 if (calls.isEmpty() && !shouldCloseConnection.get() && running.get()) {
long timeout = maxIdleTime-
(Time.now()-lastActivity.get());
if (timeout>0) {
try {
wait(timeout);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
//在有处理的call且连接可用,client尚在运行,返回true
if (!calls.isEmpty() && !shouldCloseConnection.get() && running.get()) {
return true;
//其他状况则返回false,并标记shouldCloseConnection为true
} else if (shouldCloseConnection.get()) {
return false;
} else if (calls.isEmpty()) { //> markClosed(null);
return false;
} else { // get stopped but there are still pending requests
markClosed((IOException)new IOException().initCause(
new InterruptedException()));
return false;
}
}
waitForWork方法主要作用就是判断当前在所有情况都正常时,有没有可处理的call,有返回true,没有等待到最大空闲时间(这段时间内会被addCalls中的notify唤醒,由于有了新的call要处理所有要唤醒),如果这段时间当中扔没有要处理的call则返回false,其他情况均返回false,并标记shouldCloseConnection为true。
addCall
private synchronized boolean addCall(Call call) {//如果当前连接不可用则返回false。 if (shouldCloseConnection.get())
return false;
//将call对象放入Connection正在处理的call队列里。
calls.put(call.id, call);
//唤醒在waitForWork中被wait的连接,如果没有这略过
notify();
return true;
}
Addcall 方法是在上面client解析中getConnection的方法中调用。因为连接会复用,所以方法中会判断连接是否可用。
receiveRpcResponse
下面看一下Connection接受返回结果的receiveRpcResponse方法。HadoopIPC连接采用的是变长格式的消息,所以每次发送消息是先发送消息的长度,让后是消息的内容。
private void receiveRpcResponse() {if (shouldCloseConnection.get()) {return; }
touch();
try {//获取消息长度 int totalLen = in.readInt();
读取消息内容
RpcResponseHeaderProto header =
RpcResponseHeaderProto.parseDelimitedFrom(in);
//结果校验
checkResponse(header);
int headerLen = header.getSerializedSize();
headerLen += CodedOutputStream.computeRawVarint32Size(headerLen);
//获取对应处理的call
int callId = header.getCallId();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled())
LOG.debug(getName() + " got value #" + callId);
//找到对应的call并将结果放到call对象的RpcResponse中
Call call = calls.get(callId);
//查看处理结果的状态,是否为success
RpcStatusProto status = header.getStatus();
if (status == RpcStatusProto.SUCCESS) {
//状态success将返回值放入call的rpcresponse中
Writable value = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(valueClass, conf);
value.readFields(in); // read value
//此请求已处理完成,从calls中移除call
calls.remove(callId);
call.setRpcResponse(value);
// verify that length was correct
// only for ProtobufEngine where len can be verified easily
//如果是ProtoBuffEngine则用protocol方式将结果包裹一次,用于protocol的方式处理
if (call.getRpcResponse() instanceof ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcWrapper) {
ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcWrapper resWrapper =
(ProtobufRpcEngine.RpcWrapper) call.getRpcResponse();
if (totalLen != headerLen + resWrapper.getLength()) {
throw new RpcClientException(
"RPC response length mismatch on rpc success");
}
}
} else { // Rpc 返回错误
// Verify that length was correct
if (totalLen != headerLen) {
throw new RpcClientException(
"RPC response length mismatch on rpc error");
}
//获取错误信息
final String exceptionClassName = header.hasExceptionClassName() ?
header.getExceptionClassName() :
"ServerDidNotSetExceptionClassName";
final String errorMsg = header.hasErrorMsg() ?
header.getErrorMsg() : "ServerDidNotSetErrorMsg" ;
final RpcErrorCodeProto erCode =
(header.hasErrorDetail() ? header.getErrorDetail() : null);
if (erCode == null) {
LOG.warn("Detailed error code not set by server on rpc error");
}
RemoteException re =
( (erCode == null) ?
new RemoteException(exceptionClassName, errorMsg) :
new RemoteException(exceptionClassName, errorMsg, erCode));
if (status == RpcStatusProto.ERROR) {
//error时,将错误信息填充到call中,并将call从calls中移除
calls.remove(callId);
call.setException(re);
} else if (status == RpcStatusProto.FATAL) {
//如果是致命错误则关闭连接,可能是连接异常引起的错误
// Close the connection
markClosed(re);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
//如果发生IO错误则关闭连接。
markClosed(e);
}
}
Call
下面看一下client中最后一个内部类call,大概的类图如下
Id call的唯一id 来自于client的callId
Retry 重试次数,来自于client的retryCount
rpcRequest 请求内容序列化后的
rpcResponese 返回结果序列化后的
error 错误信息
rpcKind rpc引擎
done 此请求是否完成
setRpcResponse
下面看一下Connection中receiveRpcResponse方法里所调用的setRPCResponse方法。看看结果是如何设置并返回到client中的call方法里的(前面有记载)。
//其实方法很简单只是将receiveRpcResponse中序列化好的结果放到了call的RPCResponse中。并调用了callComplete。
public synchronized void setRpcResponse(Writable rpcResponse) {
this.rpcResponse = rpcResponse;
callComplete();
}
callComplete
那么看看callComplete中又做了什么。
protected synchronized void callComplete() {//标记此次请求已完成 this.done = true;
notify(); // notify caller
}
还记得在client的call方法中,有一段判断call的done字段是否为true么,如下
如果当前正在处理的call没有做完,就wait等待,直到完成notify唤醒,或者是线程被中断。
while (!call.done) {try { call.wait();
// wait for the result } catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// save the fact that we were interrupted
interrupted = true;
}
}
Client图解
以上所有就是client端的全部内容。下面一个整体的client端的一个图解。
|
|