|
|
MapReduce with MongoDB and Python
从 Artificial Intelligence in Motion 作者:Marcel Pinheiro Caraciolo (由于Artificial Intelligence in Motion发布的图在墙外,所以将图换到cnblogs)
Hi all,
In this post, I'll present a demonstration of a map-reduce example with MongoDB and server side JavaScript. Based on the fact that I've been working with this technology recently, I thought it would be useful to present here a simple example of how it works and how to integrate with Python.
But What is MongoDb ?
For you, who doesn't know what is and the basics of how to use MongoDB, it is important to explain a little bit about the No-SQL movement. Currently, there are several databases that break with the requirements present in the traditional relational database systems. I present as follows the main keypoints shown at several No-SQL databases:
- SQL commands are not used as query API (Examples of APIs used include JSON, BSON, etc.)
- Doesn't guarantee atomic operations.
- Distributed and horizontally scalable.
- It doesn't have to predefine schemas. (Non-Schema)
- Non-tabular data storing (eg; key-value, object, graphs, etc).
Although it is not so obvious, No-SQL is an abbreviation to Not Only SQL. The effort and development of this new approach have been doing a lot of noise since 2009. You can find more information about it here and here. It is important to notice that the non-relational databases does not represent a complete replacement for relational databases. It is necessary to know the pros and cons of each approach and decide the most appropriate for your needs in the scenario that you're facing.
MongoDB is one of the most popular No-SQL today and what this article will focus on. It is a schemaless, document oriented, high performance, scalable database that uses the key-values concepts to store documents as JSON structured documents. It also includes some relational database features such as indexing models and dynamic queries. It is used today in production in over than 40 websites, including web services such as SourceForge, GitHub, Eletronic Arts and The New York Times..
One of the best functionalities that I like in MongoDb is the Map-Reduce. In the next section I will explain how it works illustrated with a simple example using MongoDb and Python.
If you want to install MongoDb or get more information, you can download it here and read a nice tutorial here.
Map- Reduce
MapReduce is a programming model for processing and generating large data sets. It is a framework introduced by Google for support parallel computations large data sets spread over clusters of computers. Now MapReduce is considered a popular model in distributed computing, inspired by the functions map and reduce commonly used in functional programming. It can be considered 'Data-Oriented' which process data in two primary steps: Map and Reduce. On top of that, the query is now executed on simultaneous data sources. The process of mapping the request of the input reader to the data set is called 'Map', and the process of aggregation of the intermediate results from the mapping function in a consolidated result is called 'Reduce'. The paper about the MapReduce with more details it can be read here.
Today there are several implementations of MapReduce such as Hadoop, Disco, Skynet, etc. The most famous is Hadoop and is implemented in Java as an open-source project. In MongoDB there is also a similar implementation in spirit like Hadoop with all input coming from a collection and output going to a collection. For a practical definition, Map-Reduce in MongoDB is useful for batch manipulation of data and aggregation operations. In real case scenarios, in a situation where you would have used GROUP BY in SQL, map/reduce is the equivalent tool in MongoDB.
Now thtat we have introduced Map-Reduce, let's see how access the MongoDB by Python.
PyMongo
PyMongo is a Python distribution containing tools for working with MongoDB, and is the recommended way to work with MongoDB from Python. It's easy to install and to use. See here how to install and use it.
Map-Reduce in Action
Now let's see Map-Reduce in action. For demonstrate the map-reduce I've decided to used of the classical problems solved using it: Word Frequency count across a series of documents. It's a simple problem and is suited to being solved by a map-reduce query.
I've decided to use two samples for this task. The first one is a list of simple sentences to illustrate how the map reduce works. The second one is the 2009 Obama's Speech at his election for president. It will be used to show a real example illustrated by the code.
Let's consider the diagram below in order to help demonstrate how the map-reduce could be distributed. It shows four sentences that are split in words and grouped by the function map and after reduced independently (aggregation) by the function reduce. This is interesting as it means our query can be distributed into separate nodes (computers), resulting in faster processing in word count frequency runtime. It's also important to notice the example below shows a balanced tree, but it could be unbalanced or even show some redundancy.
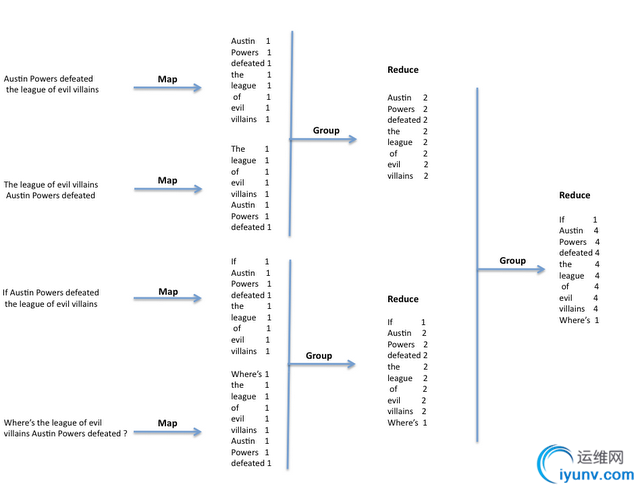
Map-Reduce Distribution
Some notes you need to know before developing your map and reduce functions:
- The MapReduce engine may invoke reduce functions iteratively; thus; these functions must be idempotent. That is, the following must hold for your reduce function:
for all k,vals : reduce( k, [reduce(k,vals)] ) == reduce(k,vals)
- Currently, the return value from a reduce function cannot be an array (it's typically an object or a number)
- If you need to perform an operation only once, use a finalize function.
Let's go now to the code. For this task, I'll use the Pymongo framework, which has support for Map/Reduce. As I said earlier, the input text will be the Obama's speech, which has by the way many repeated words. Take a look at the tags cloud (cloud of words which each word fontsize is evaluated based on its frequency) of Obama's Speech.

Obama's Speech in 2009
For writing our map and reduce functions, MongoDB allows clients to send JavaScript map and reduce implementations that will get evaluated and run on the server. Here is our map function.
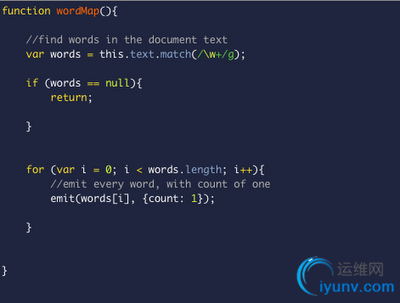
wordMap.js
As you can see the 'this' variable refers to the context from which the function is called. That is, MongoDB will call the map function on each document in the collection we are querying, and it will be pointing to document where it will have the access the key of a document such as 'text', by calling this.text. The map function doesn't return a list, instead it calls an emit function which it expects to be defined. This parameters of this function (key, value) will be grouped with others intermediate results from another map evaluations that have the same key (key, [value1, value2]) and passed to the function reduce that we will define now.
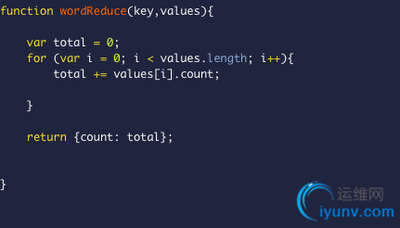
wordReduce.js
The reduce function must reduce a list of a chosen type to a single value of that same type; it must be transitive so it doesn't matter how the mapped items are grouped.
Now let's code our word count example using the Pymongo client and passing the map/reduce functions to the server.
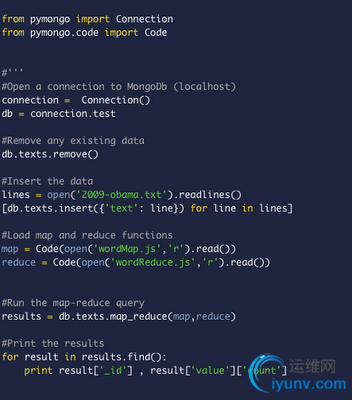
mapReduce.py
Let's see the result now:
And it works! :D
With Map-Reduce function the word frequency count is extremely efficient and even performs better in a distributed environment. With this brief experiment we can see the potential of map-reduce model for distributed computing, specially on large data sets.
All code used in this article can be download here.
My next posts will be about performance evaluation on machine learning techniques. Wait for news!
Marcel Caraciolo
References
- http://nosql.mypopescu.com/post/394779847/mongodb-tutorial-mapreduce
- http://fredzvt.wordpress.com/2010/04/24/no-sql-mongodb-from-introduction-to-high-level-usage-in-csharp-with-norm/
|
|