|
|
由于目前线上的两台NFS服务器,一台为主,一台为备。主到备的数据同步,靠rsync来做。由于数据偏重于图片业务,并且还是千万级的碎图片。在目前的业务框架下,NFS服务是存在单点的,并且数据的同步也不能做完全实时性,从而导致不能确保一致性。因此,出于对业务在线率和数据安全的保障,目前需要一套新的架构来解决 NFS 服务单点和数据实时同步的问题。 然后,就没有然后了。
下面是一个丑到爆的新方案架构图,已经在公司测试环境的部署,并且进行了不完全充分的测试。
架构拓扑:
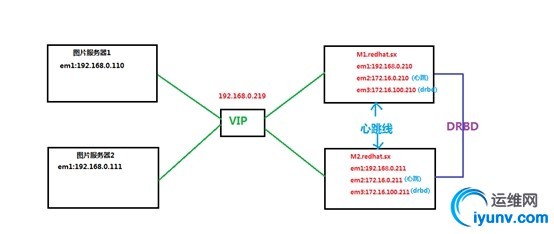
简单描述:
两台 NFS 服务器,通过 em1 网卡与内网的其他业务服务器进行通信,em2网卡主要负责两台 NFS 服务器之间心跳通信,em3网卡主要负责drbd数据同步的传输。
前面的2台图片服务器通过 NFS 集群提供出来的一个VIP 192.168.0.219 来使用 NFS 集群服务。
一、项目基础设施及信息介绍
1、设备信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| 现有的两台 NFS 存储服务器的硬件配置信息:
CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2609 0 @ 2.40GHz
MEM: 16G
Raid: RAID 1
Disk: SSD 200G x 2
网卡:集成的 4 个千兆网卡 Link is up at 1000 Mbps, full duplex
前端两台静态图片服务器硬件配置信息:
略
|
2、网络
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 浮动 VIP : 192.168.0.219 # 漂浮在M1和M2上,负责对外提供服务
现有的两台 NFS 存储服务器的网络配置信息:
主机名:M1.redhat.sx
em1:192.168.0.210 内网
em2:172.16.0.210 心跳线
em3:172.16.100.210 DRBD千兆数据传输
主机名:M2.redhat.sx
em1:192.168.0.211 内网
em2:172.16.0.211 心跳线
em3:172.16.100.211 DRBD千兆数据传输
|
3、系统环境
1
2
3
4
5
| 内核版本:2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64
系统版本:CentOS 6.5
系统位数:x86_64
防火墙规则清空
selinux关闭
|
4、软件版本
1
2
3
4
| heartbeat-3.0.4-2.el6.x86_64
drbd-8.4.3
rpcbind-0.2.0-11.el6.x86_64
nfs-utils-1.2.3-54.el6.x86_64
|
二、基础服务配置
这里仅以 M1 服务的配置为例,M2 服务器配置与此相同。
1、配置时间同步
M1端:
1
2
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ntpdate pool.ntp.org
12 Nov 14:45:15 ntpdate[27898]: adjust time server 42.96.167.209 offset 0.044720 sec
|
M2端:
1
2
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ntpdate pool.ntp.org
12 Nov 14:45:06 ntpdate[24447]: adjust time server 42.96.167.209 offset 0.063174 sec
|
2、配置/etc/hosts文件
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.0.210 M1.redhat.sx
192.168.0.211 M2.redhat.sx
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.0.210 M1.redhat.sx
192.168.0.211 M2.redhat.sx
|
3、增加主机间路由
首先先验证 M1 和 M2 的服务器 IP 是否合乎规划
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ifconfig|egrep 'Link encap|inet addr' # 验证现有 IP 信息
em1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:00:2F
inet addr:192.168.0.210 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
em2 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:00:30
inet addr:172.16.0.210 Bcast:172.16.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
em3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:00:31
inet addr:172.16.100.210 Bcast:172.16.100.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ifconfig|egrep 'Link encap|inet addr'
em1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:DE:37
inet addr:192.168.0.211 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
em2 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:DE:38
inet addr:172.16.0.211 Bcast:172.16.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
em3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr B8:CA:3A:F1:DE:39
inet addr:172.16.100.211 Bcast:172.16.100.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
|
查看现有路由,然后增加相应的心跳线和drbd数据传输线路的端到端的静态路由条目。目的是为了让心跳检测和数据同步不受干扰。
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| [iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
172.16.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em3
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em2
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1003 0 0 em2
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1004 0 0 em3
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 em1
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# /sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.211 dev em2
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# /sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.211 dev em3
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# echo '/sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.211 dev em2' >> /etc/rc.local
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# echo '/sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.211 dev em3' >> /etc/rc.local
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# tail -2 /etc/rc.local
/sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.211 dev em1
/sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.211 dev em1
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
172.16.0.211 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 em2
172.16.100.211 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 em3
172.16.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em3
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em2
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1003 0 0 em2
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1004 0 0 em3
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 em1
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# traceroute 172.16.0.211
traceroute to 172.16.0.211 (172.16.0.211), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 172.16.0.211 (172.16.0.211) 0.820 ms 0.846 ms 0.928 ms
[iyunv@M1 network-scripts]# traceroute 172.16.100.211
traceroute to 172.16.100.211 (172.16.100.211), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 172.16.100.211 (172.16.100.211) 0.291 ms 0.273 ms 0.257 ms
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| [iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
172.16.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em3
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em2
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1003 0 0 em2
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1004 0 0 em3
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 em1
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# /sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.210 dev em2
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# /sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.210 dev em3
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# echo '/sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.210 dev em2' >> /etc/rc.local
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# echo '/sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.210 dev em3' >> /etc/rc.local
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# tail -2 /etc/rc.local
/sbin/route add -host 172.16.0.210 dev em1
/sbin/route add -host 172.16.100.210 dev em1
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
172.16.0.210 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 em2
172.16.100.210 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 em3
172.16.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em3
172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em2
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 em1
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1003 0 0 em2
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1004 0 0 em3
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 em1
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# traceroute 172.16.0.210
traceroute to 172.16.0.210 (172.16.0.210), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 172.16.0.210 (172.16.0.210) 0.816 ms 0.843 ms 0.922 ms
[iyunv@M2 network-scripts]# traceroute 172.16.100.210
traceroute to 172.16.100.210 (172.16.100.210), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 172.16.100.210 (172.16.100.210) 0.256 ms 0.232 ms 0.215 ms
|
三、部署 heartbeat 服务
此处仅演示 M1 服务端的安装,M2 的不做复述。
1、安装heartbeat软件
2、配置heartbeat服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 yum.repos.d]# cd /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-3.0.4/
[iyunv@M1 heartbeat-3.0.4]# ll |egrep 'ha.cf|authkeys|haresources'
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 645 Dec 3 2013 authkeys # heartbeat服务的认证文件
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 10502 Dec 3 2013 ha.cf # heartbeat服务主配置文件
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5905 Dec 3 2013 haresources # heartbeat资源文件
[iyunv@M1 heartbeat-3.0.4]# cp ha.cf authkeys haresources /etc/ha.d/
[iyunv@M1 heartbeat-3.0.4]# cd /etc/ha.d/
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# ls
authkeys ha.cf harc haresources rc.d README.config resource.d shellfuncs
|
注意:主备节点两端的配置文件(ha.cf,authkeys,haresource)完全相同,下面是各个节点的文件内容
针对heartbeat的配置,主要就是修改ha.cf、authkeys、haresources这三个文件,下面我列出这三个文件的配置信息,大家仅作参考!
a、ha.cf 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /etc/ha.d/ha.cf
debugfile /var/log/ha-debug
logfile /var/log/ha-log
logfacility local0
keepalive 2
deadtime 10
warntime 6
#initdead 120
udpport 694
#bcast em2
mcast em2 225.0.0.192 694 1 0
auto_failback on
respawn hacluster /usr/lib64/heartbeat/ipfail
node M1.redhat.sx
node M2.redhat.sx
ping 192.168.0.1
|
b、authkeys 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# cat authkeys
auth 1 # 采用何种加密方式
1 crc # 无加密
#2 sha1 HI! # 启用sha1的加密方式
#3 md5 Hello! # 采用md5的加密方式
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# chmod 600 authkeys # 该文件必须设置为600权限,不然heartbeat启动会报错
|
c、haresources 文件
1
2
3
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# cat haresources
M1.redhat.sx IPaddr::192.168.0.219/24/em1
#NFS IPaddr::192.168.0.219/24/em1 drbddisk::data Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext4 rpcbind nfsd
|
注意:这个里的nfsd并不是heartbeat自带的,需要自己编写。
针对该脚本的编写需要满足一下需求:
1、有可执行权限
2、必须存放在/etc/ha.d/resource.d或/etc/init.d目录下
3、必须有start、stop这两个功能
具体脚本信息,下文会写。
4、启动heartbeat
1
2
3
4
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
Starting High-Availability services: INFO: Resource is stopped
Done.
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# chkconfig heartbeat off
|
说明:关闭开机自启动。当服务重启时,需要人工去启动。
5、测试heartbeat
在此步测试之前,请先在 M2 上操作如上步骤!
a、正常状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1 # 之前在heartbeat资源文件中定义的 VIP
[iyunv@M2 ha.d]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
|
说明:M1主节点拥有vip地址,M2节点没有。
b、模拟主节点宕机后的状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop
Stopping High-Availability services: Done.
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M2 ha.d]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
|
说明:M1宕机后,VIP地址漂移到M2节点上,M2节点成为主节点
c、模拟主节点故障恢复后的状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [iyunv@M1 ha.d]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
Starting High-Availability services: INFO: Resource is stopped
Done.
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
|
说明:M1节点恢复之后,又抢占回了VIP资源
四、DRBD安装部署
1、新添加(初始)硬盘
过程略
2、安装drbd
针对drbd的安装,我们不仅可以使用yum的方式,还可以使用编译安装的方式。由于我在操作的时候,无法从当前yum源取得drbd的rpm包,因此我就采用了编译的安装方式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ kernel-devel kernel-headers flex make
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cd /usr/local/src
[iyunv@M1 src]# wget http://oss.linbit.com/drbd/8.4/drbd-8.4.3.tar.gz
[iyunv@M1 src]# tar zxf drbd-8.4.3.tar.gz
[iyunv@M1 src]# cd drbd-8.4.3
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/drbd --with-km --with-heartbeat
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# make KDIR=/usr/src/kernels/2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64/
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# make install
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# mkdir -p /usr/local/drbd/var/run/drbd
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# cp /usr/local/drbd/etc/rc.d/init.d/drbd /etc/init.d/
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/drbd
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# modprobe drbd # 执行命令加载drbd模块到内核
[iyunv@M1 ha.d]# lsmod|grep drbd # 检查drbd是否被正确的加载到内核
drbd 310236 3
libcrc32c 1246 1 drbd
|
3、配置DRBD
有关DRBD涉及到的配置文件主要是global_common.conf和用户自定义的资源文件(当然,该资源文件可以写到global_common.conf中)。
注意:M1和M2这两个主备节点的以下配置文件完全一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/global_common.conf
global {
usage-count no;
}
common {
protocol C;
disk {
on-io-error detach; # 配置I/O错误处理策略为分离
no-disk-flushes;
no-md-flushes;
}
net {
cram-hmac-alg "sha1"; # 设置加密算法
shared-secret "allendrbd"; # 设置加密密钥
sndbuf-size 512k;
max-buffers 8000;
unplug-watermark 1024;
max-epoch-size 8000;
after-sb-0pri disconnect;
after-sb-1pri disconnect;
after-sb-2pri disconnect;
rr-conflict disconnect;
}
syncer {
rate 1024M; # 设置主备节点同步时的网络速率
al-extents 517;
}
}
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/drbd.res
resource drbd { # 定义一个drbd的资源名
on M1.redhat.sx { # 主机说明以on开头,后面跟主机名称
device /dev/drbd0; # drbd设备名称
disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_drbd; # drbd0 使用的是逻辑卷/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_drbd
address 172.16.100.210:7789; # 设置DRBD监听地址与端口
meta-disk internal; # 设置元数据盘为内部模式
}
on M2.redhat.sx {
device /dev/drbd0;
disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_drbd;
address 172.16.100.211:7789;
meta-disk internal;
}
}
|
4、初始化meta分区
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# drbdadm create-md drbd
Writing meta data...
initializing activity log
NOT initializing bitmap
New drbd meta data block successfully created.
|
5、启动drbd服务
此处,我们可以看下M1 和M2 启动drbd服务前后,drbd设备发生的变化
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# cat /proc/drbd # 启动前 drbd 设备信息
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# drbdadm up all # 启动drbd,这里也可以使用脚本去启动
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# cat /proc/drbd # 启动后 drbd 设备信息
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Secondary ds:Inconsistent/Inconsistent C r-----
ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:133615596
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
[iyunv@M2 ~]# drbdadm up all
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Secondary ds:Inconsistent/Inconsistent C r-----
ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:133615596
|
6、初始化设备同步,并确立主节点(覆盖备节点,保持数据一致)
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# drbdadm -- --overwrite-data-of-peer primary drbd
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:SyncSource ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/Inconsistent C r---n-
ns:140132 nr:0 dw:0 dr:144024 al:0 bm:8 lo:0 pe:17 ua:26 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:133477612
[>....................] sync'ed: 0.2% (130348/130480)M
finish: 0:16:07 speed: 137,984 (137,984) K/sec
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:SyncTarget ro:Secondary/Primary ds:Inconsistent/UpToDate C r-----
ns:0 nr:461440 dw:461312 dr:0 al:0 bm:28 lo:2 pe:75 ua:1 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:133154284
[>....................] sync'ed: 0.4% (130032/130480)M
finish: 0:19:13 speed: 115,328 (115,328) want: 102,400 K/sec
|
同步完毕之后状态:
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:133615596 nr:0 dw:0 dr:133616260 al:0 bm:8156 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:0 nr:133615596 dw:133615596 dr:0 al:0 bm:8156 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
7、挂载drbd分区到data数据目录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/drbd0
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
8355840 inodes, 33403899 blocks
1670194 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=4294967296
1020 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 21 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# mount /dev/drbd0 /data/
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root
50G 5.6G 42G 12% /
tmpfs 7.8G 0 7.8G 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 477M 46M 406M 11% /boot
/dev/drbd0 126G 60M 119G 1% /data
|
8、测试主节点写入,备节点是否能同步
M1端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/data/test bs=1G count=1
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB) copied, 1.26333 s, 850 MB/s
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:135840788 nr:0 dw:2225192 dr:133617369 al:619 bm:8156 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# umount /data/
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# drbdadm down drbd # 关闭名字为drbd的资源
|
M2端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd # 主节点关闭资源之后,查看备节点的信息,可以看到主节点的角色已经变为UnKnown
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:WFConnection ro:Secondary/Unknown ds:UpToDate/DUnknown C r-----
ns:0 nr:136889524 dw:136889524 dr:0 al:0 bm:8156 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
[iyunv@M2 ~]# drbdadm primary drbd # 确立自己的角色为primary,即主节点
[iyunv@M2 ~]# mount /dev/drbd0 /data
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cd /data
[iyunv@M2 data]# ls # 发现数据还在
lost+found test
[iyunv@M2 data]# du -sh test
1.1G test
[iyunv@M2 data]# cat /proc/drbd # 查看当前 drbd 设备信息
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:WFConnection ro:Primary/Unknown ds:UpToDate/DUnknown C r-----
ns:0 nr:136889524 dw:136889548 dr:1045 al:3 bm:8156 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:24
|
五、NFS安装部署
该操作依旧仅以M1为例,M2操作亦如此。
1、安装nfs
1
2
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# yum install nfs-utils rpcbind -y
[iyunv@M2 ~]# yum install nfs-utils rpcbind -y
|
2、配置 nfs 共享目录
1
2
3
4
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# cat /etc/exports
/data 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash,anonuid=0,anongid=0)
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /etc/exports
/data 192.168.0.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash,anonuid=0,anongid=0)
|
3、启动 rpcbind 和 nfs 服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| [iyunv@M1 drbd]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind start;chkconfig rpcbind off
[iyunv@M1 drbd]# /etc/init.d/nfs start;chkconfig nfs off
Starting NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Starting RPC idmapd: [ OK ]
[iyunv@M2 drbd]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind start;chkconfig rpcbind off
[iyunv@M2 drbd]# /etc/init.d/nfs start;chkconfig nfs off
Starting NFS services: [ OK ]
Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ]
Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ]
Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ]
Starting RPC idmapd: [ OK ]192
|
4、测试 nfs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| [iyunv@C1 ~] # mount -t nfs -o noatime,nodiratime 192.168.0.219:/data /xxxxx/
[iyunv@C1 ~] # df -h|grep data
192.168.0.219:/data 126G 1.1G 118G 1% /data
[iyunv@C1 ~] # cd /data
[iyunv@C1 data] # ls
lost+found test
[iyunv@C1 data] # echo 'nolinux' >> nihao
[iyunv@C1 data] # ls
lost+found nihao test
[iyunv@C1 data] # cat nihao
nolinux
|
六、整合Heartbeat、DRBD和NFS服务
注意,一下修改的heartbeat的文件和脚本都需要在M1和M2上保持相同配置!
1、修改 heartbeat 资源定义文件
修改heartbeat的资源定义文件,添加对drbd服务、磁盘挂载、nfs服务的自动管理,修改结果如下:
1
2
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /etc/ha.d/haresources
M1.redhat.sx IPaddr::192.168.0.219/24/em1 drbddisk::drbd Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext4 nfsd
|
这里需要注意的是,配置文件中使用的IPaddr、drbddisk都是存在于/etc/ha.d/resource.d/目录下的,该目录下自带了很多服务管理脚本,来提供给heartbeat服务调用。而后面的nfsd,默认heartbeat是不带的,这里附上该脚本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| [iyunv@M1 /]# vim /etc/ha.d/resource.d/nfsd
#!/bin/bash
#
case $1 in
start)
/etc/init.d/nfs restart
;;
stop)
for proc in rpc.mountd rpc.rquotad nfsd nfsd
do
killall -9 $proc
done
;;
esac
[iyunv@M1 /]# chmod 755 /etc/ha.d/resource.d/nfsd
|
虽然,系统自带了nfs的启动脚本,但是在 heartbeat 调用时无法彻底杀死 nfs 进程,因此才需要我们自己编写启动脚本。
2、重启heartbeat,启动 NFS 高可用
一下操作,最好按顺序!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop
Stopping High-Availability services:
Done.
[iyunv@M2 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop
Stopping High-Availability services:
Done.
[iyunv@M1 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
Starting High-Availability services: INFO: Resource is stopped
Done.
[iyunv@M2 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
Starting High-Availability services: INFO: Resource is stopped
Done.
[iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a |grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:24936 nr:13016 dw:37920 dr:17307 al:15 bm:5 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:84 nr:24 dw:37896 dr:10589 al:14 bm:5 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
C1 端挂载测试:
[iyunv@C1 ~] # mount 192.168.0.219:/data /data
[iyunv@C1 ~] # df -h |grep data
192.168.0.219:/data 126G 60M 119G 1% /data
|
OK,可以看出C1客户端能够通过VIP成功挂载NFS高可用存储共享出来的NFS服务。
3、测试
这里,将进行对NFS高可用集群进行测试,看遇到故障之后,是否服务能够正常切换。
a、测试关闭heartbeat服务后,nfs服务是否正常
M1端heartbeat服务宕前,M1端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:8803768 nr:3736832 dw:12540596 dr:5252 al:2578 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
M1端heartbeat服务宕前,M2端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:4014352 nr:11417156 dw:15431508 dr:5941 al:1168 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
宕掉M1端heartbeat服务:
1
2
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat stop
Stopping High-Availability services: Done.
|
M1端heartbeat服务宕后,M1端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:11417152 nr:4014300 dw:15431448 dr:7037 al:3221 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
M1端heartbeat服务宕后,M2端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:4014300 nr:11417152 dw:15431452 dr:5941 al:1168 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
恢复M1端的heartbeat服务,看M2是否回切
恢复M1端heartbeat服务:
1
2
3
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# /etc/init.d/heartbeat start
Starting High-Availability services: INFO: Resource is stopped
Done.
|
M1端heartbeat服务恢复后,M1端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:11417156 nr:4014352 dw:15431504 dr:7874 al:3221 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
M1端heartbeat服务恢复后,M2端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:4014352 nr:11417156 dw:15431508 dr:5941 al:1168 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
C1端针对NFS切换的受影响效果分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| [iyunv@C1 ~] # for i in `seq 1 10000`;do dd if=/dev/zero of=/data/test$i bs=10M count=1;stat /data/test$i|grep 'Access: 2014';done # 这里仅仅截取部分输出
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
10485760 bytes (10 MB) copied, 15.1816 s, 691 kB/s
Access: 2014-11-12 23:26:15.945546803 +0800
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
10485760 bytes (10 MB) copied, 0.20511 s, 51.1 MB/s
Access: 2014-11-12 23:28:11.687931979 +0800
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
10485760 bytes (10 MB) copied, 0.20316 s, 51.6 MB/s
Access: 2014-11-12 23:28:11.900936657 +0800
|
注意:目测,NFS必须需要2分钟的延迟。测试了很多方法,这个问题目前尚未解决!
b、测试关闭心跳线之外的网络后,nfs服务是否正常
M1端em1网口宕前,M1端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:11417156 nr:4014352 dw:15431504 dr:7874 al:3221 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
宕掉M1端的em1网口:
1
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ifdown em1
|
M1端em1网口宕后,M1端状态:(在M2端上通过心跳线,SSH到M1端)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state DOWN qlen 1000
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:11993288 nr:4024660 dw:16017944 dr:8890 al:3222 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
M1端em1网口宕后,M2端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:4024620 nr:11993288 dw:16017908 dr:7090 al:1171 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
恢复M1端的em1网口:
恢复M1端的em1网口,M1端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| [iyunv@M1 ~]# ip a |grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.210/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
inet 192.168.0.219/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global secondary em1
[iyunv@M1 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M1.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:20:26
0: cs:Connected ro:Primary/Secondary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:11993292 nr:4024680 dw:16017968 dr:9727 al:3222 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
恢复M1端的em1网口,M2端状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@M2 ~]# ip a|grep em1
2: em1:
mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.211/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global em1
[iyunv@M2 ~]# cat /proc/drbd
version: 8.4.3 (api:1/proto:86-101)
GIT-hash: 89a294209144b68adb3ee85a73221f964d3ee515 build by root@M2.redhat.sx, 2014-11-11 16:25:08
0: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Primary ds:UpToDate/UpToDate C r-----
ns:4024680 nr:11993292 dw:16017972 dr:7102 al:1171 bm:1 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:d oos:0
|
有关heartbeat和keepalived的脑裂问题,此处不做描述,后面另起文章去写。
以上文章是前一段公司存储改造时,我写的方案,此处分享给大家。
后来在测试过程中,由于NFS是靠RPC机制来进行通信的,受RPCBIND机制的影响,导致NFS服务端切换之后,NFS的客户端会受到1-2分的延迟。在NFS客户端频繁写入的情况下时间可能会更久,在NFS客户端无写入时,依旧需要一分钟多。因此,后来弃用了这种架构。不知道51的博友们,是如何解决NFS服务端切换导致NFS挂载客户端延时这个问题的呢?
|
|