|
|
引言
EMS(Exchange Management Shell)是管理Exchange的常用手段之一,可以把他看作是加载了Exchange管理模块的PowerShell。所以一般有两种方式启动Exchange的命令行管理。第一是启动EMS,第二是启动PowerShell然后加载Exchange管理模块。要启动Exchange的管理模块,有两种方式,第一是在目录找到PowrShell Modules(如图左)。另一种方式是使用PSSession来加载(如图右)。

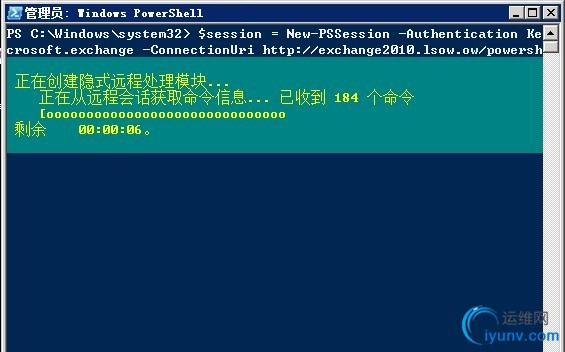
所调用的指令为:
 View Code
View Code
PS C:\Windows\system32> $session = New-PSSession -Authentication Kerberos -Credential lsow\exadmin -ConfigurationName mi
crosoft.exchange -ConnectionUri http://exchange2010.lsow.ow/powershell
PS C:\Windows\system32> Import-PSSession $session
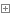
接下来是使用EMS和两种模块加载模式执行一条获取邮箱的操作,证明他们的执行结果是一致的。如图,他们都返回同一个邮箱账户,是一致的。
要使.NET调用PowerShell组建能够管理Exchange必须在调用的时候加载管理模块,否则和Exchange相关的指令就不被支持。虽然并不是很明白这两种加载模块方式的具体区别,但是由于手动加载Exchange管理模块有两种方式,.NET(或者直接说C#)管理Exchange就有2种方式。第一种方式是将代码编译成COM+组建,注册到COM+应用程序中,以供客户机代码调用。这种方式来自其他网友的指导,稍后我会给出链接;第二种方式不需要注册COM+组建,更大程度得益于“远程管理”,第二种的调用方式五花八门,详情可以参考Exchange小组的技术博客,稍后我会给出链接。哦对了,如果你希望重现截图中的调用,记得不要使用X86版本的PowerShell。
.NET管理Exchange
首先是.NET调用PowerShell
总的来说就是引用一个程序集,调用里面的对象模型。说到引用程序集就会有版本问题,楼主我测试过程中(主要是第二种方式调用),引用了win8的PowerShell程序集,去管理Exchange,结果悲剧了。win8上的是1.0版本的,服务器的是3.0版的。最要命的是,调用不会出错,但是取不到数据,这才是真正让人抓狂的。详情点击这里:http://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/zh-CN/sharepointwebpartzhchs/thread/2315f4dd-9fcc-4291-955f-4e0d1edc100e。由于单纯调用这部分内容网上很多这里就不列举了。http://blogs.technet.com/b/exchange/archive/2009/11/02/3408653.aspx,这是Exchange团队的技术博客里的一篇文章。里面列举了执行远程指令的多种方式,比如,一种是直下载,另一种是指定一个PSSession,所以通过.NET调用也有多种形式。
第一种方式,COM+应用程序
这种方式是我最初在网上寻求解决方案的时候找到的。有两个版本(我所知的),第二个版本是在第一个版本之上详细补充的。这里我必须引用原文。
版本1:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaogelove/archive/2011/02/17/1956617.html
版本2:http://www.cnblogs.com/gongguo/archive/2012/03/12/2392049.html
不得不说,第二个版本已经非常详细...详细到“启动VS-新建项目”,所以我没有信心写的更详细,这里就略过。只贴出代码实现,另外,以上两个版本在权限设置里的说明不够,导致部署会出现问题,我会在这里补充说明几点。我对以上两个版本的代码进行了修改,测试可用。
View Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.EnterpriseServices;
using System.Linq;
using System.Management.Automation;
using System.Management.Automation.Runspaces;
using System.Security;
using System.Text;
namespace OLC.EMps
{
public class ExShellRunner : ServicedComponent
{
#region 私有成员
private Runspace runspace;
private PSSnapInException exception;
private bool hasRead;
#endregion
#region 私有方法
private void initial()
{//初始化
runspace = CreateRunspace2010(out exception);
}
private static Runspace CreateRunspace(string exchangeVertion,
out PSSnapInException exception)
{
//返回运行环境
RunspaceConfiguration config = RunspaceConfiguration.Create();
config.AddPSSnapIn(exchangeVertion, out exception);
Runspace runspace = RunspaceFactory.CreateRunspace(config);
return runspace;
}
private static Runspace CreateRunspace2010(out PSSnapInException exception)
{
//针对Exchange2010的默认版本
return CreateRunspace("Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.E2010",
out exception);
}
//PSObject无法序列化,所以标记为公开方法无意义
private Collection<PSObject> RunSingleCommand2010(string name, params object[] args)
{//执行一条指令
int argCount = args.Count();//一般性验证
if (argCount % 2 != 0)
throw new Exception("命令不完整,请核对。");
int pair = argCount / 2;
initial();
try
{
runspace.Open();
Pipeline line = runspace.CreatePipeline();
Command command = new Command(name);
for (int i = 0; i < pair; i++)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(args[2 * i + 1].ToString()))
//空串忽略参数
command.Parameters.Add(args[2 * i].ToString());
else
command.Parameters.Add(args[2 * i].ToString(), args[2 * i + 1]);
}
line.Commands.Add(command);
var result = line.Invoke();
runspace.Close();
return result;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string argStr = args
.Select(i => i.ToString())
.Aggregate((c, n) => c + "," + n);
throw new Exception(argStr + "," + ex.Message);
}
}
#endregion
public PSSnapInException RunExceptionReadOnce
{
//异常应该被及时获取
get
{
if (hasRead)
{
hasRead = false;
exception = null;
return null;
}
else
{
hasRead = true;
return exception;
}
}
}
public bool IsExistMailBox(string identity)
{//根据id判断邮箱是否存在
Collection<PSObject> result = RunSingleCommand2010("Get-Mailbox", "Identity", identity);
return result != null && result.Count != 0;
}
public string GetMailboxSize(string identity)
{//查询邮箱容量
Collection<PSObject> result = RunSingleCommand2010("Get-Mailbox", "Identity", identity);
return result.First().Members["ProhibitSendQuota"].Value.ToString();
}
public void SetMaiboxSize(string identity, string warningSize, string disableSendSize,
string disableSize)
{//设置邮箱容量,可以使用0.5GB这样的值
RunSingleCommand2010("Set-Mailbox", "Identity",identity,"IssueWarningQuota", warningSize,
"ProhibitSendQuota",disableSendSize,"ProhibitSendReceiveQuota", disableSize);
}
public int GetMaiboxCountByOU(string ouPath)
{//根据指定的OU获取邮箱用户数目
var result = RunSingleCommand2010("Get-Mailbox", "OrganizationalUnit", ouPath ,"ResultSize","unlimited");
return result.Count;
}
public void RemoveMailbox(string identity)
{//根据指定的id移除邮箱
RunSingleCommand2010("Remove-Mailbox", "Identity", identity, "Confirm", false);
}
public bool NewMailbox(string name, string userprincipalName, string password, string displayName
, string organizationUnit, string database, string domainName)
{//添加邮箱帐户
string upn = userprincipalName + domainName;
bool isExist = this.IsExistMailBox(upn);
if (isExist)
throw new Exception("已存在的邮箱。");
SecureString ss = new SecureString();
foreach (var i in password) ss.AppendChar(i);
var result = RunSingleCommand2010("New-Mailbox", "Name", name, "UserPrincipalName"
, upn, "Password", ss, "DisplayName", displayName, "OrganizationalUnit"
, organizationUnit, "DataBase", database);
return result != null && result.Count != 0;
}
public bool IsAllExchangeDatabaseMounted(out string returnMessage)
{//空串表示忽略参数
bool anyDismouted = false;
try
{
var databases = this.RunSingleCommand2010("Get-Mailboxdatabase","Status","");
StringBuilder errorMessage = null;
errorMessage = new StringBuilder(
"一些邮件服务器的数据库工作不正常,名称分别为:");
foreach (var i in databases)
{
var obj = i.Properties["Mounted"];
var mountedStr = obj.Value.ToString();
bool mounted = bool.Parse(mountedStr.ToString());
if (mounted == false)
errorMessage.AppendFormat("{0},", i.Members["Name"]);
anyDismouted = anyDismouted || !mounted;
}
string message = anyDismouted ? errorMessage.ToString()
: "所有邮件服务器数据工作正常!";
returnMessage = message;
return !anyDismouted;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{//抛出异常
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
以下是部署时候碰到的几个问题:
1.按照以上引用的博文的顺序操作,并将程序集编译为64位,忽略VS的警告。
2.在本地IIS上进行测试,不使用IISExpress(VS以管理员权限运行)。
3.COM+应用程序设置中有个“标识”页,给他提供能够管理Exchange的用户。否则查询操作可以进行,但是增删就有问题了。
4.COM+应用程序有个用户[角色-Creator-用户],向里面添加IIS用户(IIS_IUSERS)。
目前我使用这种方式完成,这里是运行截图。

第二种方式,远程调用
没什么特别的,这里直接贴上代码。总共有三个类型...呃,本来是想弄好一点,后来越弄越没信心。
主要的类型。
View Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Management.Automation;
using System.Management.Automation.Runspaces;
using System.Text;
namespace OLC.PowerShellInvoke
{
public class PowerShellInvoker
{
protected Runspace runspace;
public PowerShellInvoker()
{//调用本地powershell命令
runspace = RunspaceFactory.CreateRunspace();
}
private Collection<PSObject> runSingleCommand(string name, object[] args)
{
//执行一条指令,为了正确使用上下文,这里不执行初始化
int argCount = args.Count();//一般性验证
if (argCount % 2 != 0)
throw new Exception("命令不完整,请核对。");
int pair = argCount / 2;
//initial();
try
{
runspace.Open();
Pipeline line = runspace.CreatePipeline();
Command command = new Command(name);
for (int i = 0; i < pair; i++)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(args[2 * i + 1].ToString()))
//空串忽略参数
{
CommandParameter cp = new CommandParameter(args[2 * i].ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(cp);
}
else
command.Parameters.Add(args[2 * i].ToString(), args[2 * i + 1]);
}
line.Commands.Add(command);
var result = line.Invoke();
runspace.Close();
return result;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
//关闭运行空间
runspace.Close();
string argStr = args
.Select(i => i.ToString())
.Aggregate((c, n) => c + "," + n);
throw new Exception(argStr + "," + ex.Message);
}
}
public Collection<PSObject> RunSingleCommand(string name, params object[] args)
{
return runSingleCommand(name, args);
}
public Collection<PSObject> RunSingleCommandWithArrayArgs(string name, object[] args)
{//提供传递数组作为参数的版本
return runSingleCommand(name, args);
}
}
}
供远程调用的类型,其实就构造函数有区别...
View Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Management.Automation;
using System.Management.Automation.Runspaces;
using System.Security;
using System.Text;
namespace OLC.PowerShellInvoke
{
public class PowerShellRemoteInvoker:PowerShellInvoker
{
public PowerShellRemoteInvoker(string uri, string username, string password)
{
this.uri = uri;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
initial();
}
protected string uri;
protected string username;
protected string password;
protected void initial()
{
SecureString ss = new SecureString();
foreach (var c in password) ss.AppendChar(c);
//在powershell中,也只能通过.net的方式实例化这个类型
PSCredential credentail = new PSCredential(username, ss);
WSManConnectionInfo connection = new WSManConnectionInfo(new Uri(uri),//"",
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/powershell/Microsoft.Exchange",
credentail);
runspace = RunspaceFactory.CreateRunspace(connection);
}
}
}
最后一个是用来处理SecurityString的,没用上。
View Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Management.Automation;
using System.Text;
namespace OLC.PowerShellInvoke
{
public class CredentialCreator
{
public static PSCredential Create(string username, string password)
{
System.Security.SecureString ss = new System.Security.SecureString();
foreach (var c in password) ss.AppendChar(c);
return new PSCredential(username, ss);
}
}
}
注意,凭据不能用一般的WebCredentials。
写了个脚本测试了下,获取某个邮箱的配额(在AD的一个远程机子上运行的。)
View Code
#I @"E:\EBackUp\MoniRoot\Sort\Exchange\Code\ExhangeMailboxDatabaseDetectionService\OLC.PowerShell\bin\Debug"
#r "OLC.PowerShellInvoke.dll"
#r "System.Management.Automation.dll"
open OLC.PowerShellInvoke;
let rinvoker = new PowerShellRemoteInvoker("http://exsvr.search.ow/powershell","search\exadmin","*****");
printf "%s" (rinvoker.RunSingleCommand("Get-Mailbox","Identity","czq@search.ow").Item(0).Members.Item("ProhibitSendQuota").Value.ToString())
System.Console.ReadKey()
结果是这样的。

嗯,我用F#有两个原因,第一,好玩...;第二,脚本片段易于保存和重现。有空会测试IIS调用的情况,并补充到本文中。
对比
简要对比下:
1.COM+:要求部署在Exchange服务器上(因为有PowerShell Modules),一般选用CAS服务器。另外COM+应用程序在没有使用的情况下会自动关闭,一有请求又开启,所以第一次调用会显得有点慢。
2.远程调用。主要是要基于Kerberos的身份验证,使用SSL加密模式也可以,但是就要配置证书,所以目前我使用的都是Kerberos模式的身份验证。可以在同一个AD上部署,或者在建立了信任关系的其他AD中部署。相比第一种来说灵活(差别不大),也干净一点。但是我尚未测试使用WEB调用的情况,所以有没有其他问题尚未明确。
结语
我的两篇“小系列”就到这里结束了。如果各位朋友对本文的主题感兴趣,欢迎跟帖讨论!任何问题可以留言,初到博客园,我要做辛勤的园丁。
|
|