大纲
一、Linux系统启动流程图
二、Linux系统启动流程详解之一:POST
三、Linux系统启动流程详解之二:BIOS(Boot Sequence)
四、Linux系统启动流程详解之三:MBR(BootLoader)
五、Linux系统启动流程详解之四:kernel和initrd
六、Linux系统启动流程详解之五:/sbin/init
一、Linux系统启动流程简述
二、Linux系统启动流程详解之一:POST 加电自检又称为开机自我检测(英文Power-On Self-Test,常用简称POST),是计算机BIOS的一个功能,在开机后会运行,针对计算机硬件如CPU、主板、存储器等进行检测,结果会显示在固件可以控制的输出界面,像屏幕、LED、打印机等等设备上。如果设备健康状态监测出了问题,就会有各种含义的蜂鸣声。 测试流程: - 开机系统重置REST启动CPU。
- CPU指向BIOS自我测试的地址FFFFOH并打开CPU运行第一个指令。
- CPU内部寄存器的测试。
- CMOS 146818 SRAM检查。
- ROM BIOS检查码测试。
- 8254计时/计数器测试。
- 8237 DMA控制器测试。
- 74612页寄存器测试。
- REFRESH刷新电路测试。
- 8042键盘控制器测试。
- DRAM 64KB基本存储器测试。
- CPU保护模式的测试。
- 8259中断控制器的测试。
- CMOS 146818电力及检查码检查。
- DRAM IMB以上存储器检查。
- 显卡测试。
- NMI强制中断测试。
- 8254计时/计数器声音电路测试。
- 8254计时/计数器计时测试。
- CPU保护模式SHUT DOWN测试。
- CPU回至实模式(REAL MODE)。
- 键盘鼠标测试。
- 8042键盘控制器测试。
- 8259中断控制器IRQ0至IRQ18创建。
- 磁盘驱动器及界面测试。
- 设置并行打印机及串列RS232的界面。
- 检查CMOS IC时间、日期。
- 检查完成
如果没有显示器,我们可以通过POST CARD来完全上面的测试工作。
三、Linux系统启动流程详解之二:BIOS(Boot Sequence)
当硬件自检完成之后,BIOS就会依据定义在Boot Sequence中自上而下的寻找MBR,如果第一个设备找不到MBR,则会找第二个,以此类推,如果第一个设备有MBR,但是损坏了,它不会去找第二个设备的MBR。所以只有当找不到MBR时,才会去另一个设备。当找到某个设备的MBR时,再将计算机的控制权转交给MBR中位于前446字节的BootLoader。

补充:BIOS与CMOS的关系
CMOS是计算机上另一个重要的存储器。之所以提到它,是因为BIOS程序的设置结果就保存在CMOS中。而且,在BIOS程序引导计算机启动后,计算机需要载入CMOS中的用户信息和常规设置后才能正常使用。
四、Linux系统启动流程详解之三:MBR(BootLoader)
1、Linux上常见BootLoader
BootLoader分MBR前446字节存放的就是BootLoader;其本质是用于引导操作系统的代码段X86的工作站和服务器上一般使用LILO和GRUB( GRand Unified Bootloader)。LILO曾经是Linux发行版主流的BootLoader,不过,它不能引导1024柱面以后的分区,所以现在几乎所有的发行版都已经使用了GRUB,GRUB比LILO有更友好的显示接口,使用配置也更加灵活方便。
2、grub启动阶段
stage1:存储于MBR中前446字节,用于实现引导stage2
stage1.5:存储于/boot/grub目录中,用于识别各种常见的文件系统
stage2:存储于/boot/grub目录中,真正实现引导操作系统
3、grub的配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| [iyunv@CentOS5 grub]# cat /boot/grub/grub.conf
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.
# root (hd0,0)
# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00
# initrd /initrd-version.img
#boot=/dev/sda
default=0 # 设定默认启动的title的编号,从0开始
timeout=5 # 等待用户选择的超时时长,单位是秒
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz # grub的背景图片定义
hiddenmenu # 隐藏菜单,需要按键才会显示菜单
passwd --md5 $1$iR1wX$Q5NDrU92ypjCLAUHHHg260 # 密码设置在此处时,则需要先输入密码才能编辑grub菜单,按p提示输入grub密码
title CentOS (2.6.18-308.el5) # 内核标题,或操作系统名称,字符串,可自由修改
root (hd0,0) # 内核文件所在的设备;对grub而言,所有类型硬盘一律hd,格式为(hd#,N);hd#, #表示第几个磁盘;最后的N表示对应磁盘的分区;
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-308.el5 ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 # 内核文件路径,及传递给内核的参数
initrd /initrd-2.6.18-308.el5.img # ramdisk文件路径
passwd --md5 $1$4G2wX$Jb7Nvqdubza6oXH3C/BlL. #密码设置在此处时,则需要先输入密码,才能启动内核
如需更改grub背景图片,则用gimp制作一个640X480大小的xpm格式图片,再gzip压缩放于/boot/grub/目录下即可
当前boot分区是一个独立的分区,在kernel这一行定义时,是直接在根下,而不是/boot下
因为各分区在物理上是并行的。虽然boot目录是在根下,但boot目录下的文件则是在另一个独立分区上。
所以在grub看来,要想访问kernel文件,即把这个单独分区当做根,那么文件即是直接在根下,而不是在/boot下
|
4、给grub添加密码以及如何进入单用户模式
(1)、生成md5加密的密码
1
2
3
4
| [iyunv@CentOS5 grub]# grub-md5-crypt # grub自带的加密工具
Password:
Retype password:
$1$hj5wX$ekbrytcIyl3C7TiGPBOUR1
|
(2)、编辑grub的配置文件/boot/grub/grub.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| [iyunv@CentOS5 grub]# cat /boot/grub/grub.conf
# grub.conf generated by anaconda
#
# Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file
# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that
# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.
# root (hd0,0)
# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00
# initrd /initrd-version.img
#boot=/dev/sda
default=0
timeout=5
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz
hiddenmenu
password --md5 $1$hj5wX$ekbrytcIyl3C7TiGPBOUR1 # 此行就是我们添加的grub菜单密码
title CentOS (2.6.18-308.el5)
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.18-308.el5 ro root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00
initrd /initrd-2.6.18-308.el5.img
|
(3)、重启计算机
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@CentOS5 grub]# reboot
Broadcast message from root (pts/2) (Wed Dec 2 18:45:32 2015):
The system is going down for reboot NOW!
|
(4)、grub显示界面,敲一下p键

(5)、输入密码之后按回车键
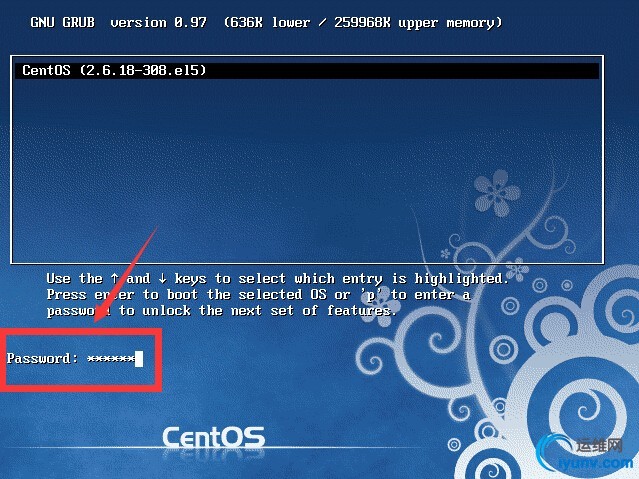
(6)、此时可以看到下方编辑菜单已经解锁,用户可以自行编辑了,此时我们敲e键

(7)、将光标挪至第二行,也就是kernel这一行,再敲一下e键
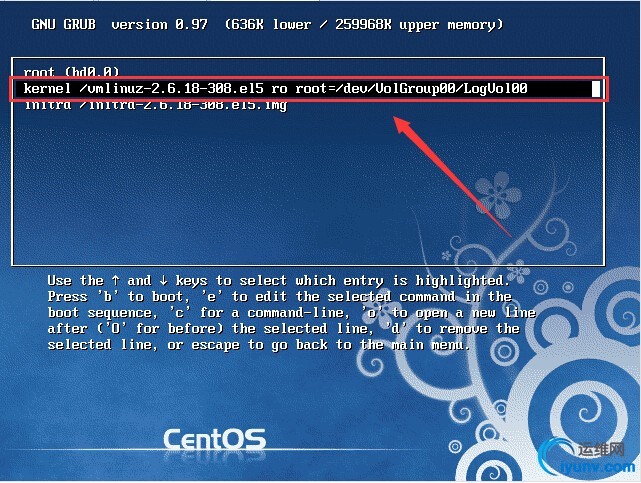
(8)、此时就进入kernel的编辑菜单里,我们只需要在行尾加一个数字1之后按回车
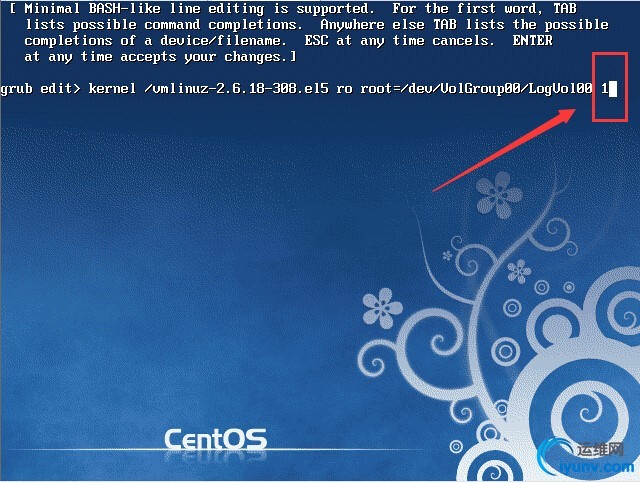
(9)、此时敲一下b键,即可重新启动系统

(10)、此时系统已重新启动,启动完成之后,就是单用户模式,直接修改root密码
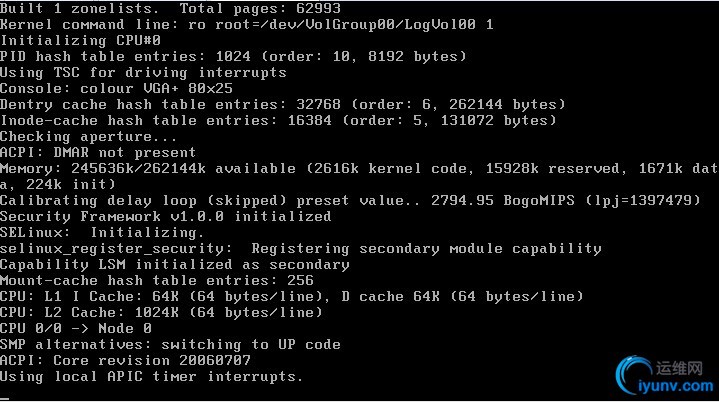
(11)、此时是root用户直接登录,输入passwd修改root密码,再重启进入级别3即可

5、安装grub
(1)、grub命令行方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| [iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# mount
/dev/mapper/VolGroup00-LogVol00 on / type ext3 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext3 (rw) # 可以看到boot为独立分区
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
sunrpc on /var/lib/nfs/rpc_pipefs type rpc_pipefs (rw)
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 21.4 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 14 2610 20860402+ 8e Linux LVM
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=200 count=1 # 模拟bootloader损坏
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
200 bytes (200 B) copied, 0.000158 seconds, 1.3 MB/s
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# sync # 同步至磁盘
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# grub # 进入grub命令行界面
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
GNU GRUB version 0.97 (640K lower / 3072K upper memory)
[ Minimal BASH-like line editing is supported. For the first word, TAB
lists possible command completions. Anywhere else TAB lists the possible
completions of a device/filename.]
grub> root (hd0,0) # 指定内核所在磁盘及分区,自己指定
root (hd0,0)
Filesystem type is ext2fs, partition type 0x83
grub> setup (hd0) # 安装grub,指定磁盘
setup (hd0)
Checking if "/boot/grub/stage1" exists... no
Checking if "/grub/stage1" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/stage2" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/e2fs_stage1_5" exists... yes
Running "embed /grub/e2fs_stage1_5 (hd0)"... 15 sectors are embedded.
succeeded
Running "install /grub/stage1 (hd0) (hd0)1+15 p (hd0,0)/grub/stage2 /grub/grub.conf"... succeeded
Done.
grub> quit
quit
|
(2)、grub-install命令方式:grub安装在当前磁盘上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| grub-install --root-directory=/path/to/boot's_parent_dir /PATH/TO/DEVICE
此时需要注意--root-directory指向的是boot的父目录
grub在安装时,会自动在根下找boot目录,然后在boot目录里创建stage1.5和stage2等各种文件
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=200 count=1 # 模拟损坏bootloader
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
200 bytes (200 B) copied, 0.000229 seconds, 873 kB/s
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# sync # 同步至磁盘
[iyunv@CentOS5 ~]# grub-install --root-directory=/ /dev/sda # 安装grub
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map //boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
# this device map was generated by anaconda
(hd0) /dev/sda
|
(3)、grub-install命令方式:grub安装在另一块磁盘上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
| [iyunv@soysauce ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sda
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# fdisk /dev/sda # 新建一个20M的分区,存放grub配置文件及启动文件
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x7dd89809.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +20M
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x7dd89809
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 1 4 32098+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# cat /proc/partitions # 此时刚才创建的sda1已经被内核识别
major minor #blocks name
8 0 20971520 sda
8 1 32098 sda1
8 16 20971520 sdb
8 17 512000 sdb1
8 18 20458496 sdb2
253 0 18423808 dm-0
253 1 2031616 dm-1
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# mke2fs -j /dev/sda1 # 创建ext3文件系统
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
8032 inodes, 32096 blocks
1604 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=33030144
4 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group
2008 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (1024 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 39 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# mkdir /mnt/boot # 以mnt为根,在其目录下创建一个boot目录
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/boot/ # 挂载sda1分区至boot目录下
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# ls /mnt/boot/
lost+found # 分区已挂载成功
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# grub-install --root-directory=/mnt/ /dev/sda # 安装grub
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map /mnt//boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
(fd0) /dev/fd0
(hd0) /dev/sda
(hd1) /dev/sdb
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# sync # 同步内存数据至磁盘
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# vim /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf # 编辑grub配置文件
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# cat /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=5
title My Linux
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz
initrd /initrd
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# sync # 同步内存数据至磁盘
[iyunv@soysauce ~]# umount /mnt/boot/ # 卸载此磁盘,挂载至其他计算机上
|

6、当grub配置文件丢失时
(1)、当grub.conf配置文件丢失时,重启系统时就会是这样
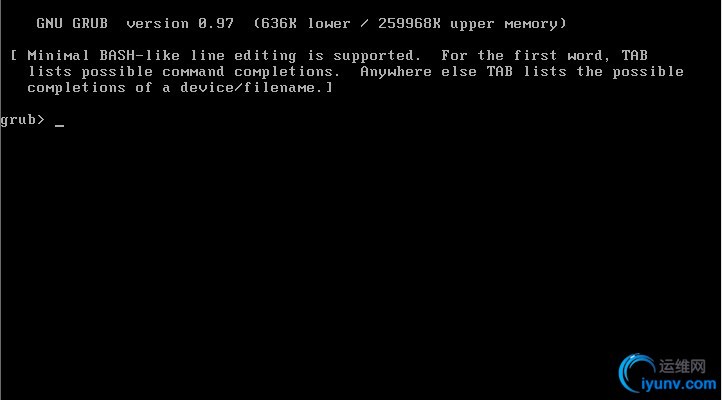
(2)、此时我们只需要指定/所在的磁盘及分区、内核文件路径、initrd文件路径即可

启动完成之后显示如下

注:此处find命令十分好用,指定root、kernel、initrd即可启动
(3)、重建grub.conf配置文件即可

五、Linux系统启动流程详解之四:kernel和initrd
1、kernel初始化过程
①设备探测
②驱动初始化(可能会从initrd(initramfs)文件中装载驱动模块)
③以只读挂载根文件系统;
④装载第一个进程init(PID:1)
2、inittab文件
(1)、定义格式 id:runlevels:action:process
①id:标识符
②runlevels:在哪个级别运行此行
③action:在什么情况下执行此行
④process:要运行程序
ACTION: ①initdefault:设定默认运行级别 ②sysinit:系统初始化 ③wait:等待级别切换至此级别时执行 ④respawn:一旦程序终止,会重新启动
(2)、/etc/inittab的任务
①设定默认运行级别
②运行系统初始化脚本
③运行指定运行级别对应的目录下的脚本
④设定Ctrl+Alt+Del组合键的操作
⑤定义UPS电源在电源故障/恢复时执行的操作
⑥启动虚拟终端(2345级别)
⑦启动图形终端(5级别)
3、/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit的任务
①激活udev和selinux
②根据/etc/sysctl.conf文件,来设定内核参数
③设定时钟时钟
④装载键盘映射
⑤启用交换分区和设置主机名
⑥根文件系统检测,并以读写方式重新挂载
⑦激活RAID和LVM设备
⑧启用磁盘配额
⑨根据/etc/fstab,检查并挂载其它文件系统
⑩清理过期的锁和PID文件
|