|
|
1.范例5:通过read读入变量方式的多分支if语句
[iyunv@server2 ~]# cat if-mult.sh
#!/bin/bash
#this scripts is created by hy 2015-01-25
#1020659371@qq.com
#function:compare two num.
#v1.0
read -t 10 -p "please input two num:" a b
if [ $a -gt $b ];then
echo "yes $a > $b"
elif [ $a -eq $b ];then
echo "yes $a = $b"
else
echo "yes $a < $b"
fi
范例6(生产):生产环境监控Mysql服务的实战例子
问题描述:监控Mysql服务是否正常启动,如果未正常启动,就启动Mysql服务。
法一:db_status1.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 portNum=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | awk '{print $4}' |awk -F : '{print $2}' `
3 if [ "$portNum" = "3306" ];then
4 echo "mysql server is running."
5 else
6 echo "mysql server is stop."
7 fi
法二:db_status2.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 portNum=`ps -ef |awk '{print $1}'|grep mysql`
3 if [ "$portNum" = "3306" ];then
4 echo "mysql server is running."
5 else
6 echo "mysql server is stop."
7 fi
法三:db_status3.sh
/etc/init.d/mysqld status //通过这个命令去监控
法四:db_status4.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 portNum=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | awk -F '[ :]+' '{print $5}'`
//这里为了体现出正则表达式的用法
3 if [ "$portNum" = "3306" ];then
4 echo "mysql server is running."
5 else
6 echo "mysql server is stop."
7 fi
法五:db_status5.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 a=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | wc -l` //这里体现了解决问题不同的思想
3 if [ $a -eq 1 ];then
4 echo "mysql server is running."
5 else
6 {
7 /etc/init.d/mysqld start >/dev/null
8 echo "mysql server have been restart."
9 }
10 fi
如果在一台主机上有多个数据库,我们可以使用egrep更加精确的匹配出他们:
[iyunv@server2 ~]# netstat -antlp | egrep "3306|3307" | wc -l
1
[iyunv@server2 ~]# netstat -antlp | egrep "330" | wc -l
1
通过检查端口号和进程同时存在来判断mysql是否正常运行,如果没有运行则启动:
db_status6.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 a=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | wc -l`
3 b=`ps -ef | grep mysqld | grep -v grep | wc -l`
4 #if [ $a = 1 ]&&[ $b = 2 ];then
5 if [ $a -eq 1 -a $b -eq 2 ];then
6 echo "mysql server is running."
7 else
8 {
9 /etc/init.d/mysqld start >/dev/null
10 echo "mysql server have been restart."
11 }
12 fi
将这个脚本完善一下:
1 #!/bin/bash
2 MYSQL=/etc/init.d/mysqld
3 LogPath=/tmp/mysql.log
4 a=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | wc -l`
5 b=`ps -ef | grep mysqld | grep -v grep | wc -l`
6 #if [ $a = 1 ]&&[ $b = 2 ];then
7 if [ $a -eq 1 -a $b -eq 2 ];then
8 echo "mysql server is running."
9 else
10 {
11 $MYSQL start > $LogPath
12 sleep 10
13 a=`netstat -antlp | grep 3306 | wc -l`
14 b=`ps -ef | grep mysqld | grep -v grep | wc -l`
15 if [ $a -eq 1 -a $b -eq 2 ];then
16 while true
17 do
18 killall -9 mysqld >/dev/null 2>&1
19 [ $? -ne 0 ] && break
20 sleep 1
21 done
22 $MYSQL start >> $LogPath && status = "successfully" || status = "failure"
23 mail -s "mysql startup status is $status" < 1020659371@qq.com &/dev/null //这里-e是不用交互,不然会进到mysql里面出不来
3 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
4 echo "db is running"
5 else
6 /etc/init.d/mysqld start
7 fi
法二:
[iyunv@server10 scripts]# vim db_status08.sh //改进后的脚本
改进1:
1 #!/bin/bash
2 MYSQL=/etc/init.d/mysqld
3 LogPath=/tmp/mysql.log
4 mysql -u root -p'mysql' -S /usr/local/lanmp/mysql/data/mysql.sock -e "select versio n();" >&/dev/null
5 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
6 echo "mysql server is running."
7 else
8 $MYSQL start > $LogPath
9 sleep 10
10 mysql -u root -p'mysql' -S /usr/local/lanmp/mysql/data/mysql.sock -e "selec t version();" >&/dev/null
11 if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
12 while true
13 do
14 killall -9 mysqld >/dev/null 2>&1
15 [ $? -ne 0 ] && break
16 sleep 1
17 done
18 $MYSQL start >> $LogPath && status = "successfully" || status = "failure"
19 mail -s "mysql startup status is $status" < 1020659371@qq.com &/dev/null
5 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
6 echo "mysql server is running."
7 exit 0
8 else
9 [ -x $MYSQL ] && $MYSQL start > $LogPath
10 sleep 10
11 mysql -u root -p'mysql' -S /usr/local/lanmp/mysql/data/mysql.sock -e "selec t version();" >&/dev/null
12 if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
13 while true
14 do
15 killall -9 mysqld >/dev/null 2>&1
16 [ $? -ne 0 ] && break
17 sleep 1
18 done
19 [ -x $MYSQL ] && $MYSQL start >> $LogPath && status = "successfully" || sta tus = "failure"
20 mail -s "mysql startup status is $status" < 1020659371@qq.com select user,host from mysql.user;
+------+----------------------+
| user | host |
+------+----------------------+
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| | localhost |
| root | localhost |
| | server10.example.com |
| root | server10.example.com |
+------+----------------------+
6 rows in set (0.07 sec)
如果我们要连接或监控远端的数据库用-h指定IP进行连接,这里我们需要了解如何给数据库授权通过远程连接
[iyunv@server28 ~]# mysql -u root -p'mysql' -S /usr/local/lanmp/mysql/data/mysql.sock -h 127.0.0.1 -e "select version();"
+------------+
| version() |
+------------+
| 5.5.12-log |
+------------+
法三:通过php/java程序监控Mysql
还记得在lanmp环境部署时讲的test_mysql的脚本么?请大家发出来
提示:此法是监控数据库是否异常的最佳的方法。
1
回顾下监控Mysql数据库是否异常的多种方法:
l 根据Mysql端口号监控Mysql(本地)。
此处是本地监控,端口在,服务可能不正常,例如:负载很高,cpu很高,连接数满了,另,端口也可以远程监控。
l 根据Mysql进程监控Mysql(本地)。
只能本地监控,进程在服务可能不正常,例如:负载很高,cpu很高,连接数满了,也可以远程监控,例如:通过ssh key,expect。
l 通过Mysql客户端命令端口及账户连接Mysql,然后根据返回命令状态或返回内容确认mysql是否正常(远程连接)。
必须要有mysql客户端,要有数据库的账号和密码,及连接数据库主机授权。
l 通过php/java程序url监控Mysql(推荐)。
最接近用户访问,效果最好,报警的最佳方式不是服务是否开启了,而是网站的用户是否还访问正常。(这里是从用户的角度考虑问题,所以说是最佳的)
l 以上4种方法的综合运用。
请思考,(1)还有没有其他方法?(2)以上每种方法的局限?(3)其他的业务是否可以用上述判断思想。
2.多判断条件if语句(&&、||)
这里不再讲解:基本的知道
注意:[] 、&&、||、一个[]括号以及多个括号的用法
[] || {}
2.综合范例1:开发shell脚本监控apache或nginx服务
这里以apache服务为例。
方法1:通过端口监控
1.本地监控
1 #!/bin/bash
2 a=`netstat -antlp | grep 80 | wc -l`
3
4 if [ $a -ne 0 ];then
5 echo "apache is running."
6 else
7 echo "apache is stop."
8 /usr/local/lanmp/apache/bin/apachectl start
9 fi
方法2:利用nmap进行监控:
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nmap 192.168.2.2 -p 80
Starting Nmap 5.51 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-02-03 11:30 CST
Nmap scan report for server2.example.com (192.168.2.2)
Host is up (0.00016s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.14 seconds
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nmap 192.168.2.2 -p 80 | grep open
80/tcp open http
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nmap 192.168.2.2 -p 80 | grep open | wc -l
1
方法3:通过wget去检测
[iyunv@server2 ~]# wget -T 10 -q http://192.168.2.2
[iyunv@server2 ~]# echo $?
0
[iyunv@server2 ~]# killall -9 httpd
[iyunv@server2 ~]# killall -9 httpd
httpd: 没有进程被杀死
[iyunv@server2 ~]# wget -T 10 -q http://192.168.2.2
[iyunv@server2 ~]# echo $?
4
[iyunv@server2 ~]# wget -T 10 -q --spider http://192.168.2.2
对上面的参数进行说明:-T是指定超时退出时间单位为秒,-q是通过安静模式访问,--spider是模拟网页爬虫。
我们可以通过上述命令的返回值判断服务是否正常:
1 #!/bin/bash
2 wget -T 10 -q --spider http://192.168.2.2
3 if [ $? -ne 0 ];then
4 echo "apache is running."
5 else
6 echo "apache is stop."
7 /usr/local/lanmp/apache/bin/apachectl start
8 fi
这里是模拟用户访问网站,如果这样检测的结果服务是停止的,呢么用户基本访问也不行了。
方法4:通过curl命令去访问,然后检测:
[iyunv@server2 ~]# curl -s http://192.168.2.2 //这里-s的意思是安静访问
server2.example.com
方法5:通过获取http url的header code监控
[iyunv@server2 ~]# curl -I http://192.168.2.2
HTTP/1.1 200 OK //一个网站要能正常访问的话,这里返回值为200
Date: Tue, 03 Feb 2015 03:55:34 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.15 (Red Hat)
Last-Modified: Sun, 18 Jan 2015 15:41:21 GMT
ETag: "9a41-14-50cef09a20f31"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 20
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
200 - OK,服务器成功返回网页
- Standard reponse for successful HTTP requests.
301 - Moved Permanently(永久跳转),请求的网页已永久跳转到新位置
-This and all future requests should be directed to the given.
403 - Forbidden(禁止访问),服务器拒绝请求
- forbidden requests (matches a deny filter) => HTTP 403
- The requests was a legal requests,but the seerver is refusing to respond to it.
404 - Not Found,服务器找不到请求的页面。
-The requested resource could not be found but may be available again in the future.
500 - Internal Server Error(内部服务器错误)
- internal error in haproxy => HTTP 500
- A generic error message,given when no more specific message is suitable.
502 - Bad Gateway(坏的网关),一般是网关服务器请求后端服务时,后端服务没有按照http协议正确返回结果。
- the server returned an invalid or incomplete response =》 HTTP 502
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid reponse from the upstream server.
503 - Service Unavailable(服务当前不可用),可能因为超载或停机维护。
- no server was available to handle the request => HTTP 503
- The server is currently unavailable (becuase it is overloaded or down for maintenance)
504 - Gateway Timeout(网关超时)一般是网关服务没有在特定的时间内完成服务。
- the server failed to reply in time => HTTP 504
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
Haproxy may emit the following status codes by itself:
Code When / reason
http://oldboy.blog.iyunv.com/2561410/716294
[iyunv@server2 ~]# curl -I -s http://192.168.2.2 | head -1 |cut -d " " -f 2
200
httpCode.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 httpCode=`curl -I -s http://192.168.2.2 | head -1 |cut -d " " -f 2`
3 if [ $httpCode -ne 0 ];then
4 echo "apache is running."
5 else
6 echo "apache is stop."
7 /usr/local/lanmp/apache/bin/apachectl start
8 fi
Http2.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 [ -f /etc/init.d/functions ] && . /etc/init.d/functions || exit 1
3 httpCode=`curl -I -s http://192.168.2.2 | head -1 |cut -d " " -f 2`
4 if [ $httpCode -ne 0 ];then
5 action "apache is running." /bin/true
6 else
7 action "apache is not running." /bin/false
8 sleep 1
9 /etc/init.d/httpd start >&/dev/null
10 action "apache is started." /bin/true
11 fi

http3.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 [ -f /etc/init.d/functions ] && . /etc/init.d/functions || exit 1
3 if [ $# -ne 1 ];then
4 echo "Usage:$0 argv"
5 exit 1
6 fi
7
8 httpCode=`curl -I -s $1 | head -1 |cut -d " " -f 2`
9 if [ $httpCode -ne 0 ];then
10 action "apache is running." /bin/true
11 else
12 action "apache is not running." /bin/false
13 sleep 1
14 /etc/init.d/httpd start >&/dev/null
15 action "apache is started." /bin/true
16 fi
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh http3.sh
Usage:http3.sh argv
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh http3.sh http://192.168.2.2
apache is running. [确定]
http4.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 if [ $# -ne 2 ];then
3 echo "Usage:$0 ip port"
4 exit
5 fi
6 HttpPortNUM=`nmap $1 -p $2 | grep open | grep -v grep | wc -l`
7 if [ $HttpPortNUM -eq 1 ];then
8 echo "$1 $2 is open."
9 else
10 echo "$1 $2 is closed."
11 fi
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh http4.sh 192.168.2.2
Usage:http4.sh ip port
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh http4.sh 192.168.2.2 80
192.168.2.2 80 is open.
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh http4.sh server2.example.com 81
server2.example.com 81 is closed.
监控nginx和apache同样
范例7:如何查看远程web服务是否开通tcp 80端口?
解答:
法一:此法常被用来检测是个远程端口是否通畅。
[iyunv@server2 ~]# telnet 192.168.2.2 80
Trying 192.168.2.2...
Connected to 192.168.2.2. //出现Connected表示连通了,说明192.168.2.2的80端口开放的。
Escape character is '^]'. //ctrl+]推出此地。
^]
telnet> quit
Connection closed.
如果写脚本通过telnet检查端口可以用下面的方法:
[iyunv@server2 ~]# echo -e "\n" | telnet 192.168.2.2 80 | grep Connected
Connected to 192.168.2.2.
Connection closed by foreign host.
[iyunv@server2 ~]#
法二:通过nmap来检查端口是否通畅
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nmap 192.168.2.2 -p 80
Starting Nmap 5.51 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2015-02-10 11:27 CST
Nmap scan report for server2.example.com (192.168.2.2)
Host is up (0.00010s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.09 seconds
如果写脚本通过nmap检查端口可以用下面的方法:
1 read -p "please input your ip_addr and port:" IP_ADDR PORT
2 PORT_COUNT=`nmap $IP_ADDR -p $PORT |grep open |wc -l`
3 [[ $PORT_COUNT -ge 1 ]] && echo "$IP_ADDR $PORT is ok." || echo "$IP_ADDR $PORT is unknown."
法三:通过nc命令来检查端口是否通畅
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nc -w 5 192.168.2.2 80 && echo ok
ok
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nc -w 10 192.168.2.2 80 && echo ok
ok
范例3:如果写脚本通过nc检查端口并监控memcache服务可以用下面的方法:
1 export hyTIMEOUTMemcachedIP=$1
2 export hyTIMEOUTMemcachedPort=$2
3 export hyTitle=nagios
4 export hyTimestampMD5=$1$LopE6$MccJmJ9xxq8LlY/3rJCGA0
5 export wwwServerIP=$3
6 export wwwServerPort=$4
7
8 printf "delete $hyTimestampMD5\r\n" | nc $hyTIMEOUTMemcachedIP
9 $hyTIMEOUTMemcachedPort >/dev/null 2>&1
10 sleep 1
11 judge=($(printf "HEAD/hy/$hyTitle HTTP/1.1\r\nHOST:$5\r\n\r\n"| nc $www ServerIP $wwwServerPort | head -n1 |tr "\r" "\n"))
3.case结构条件句
3.1case结构条件句语法
case “字符串变量” in
值 1)指令...
;;
值 2)指令...
;;
*)指令...
esac
3.2case结构条件句范例
范例1:根据用户的输入判断是哪个数字(case-1.sh)
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #this script is created by hy.
3 #e_mail:1020659371@qq.com
4 #qqinfo:1020659371
5 #version:1.1
6 read -p "Please input a number:" ans
7 case "$ans" in
8 1)
9 echo "the num you input is 1"
10 ;;
11 2)
12 echo "the num you input is 2"
13 ;;
14 [3-9])
15 echo "the num you input is $ans"
16 ;;
17 *)
18 echo "the num you input must be less 9."
19 exit;
20 ;;
21 esac
用if和case的区别:case-if.sh(用if需要做多次判断,比较麻烦)
1 #!/bin/bash
2 read -p "please input a number:" ans
3 if [ $ans -eq 1 ];then
4 echo "the num you input is 1"
5 elif [ $ans -eq 2 ];then
6 echo "the num you input is 2"
7 elif [ $ans -ge 3 -a $ans -le 9 ];then
8 echo "the num you input is $ans"
9 else
10 echo "the num you input must be less 9."
11 exit
12 fi
范例2:根据用户的选择输入判断是哪种水果并加上不同颜色。
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #function:case example
3 #version:1.1
4 #color defined
5 RED_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
6 GREEN_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
7 YELOW_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
8 BLUE_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
9 RES='\E[0m'
10 read -p "Please input the fruit name you like:" ans
11 case "$ans" in
12 apple|APPLE)
13 echo -e "the fruit name you like is ${RED_COLOR}"$ans."${RES}"
14 ;;
15 banana|BANANA)
16 echo -e "the fruit name you like is ${RED_COLOR}"$ans."${RES}"
17 ;;
18 pear|PEAR)
19 echo -e "the fruit name you like is ${RED_COLOR}"$ans."${RES}"
20 ;;
21 *)
22 echo -e "Here is not the fruit name you like--${BLUE_COLOR}"$ans."${RES}"
23 exit;
24 ;;
25 esac
拓展:让echo输出字符串显示不同颜色范例
范例1:直接加颜色
1、字颜色范围:30-37
[iyunv@server2 ~]# vim color.sh
1 echo -e "\033[30m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
2 echo -e "\033[31m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
3 echo -e "\033[32m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
4 echo -e "\033[33m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
5 echo -e "\033[34m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
6 echo -e "\033[35m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
7 echo -e "\033[36m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
8 echo -e "\033[37m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"

范例2:通过定义变量的方式给字体加颜色
echo-color01.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 RED_COLOR='\E[1;31m'
3 GREEN_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
4 YELLOW_COLOR='\E[1;33m'
5 BLUE_COLOR='\E[1;34m'
6 PINK='\E[1;35m'
7 RES='\E[0m'
8
9 echo -e "${RED_COLOR}=======red color======${RES}"
10 echo -e "${YELLOW_COLOR}=======yellow color======${RES}"
11 echo -e "${BLUE_COLOR}=======blue color======${RES}"
12 echo -e "${GREEN_COLOR}=======green color======${RES}"
13 echo -e "${PINK}=======pink color======${RES}"
14 echo "==============================================="
15 SETCOLOR_SUCCESS="echo -en \\033[1;32m"
16 SETCOLOR_FAILURE="echo -en \\033[1;31m"
17 SETCOLOR_WARNING="echo -en \\033[1;33m"

echo-color02.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 SETCOLOR_SUCCESS="echo -en \\033[1;32m"
3 SETCOLOR_FAILURE="echo -en \\033[1;31m"
4 SETCOLOR_WARNING="echo -en \\033[1;33m"
5 SETCOLOR_NORMAL="echo -en \\033[1;39m"
6 echo --------hy trainning------ && $SETCOLOR_SUCCESS
7 echo --------hy trainning------ && $SETCOLOR_FAILURE
8 echo --------hy trainning------ && $SETCOLOR_WARNING
9 echo --------hy trainning------ && $SETCOLOR_NORMAL
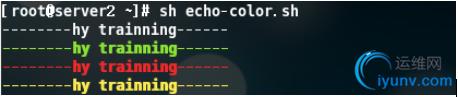
提示:以上是两种方法,最后8行的用法参考了/etc/init.d/functions系统函数库的内容
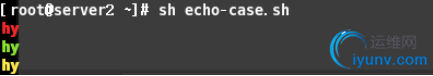
echo-case.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #function:case example
3 #version:1.1
4 #color defined
5 RED_COLOR='\E[1;31m'
6 GREEN_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
7 YELLOW_COLOR='\E[1;33m'
8 BLUE_COLOR='\E[1;34m'
9 PINK='\E[1;35m'
10 RES='\E[0m'
11 case "$2" in
12 red)
13 echo -e "${RED_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
14 ;;
15 green)
16 echo -e "${GREEN_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
17 ;;
18 yellow)
19 echo -e "${YELLOW_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
20 ;;
21 blue)
22 echo -e "${BLUE_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
23 ;;
24 *)
25 echo -e "${PINK_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
26 exit;
27 ;;
28 esac

在脚本中给指定的内容加指定的颜色
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #function:case example
3 #version:1.1
4 #color defined
5 new_chars(){
6 RED_COLOR='\E[1;31m'
7 GREEN_COLOR='\E[1;32m'
8 YELLOW_COLOR='\E[1;33m'
9 BLUE_COLOR='\E[1;34m'
10 PINK='\E[1;35m'
11 RES='\E[0m'
if [ $# -ne 2 ];then
echo "Usage $0 content {red|yellow|blue|green}"
exit
fi
12 case "$2" in
13 red)
14 echo -e "${RED_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
15 ;;
16 green)
17 echo -e "${GREEN_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
18 ;;
19 yellow)
20 echo -e "${YELLOW_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
21 ;;
22 blue)
23 echo -e "${BLUE_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
24 ;;
25 *)
26 echo -e "${PINK_COLOR}$1""${RES}"
27 exit;
28 ;;
29 esac
30 }
31 new_chars hy red
32 new_chars hy green
33 new_chars hy yellow
字颜色范围:30--37
1 echo -e "\033[30m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
2 echo -e "\033[31m 红色字hy trainning \033[0m"
3 echo -e "\033[32m 绿色字hy trainning \033[0m"
4 echo -e "\033[33m 黄色字hy trainning \033[0m"
5 echo -e "\033[34m 蓝色字hy trainning \033[0m"
6 echo -e "\033[35m 紫色字hy trainning \033[0m"
7 echo -e "\033[36m 天色字hy trainning \033[0m"
8 echo -e "\033[37m 白色字hy trainning \033[0m"
执行结果:

2.给字体添加背景色
1 echo -e "\033[40;37m 黑色字hy trainning \033[0m"
2 echo -e "\033[41;37m 红色字hy trainning \033[0m"
3 echo -e "\033[42;37m 绿色字hy trainning \033[0m"
4 echo -e "\033[43;37m 黄色字hy trainning \033[0m"
5 echo -e "\033[44;37m 蓝色字hy trainning \033[0m"
6 echo -e "\033[45;37m 紫色字hy trainning \033[0m"
7 echo -e "\033[46;37m 天色字hy trainning \033[0m"
8 echo -e "\033[47;37m 白色字hy trainning \033[0m"

最后面控制选项说明
echo -e “\033[42;37m 绿色白底 welcome to hy\033[0m” ==>就是这里就是结尾的控制选项,前面的例子都是0m。
\33[0m 关闭所有属性
\33[1m 设置高亮度
\33[4m 下划线
\33[5m 闪烁
\33[7m 反显
\33[8m 消隐
\33[30m — \33[37m 设置前景色
\33[40m — \33[47m 设置背景色
\33[nA 光标上移n行
\33[nB 光标下移n行
\33[nC 光标右移n行
\33[nD 光标左移n行
\33[y;xH 设置光标位置
\33[2J 清屏
\33[K 清屏
\33[s 保存光标位置
\33[u 恢复光标位置
\33[?251 隐藏光标
\33[?25h 显示光标
范例3:利用case语句手动开发启动apache/nginx服务的脚本(可参考系统的rpcbind脚本)
以下是三种启动httpd服务的方式
[iyunv@server2 ~]# httpd --daemon
[iyunv@server2 ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd start
[iyunv@server2 ~]# service httpd start
查看/etc/init.d/rpcbind脚本:
1 #! /bin/sh
2 #
3 # rpcbind Start/Stop RPCbind
4 #
5 # chkconfig: 2345 13 87
6 # description: The rpcbind utility is a server that converts RPC program \
7 # numbers into universal addresses. It must be running on the \
8 # host to be able to make RPC calls on a server on that machine.
9 #
10 # processname: rpcbind
11 # probe: true
12 # config: /etc/sysconfig/rpcbind
13
14
15 # This is an interactive program, we need the current locale
16 [ -f /etc/profile.d/lang.sh ] && . /etc/profile.d/lang.sh
17 # We can't Japanese on normal console at boot time, so force LANG=C.
18 if [ "$LANG" = "ja" -o "$LANG" = "ja_JP.eucJP" ]; then
19 if [ "$TERM" = "linux" ] ; then
20 LANG=C
21 fi
22 fi
23
24 # Source function library.
25 . /etc/init.d/functions
26
27 # Source networking configuration.
28 [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network ] && . /etc/sysconfig/network
29
30 prog="rpcbind"
31 [ -f /etc/sysconfig/$prog ] && . /etc/sysconfig/$prog
32
33 RETVAL=0
34 uid=`id | cut -d\( -f1 | cut -d= -f2`
35 下面我们可以看到用函数的意义所在
36 start() {
37 # Check that networking is up.
38 [ "$NETWORKING" = "yes" ] || exit 6
39
40 [ -f /sbin/$prog ] || exit 5
41
42 # Make sure the rpcbind is not already running.
43 if status $prog > /dev/null ; then
44 exit 0
45 fi
46
47 # Only root can start the service
48 [ $uid -ne 0 ] && exit 4
49
50 echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
51 daemon $prog $1 "$RPCBIND_ARGS"
52 RETVAL=$?
53 echo
54 if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] ; then
55 touch /var/lock/subsys/$prog
56 [ ! -f /var/run/rpcbind.pid ] &&
57 /sbin/pidof $prog > /var/run/rpcbind.pid
58 fi
59 return $RETVAL
60 }
61
62
63 stop() {
64 echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
65 killproc $prog
66 RETVAL=$?
67 echo
68 [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && {
69 rm -f /var/lock/subsys/$prog
70 rm -f /var/run/rpcbind*
71 }
72 return $RETVAL
73 }
74
75 # See how we were called.
76 case "$1" in
77 start)
78 start
79 RETVAL=$?
80 ;;
81 stop)
82 stop
83 RETVAL=$?
84 ;;
85 status)
86 status $prog
87 RETVAL=$?
88 ;;
89 restart | reload| force-reload)
90 stop
91 start
92 RETVAL=$?
93 ;;
94 condrestart | try-restart)
95 if [ -f /var/lock/subsys/$prog ]; then
96 stop
97 start -w
98 RETVAL=$?
99 fi
100 ;;
101 *)
102 echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|reload|force-reload|condrestart|try-restart}"
103 RETVAL=2
104 ;;
105 esac
106
107 exit $RETVAL
仿照上面的例子我们写一个简单的httpd启动脚本:
Httpd.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2
3 httpd="/etc/init.d/httpd"
4 # Source function library.
5 . /etc/init.d/functions
6
7 case "$1" in
8 start)
9 $httpd start >& /dev/null
10 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is started" /bin/true || \
11 action "httpd is started" /bin/false
12 ;;
13 stop)
14 $httpd stop >& /dev/null
15 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is stopped" /bin/true || \
16 action "httpd is stopped" /bin/false
17 ;;
18 restart|reload|force-reload)
19 $httpd restart >& /dev/null
20 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is restarted" /bin/true || \
21 action "httpd is restarted" /bin/false
22 ;;
23 *)
24 echo "Usage:$0 {start|stop|restart}"
25 exit
26 ;;
27 esac


下面使用函数的形式去写:
1 #!/bin/bash
2
3 httpd="/etc/init.d/httpd"
4 # Source function library.
5 . /etc/init.d/functions
6
7 start() {
8
9 $httpd start >& /dev/null
10 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is started" /bin/true || \
11 action "httpd is started" /bin/false
12 }
13 stop() {
14 $httpd stop >& /dev/null
15 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is stopped" /bin/true || \
16 action "httpd is stopped" /bin/false
17 }
18 restart() {
19 $httpd restart >& /dev/null
20 [ $? -eq 0 ] && action "httpd is restarted" /bin/true || \
21 action "httpd is restarted" /bin/false
22 }
23 case "$1" in
24 start)
25 start
26 ;;
27 stop)
28 stop
29 ;;
30 restart|reload|force-reload)
31 sh $0 stop
32 sh $0 start
33 #[ ! -x "$0" ] && chmod +x $0
34 #$0 stop
35 #$0 start
36 ;;
37 *)
38 echo "Usage:$0" {start|stop|restart}
39 exit
40 ;;
41 esac
case结构条件句系统脚本范例
范例5:学习系统的httpd启动脚本
1 #!/bin/bash
2 #
3 # httpd Startup script for the Apache HTTP Server
4 #
5 # chkconfig: - 85 15
6 # description: The Apache HTTP Server is an efficient and extensible \
7 # server implementing the current HTTP standards.
8 # processname: httpd
9 # config: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
10 # config: /etc/sysconfig/httpd
11 # pidfile: /var/run/httpd/httpd.pid
12 #
13 ### BEGIN INIT INFO
14 # Provides: httpd
15 # Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named
16 # Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
17 # Should-Start: distcache
18 # Short-Description: start and stop Apache HTTP Server
19 # Description: The Apache HTTP Server is an extensible server
20 # implementing the current HTTP standards.
21 ### END INIT INFO
22
23 # Source function library.
24 . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
25
26 if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/httpd ]; then
27 . /etc/sysconfig/httpd
28 fi
29
30 # Start httpd in the C locale by default.
31 HTTPD_LANG=${HTTPD_LANG-"C"}
32
33 # This will prevent initlog from swallowing up a pass-phrase prompt if
34 # mod_ssl needs a pass-phrase from the user.
35 INITLOG_ARGS=""
36
37 # Set HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker in /etc/sysconfig/httpd to use a server
38 # with the thread-based "worker" MPM; BE WARNED that some modules may not
39 # work correctly with a thread-based MPM; notably PHP will refuse to start.
40
41 # Path to the apachectl script, server binary, and short-form for messages.
42 apachectl=/usr/sbin/apachectl
43 httpd=${HTTPD-/usr/sbin/httpd}
44 prog=httpd
45 pidfile=${PIDFILE-/var/run/httpd/httpd.pid}
46 lockfile=${LOCKFILE-/var/lock/subsys/httpd}
47 RETVAL=0
48 STOP_TIMEOUT=${STOP_TIMEOUT-10}
49
50 # The semantics of these two functions differ from the way apachectl does
51 # things -- attempting to start while running is a failure, and shutdown
52 # when not running is also a failure. So we just do it the way init scripts
53 # are expected to behave here.
54 start() {
55 echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
56 LANG=$HTTPD_LANG daemon --pidfile=${pidfile} $httpd $OPTIONS
57 RETVAL=$?
58 echo
59 [ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch ${lockfile}
60 return $RETVAL
61 }
62
63 # When stopping httpd, a delay (of default 10 second) is required
64 # before SIGKILLing the httpd parent; this gives enough time for the
65 # httpd parent to SIGKILL any errant children.
66 stop() {
67 echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
68 killproc -p ${pidfile} -d ${STOP_TIMEOUT} $httpd
69 RETVAL=$?
70 echo
71 [ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f ${lockfile} ${pidfile}
72 }
73 reload() {
74 echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
75 if ! LANG=$HTTPD_LANG $httpd $OPTIONS -t >&/dev/null; then
76 RETVAL=6
77 echo $"not reloading due to configuration syntax error"
78 failure $"not reloading $httpd due to configuration syntax error"
79 else
80 # Force LSB behaviour from killproc
81 LSB=1 killproc -p ${pidfile} $httpd -HUP
82 RETVAL=$?
83 if [ $RETVAL -eq 7 ]; then
84 failure $"httpd shutdown"
85 fi
86 fi
87 echo
88 }
89
90 # See how we were called.
91 case "$1" in
92 start)
93 start
94 ;;
95 stop)
96 stop
97 ;;
98 status)
99 status -p ${pidfile} $httpd
100 RETVAL=$?
101 ;;
102 restart)
103 stop
104 start
105 ;;
106 condrestart|try-restart)
107 if status -p ${pidfile} $httpd >&/dev/null; then
108 stop
109 start
110 fi
111 ;;
112 force-reload|reload)
113 reload
114 ;;
115 graceful|help|configtest|fullstatus)
116 $apachectl $@
117 RETVAL=$?
118 ;;
119 *)
120 echo $"Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|condrestart|try-restart|force-reload|reload|status|fullstatus|graceful|help|configtest}"
121 RETVAL=2
122 esac
123
124 exit $RETVAL
范例7:开发生产mysql多实例启动的脚本(以前课程的内容)
(1)mysql多实例的启动:
[iyunv@server2 ~]#/data/3306/mysql start
[iyunv@server2 ~]#/bin/sh /application/mysql/bin/mysql_safe --defaults-file=/data/3306/my.cnf 2>&1 /dev/null &
(2)mysql多实例的停止:
[iyunv@server2 ~]#/data/3306/mysql stop
[iyunv@server2 ~]# mysqladmin -u root -pwestos -S /data/3306/mysql.sock shutdown
(3)Mysql启动脚本:
1 #!/bin/bash
2
3 #init
4 port=3306
5 mysql_user="root"
6 mysql_pwd="westos"
7 CMDpath="/application/mysql/bin"
8
9 #startup function
10 function_start_mysql()
11 {
12 printf "starting Mysql...\n"
13 /bin/sh ${CMDpath}/mysql_safe --defaults-file=/data/${port}/my.cnf 2>&1 > /dev/null &
14 }
15
16 #stop function
17 function_stop_mysql()
18 {
19 printf "Stopping Mysql...\n"
20 ${CMDpath}/mysqladmin -u ${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pwd} -S /data/${port}/mysql.sock shutdown
21 }
22
23 #restart function
24 function_restart_mysql()
25 {
26 printf "Restarting Mysql...\n"
27 function_stop_mysql
28 sleep 2
29 function_start_mysql
30 }
31
32 case $1 in
33 start)
34 function_start_mysql
35 ;;
36 stop)
37 function_stop_mysql
38 ;;
39 restart)
40 function_restart_mysql
41 ;;
42 *)
43 printf "Usage: /data/${port}/mysql {start|stop|restart}"
44 esac
优化:
1 #!/bin/bash
2
3 #init
4 port=3306
5 mysql_user="root"
6 mysql_pwd="westos"
7 CMDpath="/application/mysql/bin"
8 mysql_sock="/data/${port}/mysql.sock"
9
10 #startup function
11 function_start_mysql()
12 {
13 if [ ! -e $mysql_sock ];then
14 printf "starting Mysql...\n"
15 /bin/sh ${CMDpath}/mysql_safe --defaults-file=/data/${port}/my.cnf 2>&1 > /dev/null &
16 else
17 printf "Mysql is running...\n"
18 exit
19 fi
20 }
21
22 #stop function
23 function_stop_mysql()
24 {
25 if [ ! -e $mysql_sock ];then
26 printf "Mysql is stopping...\n"
27 exit
28 else
29 printf "Stopping Mysql...\n"
30 ${CMDpath}/mysqladmin -u ${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pwd} -S /data/${port}/mysql.sock shutdown
31 }
32
33 #restart function
34 function_restart_mysql()
35 {
36 printf "Restarting Mysql...\n"
37 function_stop_mysql
38 sleep 2
39 function_start_mysql
40 }
41
42 case $1 in
43 start)
44 function_start_mysql
45 ;;
46 stop)
47 function_stop_mysql
48 ;;
49 restart)
50 function_restart_mysql
51 ;;
52 *)
53 printf "Usage: /data/${port}/mysql {start|stop|restart}"
54 esac
范例8(学生作业):开发一个rsync服务的启动脚本
正常的rsync独立进程模式启动方法为:rsync --daemon,请完成一个可以通过如下命令:
/etc/init.d/rsyncd start|stop|restart,并且可以通过chkconfig设置开机自启动。对比范例6和范例7的开头。也可以说service rsyncd start.
企业面试题:22、怎么把自己的脚本添加到服务里面,即可以使用service命令来调用
1.4.2.4要掌握的Linux系统标杆脚本
这里留个作业:请大家阅读并对下面脚本进行详细注解:
/etc/init.d/functions
/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
/etc/init.d/nfs
/etc/init.d/rpcbind
/etc/init.d/httpd
提示:此类脚本网上有人注解过的,可以参考他们的去理解总结成自己的注解
1.4.3 当型循环和直到型循环
1.4.3.1 当型和直到型循环语法
1.while 条件句
do
指令...
Done
2.until条件句
语法:
until 条件
do
指令...
done
提示:until应用场合不多见,了解就好。
1.4.3.2当型和直到型循环基本范例
下面举几个while和until条件句的例子
范例1:每隔2秒记录一次系统负载情况
[iyunv@server2 ~]# vim while-1.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 while true
3 do
4 uptime
5 sleep 2
6 done
提示:while true表示条件永远为真,因此会一直运行,象死循环一样,但是我们称呼为守护进程。
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh while-1.sh
21:29:10 up 3:02, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:29:12 up 3:02, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:29:14 up 3:02, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:29:16 up 3:02, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:29:18 up 3:02, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
法二:追加到log里,使用微妙单位。
1 #!/bin/bash
2 while [ 1 ] #===>条件这里和上面有区别
3 do
4 uptime >>./a.log
5 usleep 1000000 #===>这里是以微妙为单位
6 done
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh while-1.sh
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
21:36:47 up 3:10, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
[iyunv@server2 ~]# sh while-1.sh & 后台执行,特别是执行远端服务器上的脚本的时候
[1] 12364
[iyunv@server2 ~]# fg 将此后台执行的脚本调回到前台
sh while-1.sh
^Z 这里使用ctrl+z,暂停
[1]+ Stopped sh while-1.sh
[iyunv@server2 ~]# bg 然后将其打入到后台
[1]+ sh while-1.sh &
[iyunv@server2 ~]# jobs 当前的脚本在运行
[1]+ Running sh while-1.sh &
[iyunv@server2 ~]# fg 1 将1号脚本拿到前台
sh while-1.sh
^Z
[1]+ Stopped sh while-1.sh
[iyunv@server2 ~]# bg
[1]+ sh while-1.sh &
[iyunv@server2 ~]# ps -ef | grep while 查看这个进程是否存在
root 12364 1567 7 21:46 pts/0 00:00:51 sh while-1.sh
root 31157 1567 0 21:57 pts/0 00:00:00 grep while
a.功能和用途见如下表格:

b.执行过程演示
[iyunv@server2 ~]# tail -f a.log
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:50 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:51 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:51 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
22:10:51 up 3:44, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
拓展资料:
Linux技巧:让进程在后台可靠运行的几种方法
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-nohup
补下nohup用法:后台运行程序。
[iyunv@server2 ~]# chmod +x while-1.sh
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nohup /root/while-1.sh &
[1] 19394
[iyunv@server2 ~]# nohup: 忽略输入并把输出追加到"nohup.out"
^C
[iyunv@server2 ~]# cat nohup.out
[iyunv@server2 ~]# ps -ef |grep nohup
root 20204 1567 0 22:24 pts/0 00:00:00 grep nohup
[iyunv@server2 ~]# ps -ef |grep while
root 19394 1567 7 22:21 pts/0 00:00:12 /bin/bash /root/while-1.sh
root 25898 1567 0 22:24 pts/0 00:00:00 grep while
[iyunv@server2 ~]# fg
nohup /root/while-1.sh
^C
[iyunv@server2 ~]# tail -f a.log
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
22:30:29 up 4:03, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.00
范例2:通过while语句计算从1加到100之和
1 i=1
2 sum=0
3
4 while ((i =1)) =1 ]] |
|