Nginx是一款轻量级的Web和反向代理服务器,它的诞生主要是为了解决C10K的问题,它具有较多的特性;Nginx的特性:
1、模块化设计,具有较好的扩展性
2、具有高可靠性
3、支持热部署:可以在不影响用户使用的情况下,升级老版本;可以不停机更新配置文件、更换日志文件、更换服务器程序版本
4、低消耗内存:10K个keepalive连接模式下的非活动连接仅消耗2.5M内存
5、是event-driven事件驱动模型:具有一个主进程,多个子进程,每个子进程响应多个请求
Nginx的基本功能:
1、静态资源的web服务器
2、可以作为http协议的正反向代理服务器
正向代理:Nginx作为服务器,可直接响应资源给客户端 反向代理:Nginx作为代理器,客户端不直接和服务器交流,而是通过和代理服务器的代理器来交流;通过代理器来读取服务器中的资源,从而响应给客户端 3、支持pop3/imap4协议反向代理服务器
4、支持FastCGI、UWSGI等
5、支持模块化:例如ssl、zip
Nginx的程序架构图:
Master:Master为主进程,主要作用是加载配置文件、管理worker进程、可进行平滑升级
Worker:worker为子进程,由master主进程生成,一个worker进程可以处理多个客户端请求;主要作用是接受客户端请求、http代理、FastCGI代理、Memcache代理、在磁盘内缓存以及管理磁盘内的缓存
准备环境:
虚拟机1:nginx
| IP:172.18.42.200
| 虚拟机2:httpd(后端主机)
| IP:172.18.42.201
| 虚拟机3:httpd(后端主机)
| IP:172.18.42.202
|
一、实现“ngx_http_auth_basic_module”认证机制
1、虚拟机1安装nginx服务
1
| [iyunv@node0 ~]# yum install nginx
|
2、编辑nginx主配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| [iyunv@node0 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ##nginx的主配置文件
server {
listen 80; ##监听的端口
server_name localhost;
root /www/lweim/; ##指定读取资源路径
location /nginx {
auth_basic "Show your Information"; ##指定提示页
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.ngxpasswd; ##指定密码文件路径
}
}
[iyunv@node0 nginx]# htpasswd -c -m /etc/nginx/.ngxpasswd lweim ##创建虚拟用户“lweim”
-c:当.nginxpasswd这个文件不存在时需使用
-m:使用md5算法
[iyunv@node0 ~]# echo "172.18.42.200 Nginx 1" > /www/lweim/nginx/index.html
|
3、访问web页面
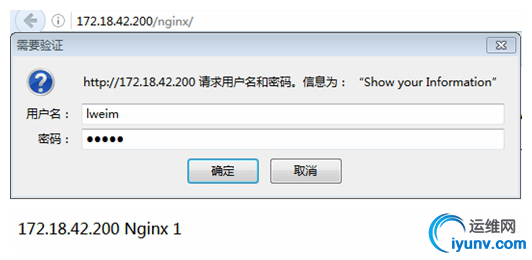
二、实现“ngx_http_stub_status_module”基本状态信息
1、编辑配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| [iyunv@node0 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /www/lweim/;
location /status { ##指明状态页面目录
stub_status on; ##开启状态页
}
}
[iyunv@node0 ~]# mkdir /www/lweim/status/ ##创建状态页目录
|
2、访问web
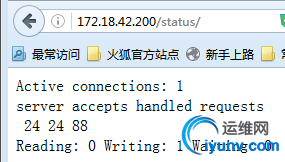
Active connections:处于活动状态的客户端连接数量
Accepts:已经接受客户端的总请求数量
Handled:已经处理客户单的总请求数量
Request:客户端发出的总请求数量
Reading:正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接数量
Writing:正在向客户端发送响应报文的连接数量
Waiting:正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲进程数
三、实现“ngx_http_ssl_module”https请求
1、在未修改配置文件之前尝试访问“https://172.18.42.200”
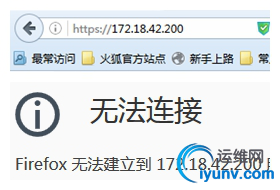
2、修改配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /www/lweim/;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl; ##https监听在tcp的443端口
server_name localhost;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/ngx.crt; ##指明ngx.crt的文件路径
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/ngx.key; ##指明ngx.key的文件路径
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location /nginx {
}
}
|
Ssl on | off:是否启用当前虚拟主机的ssl功能
Ssl_ certificate file:当前虚拟主机使用的PEM格式的证书文件
Ssl_certificate_key file:当前虚拟机使用的证书文件中的公钥配对的私钥文件路径,依然是PEM格式
Ssl_protocols [SSLv2] [SSLv3] [TLSv1] [TLSv1.1] [TLSv1.2]:表示ssl协议的版本;摩恩为后3个
Ssl_session_cache off | none | [ builtin [ : size ] ] [ shard : name : size ]:指明ssl会话缓存的机制
builtin:使用openssl内建的缓存机制,对此机制为各worker独有
shared:在各个worker进程共享的缓存
name:缓存空间的名称 size:缓存空间的大小以字节为单位,每1MB内存可缓存4000个会话 Ssl_session_time timeout:ssl会话时长,指ssl session cache中缓存条目时长
3、再次访问web
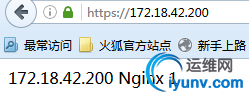
四、实现“ngx_http_rewrite_module”重写url
1、修改配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| location / {
rewrite (.*)\.html$ $1.txt last;
rewrite (.*)\.txt$ $1.jpg break;
}
##当用户第一次请求uri中以html结尾时,会把uri重写为以txt结尾并重新开始循环;
随后匹配到第二条rewrite,把uri中的txt更改为以jpg结尾的文件并响应给客户端
|
rewrite regex replacement [flag]
regex:基于正则表达式,用于匹配用户请求的url
replacement:为重写的结果
Flag:
Last:重写完成后停止对当前uri在location中的后续其他操作,而后更改为对新的uri做出新一轮处理
Break:重写完成后停止对当前uri在当前location中的后续其他操作,直接返回给客户端
Redirect:重写完成后,临时返回给客户端一个新的URL,随后浏览器在根据新的URL请求新的资源;响应码为302
Premanent:重写完成后,永久返回给客户端一个新的URL,随后浏览器在根据新的URL请求信的资源;响应码为301
2、访问web服务

五、实现“ngx_http_gizp_module”压缩功能:只能用在http上下文
1、修改nginx配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| http {
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_disable msie6;
gzip_http_version 1.0;
gzip_types text/plain;
}
|
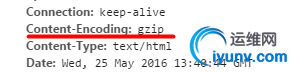
Gzip on | off:启用或禁用gzip压缩响应报文
Gzip_comp_level level:指定压缩比,1-9;默认为1
Gzip_disable regex:regex是匹配客户端浏览器类型的模式,表示对所有匹配到的浏览器下不执行压缩响应
Gzip_min_length length:触发启用先压缩功能的响应报文的最小长度
Gzip_http_version:设定启用压缩响应功能时,协议的最小版本
Gzip_types:指定仅执行压缩的资源内容类型;默认为text/html
gzip_types text/plain、text/css、text/xml、application/x-javascript 、application/xml、application/json、application/java-script;
2、访问web
六、实现“ngx_http_fastcgi_module”
1、虚拟机2安装php-fpm服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# yum install php-fpm -y ##安装php-fpm服务
[iyunv@node1 ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf ##修改php-fpm的配置文件
listen = 172.18.42.201:9000 ##监听本地能与外部通信的IP地址
listen.allowed_clients = 172.18.42.200 ##监听具有httpd服务的IP
[iyunv@node1 ~]# ss -tnl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 172.18.42.201:9000 *:*
|
Nginx和php结合的方式只有fpm;php-fpm的工作方式类似于httpd的prefork模块
Listen = :指明本地能与外部通信的地址
Listen.allow_clients = :指明具有httpd服务的IP
Pm = dynamic | static
Pm.start_servers:启动fpm进程时启动的工作进程数量
Pm.min_spare_servers:最少空闲进程数
Pm.max_spare_servers:最大空闲进程数
Pm.max_children:最大工作进程数
2、修改nginx的配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
| location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 172.18.42.201:9000; ##指明fpm-php服务的IP
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /web/lweim/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
|
Fastcgi_pass:用来指明代理那个服务器(装了php-fpm的服务器能与外部监听的地址)
Fastcgi_index:fastcgi应用的主页面名称
Fastcgi_param:传递给fpm服务器参数
3、访问web
七、实现“fastcgi_cache_path”缓存:只能用在http上下文
1、修改nginx的配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| [iyunv@node0 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
http {
fastcgi_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/fastcgi levels=1:2 keys_zone=ngxcache:10m; ##定义缓存
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 172.18.42.201:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /web/lweim/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_cache ngxcache; ##指明缓存名称
fastcgi_cache_key $request_uri; ##定义缓存键
fastcgi_cache_valid 200 302 10m; ##状态码200、302缓存10分钟
fastcgi_cache_valid 301 1h; ##状态码301缓存1个小时
fastcgi_cache_valid 404 2h; ##状态码404缓存2个小时
}
|
Fastcgi_cache_path path:指明缓存文件的路径
Fastcgi_cache zone | off:是否启用缓存,如果启用,需要指明缓存与那个cache文件中
Fastcgi_cache_key string:定义要使用的缓存键
Fastcgi_cache_methods GET | HEAD | POST:缓存那些类型的请求的相关数据
Fastcgi_cache_vaild [code..] time:对不同响应码设定其可缓存时间
2、查看缓存目录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| [iyunv@node0 ~]# tree /var/cache/nginx/fastcgi/
/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi/
├── 1
│ └── af
│ └── e251273eb74a8ee3f661a7af00915af1
├── b
│ └── fe
│ └── c86156f7dcfecf44876ca30d1bac7feb
└── e
└── 39
└── f46b8508aa08a6f8670fb088b8a9739e
|
八、实现“ngx_http_proxy_module”
1、修改nginx配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| [iyunv@node0 ]# vim nginx.conf
location ~ .*\.txt$ { ##txt结尾的文件由虚拟机2来响应
proxy_pass
}
location ~ .*\.jpg$ {
proxy_pass ##jpg结尾的文件由虚拟机3来响应
}
|
(1)当proxy_pass后面的路径不带uri时,会将其location中的uri传递给后端主机
(2)当proxy_pass后面路径是一个uri时,它会将location中的uri替换为proxy_pass的后端主机
(3)如果location定义其uri时使用了正则表达式模式匹配机制,则proxy_pass后的路径一定不能带uri
1
2
3
| location ~* \.php$ {
proxy_pass
}
|
2、配置虚拟机2
1
2
3
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# yum install httpd -y
[iyunv@node1 ~]# echo "172.18.42.201 txt" > /var/www/html/wtc.txt
[iyunv@node1 ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
|
3、配置虚拟级3
1
2
3
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# yum install httpd -y
[iyunv@node2 ~]# mv /root/wawa.jpg /var/www/html/wtc.jpg
[iyunv@node1 ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
|
4、访问web

九、实现“proxy_set_header”,让后端主机记录源IP
1、在未修改配置文件之前查看后端主机的记录日志
1
2
3
4
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# tail /var/log/httpd/access_log
172.18.42.200 - - [25/May/2016:19:20:34 +0800] "GET /wtc.txt HTTP/1.0" 200 18 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:46.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/46.0"
172.18.42.200 - - [25/May/2016:19:20:34 +0800] "GET /wtc.txt HTTP/1.0" 200 18 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:46.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/46.0"
##后端主机记录的访问IP都是nginx自身的的IP
|
2、修改nginx的配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@node0 nginx]# vim nginx.conf
location ~ .*\.txt$ {
proxy_pass http://172.18.42.201;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
}
|
3、修改虚拟机2httpd的配置文件
1
2
3
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%{X-Real_IP}i %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
|
4、访问web之后查看后端主机的记录日志
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# tail /var/log/httpd/access_log
172.18.250.14 - - [25/May/2016:19:27:41 +0800] "GET /wtc.txt HTTP/1.0" 304 - "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Wi
172.18.250.14 - - [25/May/2016:19:27:41 +0800] "GET /wtc.txt HTTP/1.0" 304 - "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Wi
172.18.250.14 - - [25/May/2016:19:27:41 +0800] "GET /wtc.txt HTTP/1.0" 304 - "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Wi
##记录的访问IP“172.18.250.14”为物理机的IP,做日志分析才有意义
|
十、实现实现“proxy_cache”缓存
1、修改nginx配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| http {
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/proxy levels=1:2 keys_zone=ngxcache:10m;
}
location ~ .*\.txt$ {
proxy_pass http://172.18.42.201;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
proxy_cache ngxcache;
proxy_cache_key $request_uri;
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 404 1h;
}
|
2、访问web之后查看缓存目录
1
2
3
4
5
| root@node0 ~]# tree /var/cache/nginx/proxy/
/var/cache/nginx/proxy/
└── 5
└── fd
└── 19cbf2faabf255f790ebd83de4a42fd5
|
十一、实现“ngx_http_upstream_module”负载均衡
1、修改nginx配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| http {
upstream web { ##定义一个服务器组
server 172.18.42.201 weight=1;
server 172.18.42.202 weight=2;
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass ##引用服务器组
}
}
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.202 Web Server 2 .
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.202 Web Server 2 .
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
##实现了负载均衡
|
Upstream name {……}
定义后端服务器组,可直接使用字符串
Server address {parameters}:指明服务器的地址和相关参数
address:
IP[ : PORT ]:给定IP地址 HOSTNAME[ : PORT ]:当后端有多个虚拟主机时,应该使用hostname定义 Unix:/path/to/some_sock_file parameters:
Weight=number:后端服务器权重 Max_fails=number:设定最大失败重试次数 Fail_timeout time:设置服务器不可用的超时时长 Backup:备用主机;定义后端主机是否为一个sorry_server Down:手动标记后自动下面,不在处理任何请求
2、实现源地址哈希调度算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| http {
upstream web {
server 172.18.42.201 weight=1;
server 172.18.42.202 weight=2;
ip_hash; ##源地址哈希算法;将来自同一用户的请求始终发往同一主机上
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://web;
}
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
[iyunv@node1 ~]# curl http://172.18.42.200
<h1>
172.18.42.201 Web Server 1
</h1>
##响应请求的始终是一台后端主机
|
Ip_hash:源地址哈希算法,只能用在upstream上下文;指定调度算法
Least_conn:最少连接调度方法,只能用在upstream上下文
Keepalive:指明尝试连接后端主机次数,只能用在upstream上下文中
3、“Health_check”对后端主机做健康检测:只能用在location上下文
Interval=number:检测的频度,默认为5s
Fails=number:判定为失败的检测次数
Passes=number:判定为检测成功的次数
Uri=uri:执行健康状态监测时请求的uri
Match=name:基于哪个match做检测结果为“成功”或者“失败”的判断
Port=port:向服务器的那个端口发起健康状态检测请求
4、“match name”对后端主机做健康状态监测时,定义其结果判断标准的标准指令:只能用于http上下文
Status:期望的响应码
Status CODE Status !CODE Status CODE~CODE Header:基于响应首部进行判断
Header HEADER=VALUE Header HEADER!=VALUE Header [!]HEADER Header Header ~ VALUE Body:期望的响应码报文的主体部分应该有的内容
Body ~ “CONTENT” Body !~ “CONNTENT”
5、“hash key”:定义调度方法,可自定义基于何种信息(key)进行绑定:只能用在upstream上下文
Hash $remote_addr:根据后端主机的IP地址进行绑定
Hash $request_uri:绑定第一次访问的服务器,以后每次的访问都指定元的的那台服务器
Hasg $cookie_username:根据客户端的cookie
|