|
|
List all of MV inoracle:
select owner, query, query_len
from dba_mviews
See content of aMV:
select *
from dba_mviews
where owner='CNTL_DATA'
A materialized viewis a database object that contains the results of a query. For example, it maybe a local copy of data located remotely, or may be a subset of the rows and/orcolumns of a table or join result, or may be a summary based on aggregations ofa
table’s data. Materialized views, which store data based on remote tables,are also known as snapshots. A snapshot can be redefined as a materializedview.
In any database managementsystem for following the relational model, a view is a virtual tablerepresenting the result of a database query. Whenever a query or an updateaddresses an ordinary view’s virtual table, the DBMS converts these intoqueries or updates
against the underlying base tables. A materialized viewtakes a different approach in which the query result is cached as a concretetable that may be updated from the original base tables from time to time. Thisenables much more efficient access, at the cost
of some data being potentiallyout-of-date. It is most useful in data warehousing scenarios, where frequentqueries of the actual base tables can be extremely expensive.
In addition, becausethe materialized view is manifested as a real table, anything that can be doneto a real table can be done to it, most importantly building indexes on anycolumn, enabling drastic speedups in query time. In a normal view, it’s typicallyonly
possible to exploit indexes on columns that come directly from (or have amapping to) indexed columns in the base tables; often this functionality is notoffered at all. Materialized views were implemented first by the OracleDatabase: the Query rewrite feature
was added from version 8i. They are alsosupported in Sybase SQL Anywhere. In IBMDB2, they are called “materialized query tables”; MS SQL called “indexed views”.
Example syntax tocreate a materialized view in oracle:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW MV_MY_VIEW
REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE
NEXT SYSDATE + 1
AS SELECT * FROM <table_name>;
Oracle usesmaterialized views to replicate data to non-master sites in a replication environmentand to cache expensive queries in a data warehouse environment.
A materialized viewis a replica of a target master from a single point in time. The master can beeither a master table at a master site or a master materialized view at amaterialized view site. Whereas in multimaster replication tables arecontinuously updated by other master sites, materialized views are update fromone or more masters through individual batch updates, known as a refreshes,from a single master site or master materialized view site.
MaterializedView Connected to a Single Master Site
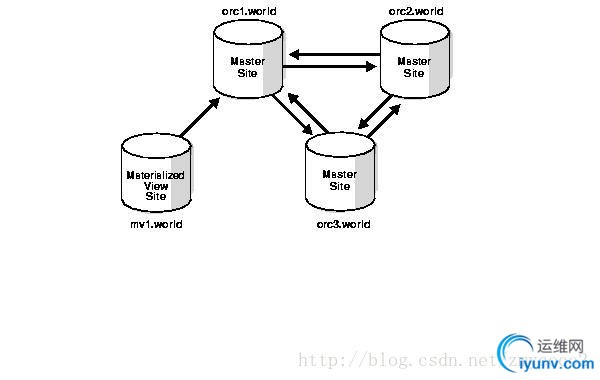
When a materializedview is fast refreshed, Oracle must examine all of the changes to the mastertable or master materialized view since the last refresh to see if any apply tothe materialized view. Therefore, if any changes were made to the master sincethe last refresh, then a materialized view refresh takes some time to apply thechanges to the materialized view. If, however, no changes at all were made tothe master since the last refresh of a materialized view, then the materializedview refresh should be very quick.
You can usematerialized views to achieve one or more of the following goals:
If one of your goals is to reduce network loads, then you can usematerialized views to distribute your corporate database to regional sites.Instead of the entire company accessing a single database server, user load isdistributed across multiple database servers. Through the use of multitiermaterialized views, you can create materialized views based on othermaterialized views, which enables you to distribute user load to an evengreater extent because clients can access materialized view sites instead ofmaster sites. To decrease the amount of data that is replicated, a materializedview can be a subset of a master table or master materialized view.Whilemultimaster replication also distributes a corporate database among multiplesites, the networking requirements for multimaster replication are greater thanthose for replicating with materialized views because of the transaction bytransaction nature of multimaster replication. Further, the ability ofmultimaster replication to provide real-time or near real-time replication mayresult in greater network traffic, and might require a dedicated network link.Materializedviews are updated through an efficient batch process from a single master siteor master materialized view site. They have lower network requirements anddependencies than multimaster replication because of the point in time natureof materialized view replication. Whereas multimaster replication requiresconstant communication over the network, materialized view replication requiresonly periodic refreshes.In addition to not requiring a dedicated networkconnection, replicating data with materialized views increases dataavailability by providing local access to the target data. These benefits,combined with mass deployment and data subsetting (both of which also reducenetwork loads), greatly enhance the performance and reliability of yourreplicated database.
- Create a Mass Deployment Environment
Deployment templates allow you to pre-create amaterialized view environment locally. You can then use deployment templates toquickly and easily deploy materialized view environments to support sales forceautomation and other mass deployment environments. Parameters allow you tocreate custom data sets for individual users without changing the deploymenttemplate. This technology enables you to roll out a database infrastructure tohundreds or thousands of users.
Materialized views allow you to replicate data basedon column- and row-level subsetting, while multimaster replication requiresreplication of the entire table. Data subsetting enables you to replicateinformation that pertains only to a particular site. For example, if you have aregional sales office, then you might replicate only the data that is needed inthat region, thereby cutting down on unnecessary network traffic.
- Enable Disconnected Computing
Materialized views do not require a dedicatednetwork connection. Though you have the option of automating the refreshprocess by scheduling a job, you can manually refresh your materialized viewon-demand, which is an ideal solution for sales applications running on alaptop. For example, a developer can integrate the replication management APIfor refresh on-demand into the sales application. When the salesperson hascompleted the day's orders, the salesperson simply dials up the network anduses the integrated mechanism to refresh the database, thus transferring theorders to the main office.
A materialized viewcan be either read-only, updatable, or writeable. Users cannot perform datamanipulation language (DML) statements on read-only materialized views, butthey can perform DML on updatable and writeable materialized views.
Read-OnlyMaterialized Views
You can make amaterialized view read-only during creation by omitting the FOR UPDATE clauseor disabling the equivalent option in the Replication Management tool.Read-only materialized views use many of the same mechanisms as updatablematerialized views, except that they do not need to belong to a materializedview group.
In addition, usingread-only materialized views eliminates the possibility of a materialized viewintroducing data conflicts at the master site or master materialized view site,although this convenience means that updates cannot be made at the remotematerialized view site. The following is an example of a read-only materializedview:
CREATE MATERIALIZEDVIEW hr.employees AS
SELECT * FROM hr.employees@orc1.world;
UpdatableMaterialized Views
You can make amaterialized view updatable during creation by including the FOR UPDATE clauseor enabling the equivalent option in the Replication Management tool. Forchanges made to an updatable materialized view to be pushed back to the masterduring refresh, the updatable materialized view must belong to a materializedview group.Updatable materialized views enable you to decrease the load onmaster sites because users can make changes to the data at the materializedview site. The following is an example of an updatable materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZEDVIEW hr.departments FOR UPDATE AS
SELECT * FROM hr.departments@orc1.world;
The followingstatement creates a materialized view group:
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MVIEW_REPGROUP (
gname => 'hr_repg',
master => 'orc1.world',
propagation_mode => 'ASYNCHRONOUS');
END;
/
The followingstatement adds the hr.departments materialized view to the materialized viewgroup, making the materialized view updatable:
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.CREATE_MVIEW_REPOBJECT (
gname => 'hr_repg',
sname => 'hr',
oname => 'departments',
type => 'SNAPSHOT',
min_communication => TRUE);
END;
/
WriteableMaterialized Views
A writeablematerialized view is one that is created using the FOR UPDATE clause but is notpart of a materialized view group. Users can perform DML operations on awriteable materialized view, but if you refresh the materialized view, thenthese changes are not pushed back to the master and the changes are lost in thematerialized view itself. Writeable materialized views are typically allowedwherever fast-refreshable read-only materialized views are allowed.
|
|