|
CentOS 7 corosync高可用集群的实现 ===============================================================================
概述:
===============================================================================
在CentOS 7上实现高可用集群案例 1.corosync安装配置 ★CentOS 7: ★安装配置: ☉前提: ☉安装: ★corosync的程序环境: 配置文件:/etc/corosync/corosync.conf 密钥文件:/etc/corosync/authkey Unit File:corosync.service
★corosync配置文件格式:
version(配置文件版本):目前取值仅有2一项可用 crypto_hash:哈希加密算法 md5, sha1, sha256, sha384 and sha512. crypto_cipher:对称加密算法 aes256, aes192, aes128 and 3des
配置示例: ★生成authkey: ★启动服务: ★验正服务启动: (1)查看日志; (2)corosync-cmapctl| grep members (3)corosync-cfgtool:管理工具;
-s:显示当前节点各ring相关的信息; -R:控制所有节点重载配置;
===============================================================================
实验:CentOS 7高可用Web集群服务
==============================================================================
实验环境描述:
- 两台CentOS 7.2 X86_64 的虚拟主机,模拟两节点集群;
- ip部署:node1:10.1.252.153 ;node2:10.1.252.161
安装前配置
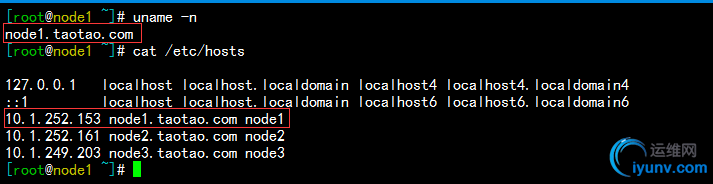
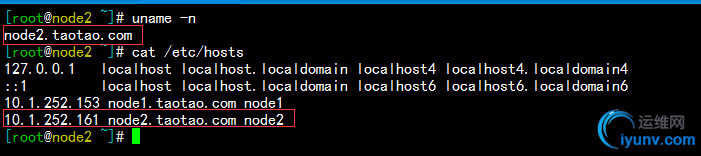
1)主机名解析(/etc/hosts),解析的结果必须要和本地使用的主机名保持一致
2)时间同步:

安装配置过程如下:
1.各节点安装相关的程序包,corosync/pacemaker
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| # 只需安装pacemaker即可,因为会把依赖的corosync程序包一并安装上
[iyunv@node1 ~]# yum install pacemaker -y
Dependencies Resolved # 以来的程序包如下:
=======================================================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
=======================================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
pacemaker x86_64 1.1.13-10.el7 CDROM 462 k
Installing for dependencies:
corosync x86_64 2.3.4-7.el7 CDROM 210 k
corosynclib x86_64 2.3.4-7.el7 CDROM 124 k
libqb x86_64 0.17.1-2.el7 CDROM 91 k
pacemaker-cli x86_64 1.1.13-10.el7 CDROM 253 k
pacemaker-cluster-libs x86_64 1.1.13-10.el7 CDROM 92 k
pacemaker-libs x86_64 1.1.13-10.el7 CDROM 519 k
resource-agents x86_64 3.9.5-54.el7 CDROM 339 k
Transaction Summary
=======================================================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+7 Dependent packages)
|
2.编辑corosync配置文件/etc/corosync/corosync.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# cd /etc/corosync
[iyunv@node1 corosync]# ls
corosync.conf.example corosync.conf.example.udpu corosync.xml.example uidgid.d
[iyunv@node1 corosync]# cp corosync.conf.example corosync.conf # 把配置文件示例复制一下
totem {
version: 2
crypto_cipher: aes256
crypto_hash: sha1
interface { # 如果有多块网卡可以配置多个interface
ringnumber: 0 #第一个必须为0
bindnetaddr: 10.1.252.153 #绑定的ip地址
mcastaddr: 239.255.100.1 #多播地址,必要使用默认的249
mcastport: 5405 #默认值即可
ttl: 1 #必须为1
}
}
logging {
fileline: off
to_stderr: no #要不要发给错误输出
to_logfile: yes #要不要发给日志文件
logfile: /var/log/cluster/corosync.log #指明日志文件
to_syslog: no
debug: off #是否记录debug级别的信息,通常在调试的时候启用
timestamp: on #是否开启时间戳
logger_subsys {
subsys: QUORUM #要不要记录子系统quorum的日志信息
debug: off
}
}
quorum {
provider: corosync_votequorum #指明使用哪一种算法来完成投票选举
}
nodelist { #节点列表
node {
ring0_addr: node1.magedu.com
nodeid: 1
}
node {
ring0_addr: node2.magedu.com
nodeid: 2
}
}
|
3.生成生成authkey:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| [iyunv@node1 corosync]# corosync-keygen
Corosync Cluster Engine Authentication key generator.
Gathering 1024 bits for key from /dev/random.
Press keys on your keyboard to generate entropy.
Press keys on your keyboard to generate entropy (bits = 888).
Press keys on your keyboard to generate entropy (bits = 936).
Press keys on your keyboard to generate entropy (bits = 984).
Writing corosync key to /etc/corosync/authkey.
[iyunv@node1 corosync]# ll
total 20
-r-------- 1 root root 128 Dec 7 16:07 authkey
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2881 Dec 7 15:30 corosync.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2881 Nov 21 2015 corosync.conf.example
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 767 Nov 21 2015 corosync.conf.example.udpu
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3278 Nov 21 2015 corosync.xml.example
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Nov 21 2015 uidgid.d
|
4.将node1的配置文件和认证authkey文件远程复制给节点node2主机一份:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| [iyunv@node1 corosync]# scp -p corosync.conf authkey node2:/etc/corosync/
corosync.conf 100% 3031 3.0KB/s 00:00
authkey 100% 128 0.1KB/s 00:00
# 在node2节点上验证文件
[iyunv@node2 ~]# cd /etc/corosync/
[iyunv@node2 corosync]# ll
total 20
-r-------- 1 root root 128 Dec 7 16:07 authkey
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3031 Dec 7 16:41 corosync.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2881 Nov 21 2015 corosync.conf.example
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 767 Nov 21 2015 corosync.conf.example.udpu
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3278 Nov 21 2015 corosync.xml.example
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Nov 21 2015 uidgid.d
|
5.启动node1和node2两节点的corosync服务,查看监听的端口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| [iyunv@node1 corosync]# systemctl start corosync.service
[iyunv@node1 corosync]# ss -tunl
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:68 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 10.1.252.153:5404 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 10.1.252.153:5405 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 239.255.100.1:5405 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:43497 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 *:514 *:*
udp UNCONN 0 0 :::30879 :::*
|
查看node1 corosync的日志文件,正常启动,如下:
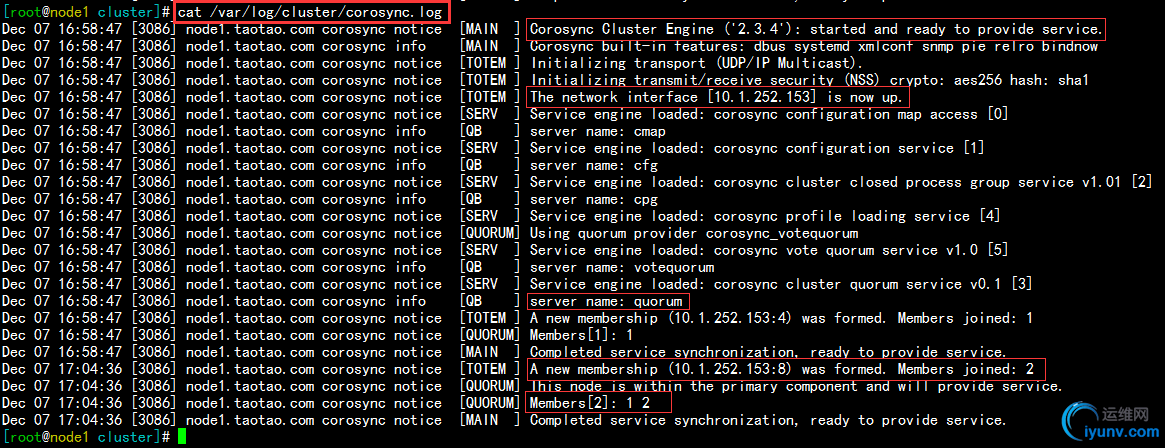
查看node2 corosync的日志文件,正常启动,如下:

6.检测集群工作是否正常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| [iyunv@node1 cluster]# corosync-cfgtool -s
Printing ring status.
Local node ID 1
RING ID 0
id = 10.1.252.153
status = ring 0 active with no faults # 没有错误
[iyunv@node2 corosync]# corosync-cfgtool -s
Printing ring status.
Local node ID 2
RING ID 0
id = 10.1.252.161
status = ring 0 active with no faults
[iyunv@node1 cluster]# corosync-cmapctl |grep member
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.1.config_version (u64) = 0
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.1.ip (str) = r(0) ip(10.1.252.153)
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.1.join_count (u32) = 1
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.1.status (str) = joined
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.2.config_version (u64) = 0
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.2.ip (str) = r(0) ip(10.1.252.161)
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.2.join_count (u32) = 1
runtime.totem.pg.mrp.srp.members.2.status (str) = joined
|
如上,就是corosync集群的配置过程,接下来我们启用pacemaker
1.在两个节点分别启动pacemaker,查看其状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| [iyunv@node1 cluster]# systemctl start pacemaker.service # 启动服务
[iyunv@node1 cluster]# systemctl status pacemaker.service # 查看其状态
● pacemaker.service - Pacemaker High Availability Cluster Manager
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/pacemaker.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2016-12-07 17:53:38 CST; 50s ago
Main PID: 3311 (pacemakerd)
CGroup: /system.slice/pacemaker.service # 启动的相关服务
├─3311 /usr/sbin/pacemakerd -f
├─3312 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/cib
├─3313 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/stonithd
├─3314 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/lrmd
├─3315 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/attrd
├─3316 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/pengine
└─3317 /usr/libexec/pacemaker/crmd
|
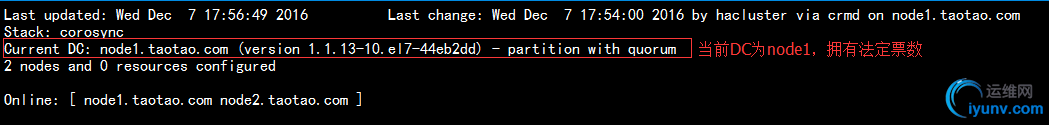
2.使用crm_mon命令监控查看服务是否正常,可以看到当前DC为node1,正常
3.配置crmsh接口
1)下载crmsh以及依赖的rpm包,然后安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # 这是我下载的crmsh的rpm包,以及依赖到的程序文件
[iyunv@node1 crmsh]# ll
total 668
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 608836 Oct 16 2015 crmsh-2.1.4-1.1.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 27080 Oct 16 2015 pssh-2.3.1-4.2.x86_64.rpm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 42980 Oct 16 2015 python-pssh-2.3.1-4.2.x86_64.rpm
# 配置好yum仓库,直接在本地安装程序包即可
[iyunv@node1 crmsh]# yum install -y ./*
|
2)运行crm命令,进入交互命令方式
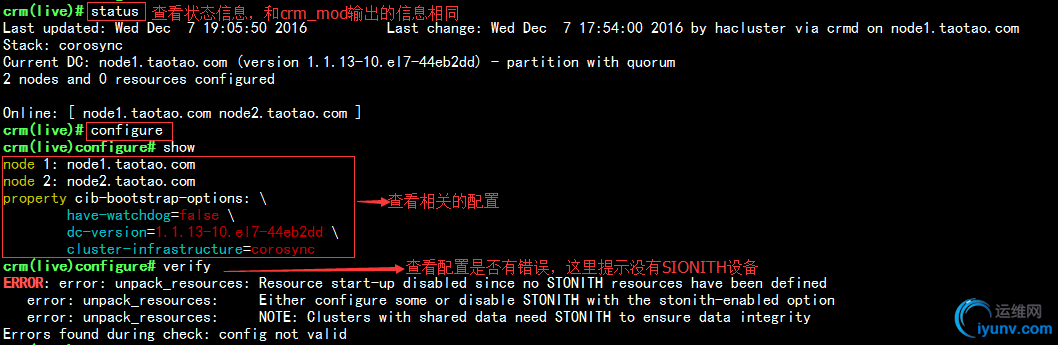
3)在configure中关闭stonith
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| crm(live)# configure
crm(live)configure# help
crm(live)configure# property # Tab键可补全
batch-limit= maintenance-mode= placement-strategy=
cluster-delay= migration-limit= remove-after-stop=
cluster-recheck-interval= no-quorum-policy= shutdown-escalation=
crmd-transition-delay= node-action-limit= start-failure-is-fatal=
dc-deadtime= node-health-green= startup-fencing=
default-action-timeout= node-health-red= stonith-action=
default-resource-stickiness= node-health-strategy= stonith-enabled=
election-timeout= node-health-yellow= stonith-timeout=
enable-acl= notification-agent= stonith-watchdog-timeout=
enable-startup-probes= notification-recipient= stop-all-resources=
have-watchdog= pe-error-series-max= stop-orphan-actions=
is-managed-default= pe-input-series-max= stop-orphan-resources=
load-threshold= pe-warn-series-max= symmetric-cluster=
crm(live)configure# property stonith-enabled=
stonith-enabled (boolean, [true]):
Failed nodes are STONITH'd
crm(live)configure# property stonith-enabled=false # 设置stonith为false
crm(live)configure# show # 再次查看发现多了一行 stonith-enabled=false
node 1: node1.taotao.com \
attributes standby=off
node 2: node2.taotao.com
property cib-bootstrap-options: \
have-watchdog=false \
dc-version=1.1.13-10.el7-44eb2dd \
cluster-infrastructure=corosync \
stonith-enabled=false
crm(live)configure# verify # 校验没有报错
crm(live)configure# commit # 确定没问题,提交
|
4.在configure中使用primitive定义一个webip的资源;

查看当前webip资源所在的节点,可以发现在节点node1上;


5.设置node1处于standby待机状态,发现资源webip转移到了节点node2上,如下:


6.现在在node1和node2两台主机上启动httpd服务,并提供测试页面,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| [iyunv@node1 html]# echo "<h1>Node1</h1>" > index.html
[iyunv@node1 html]# cat index.html
<h1>Node1</h1>
[iyunv@node2 html]# echo "<h1>Node2</h1>" > index.html
[iyunv@node2 html]# cat index.html
<h1>Node2</h1>
# 两节点启动服务,测试均可正常访问,如下:
[iyunv@node2 html]# curl 10.1.252.153
<h1>Node1</h1>
[iyunv@node2 html]# curl 10.1.252.161
<h1>Node2</h1>
|
7.在集群中定义httpd的资源,在CentOS 7 中要想使httpd出现在systemd的资源列表中,就要设定开机自启enable
1
2
3
4
5
| [iyunv@node1 ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
[iyunv@node2 html]# systemctl enable httpd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
|
1)在资源ra中查看systemd列表可以看到httpd资源,如下:
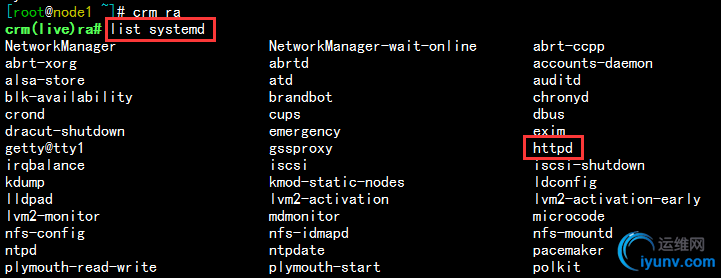
8.定义httpd的资源,并查看,发现两个资源并不在同一节点,但是高可用服务必须要求两个资源在同一个节点上,所以,我们要设定组资源或者资源约束;

9.定义组资源webservice,使webserver和webip位于同一组中,如下:

10.查看其状态,可以发现现在资源组webservice位于节点node1上,在浏览器中访问资源ip,可以正常访问node1的web界面,如下:


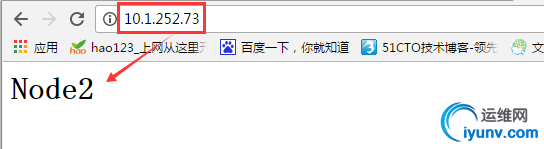
11.设置node1处于standby待机状态,发现组资源webservice转移到了节点node2上,再次访问资源ip发现为node2节点的web页面

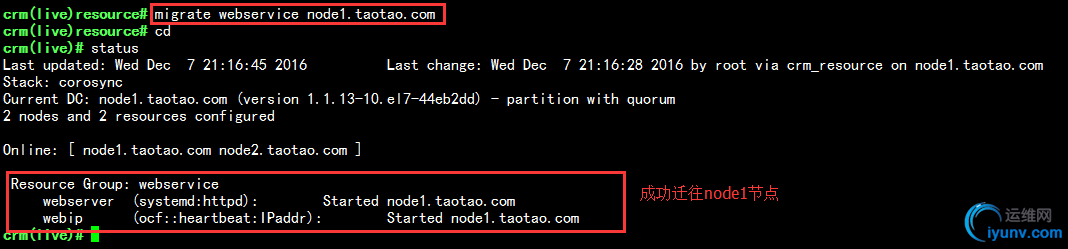
12.我们可以使用resource/migrate命令完成手动迁移资源到指定的节点上,现在我把node1上线,然后手动把资源迁移到node1,如下:

我们也可以使用resource下的stop,start,status命令控制服务的停止和启动,以及状态查看
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| crm(live)# resource
crm(live)resource# stop webservice
crm(live)resource# status
Resource Group: webservice
webserver (systemd:httpd): (target-role:Stopped) Stopped
webip (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr): (target-role:Stopped) Stopped
crm(live)resource# status webservice
resource webservice is NOT running
crm(live)resource# start webservice
crm(live)resource# status webservice
resource webservice is running on: node1.taotao.com
|
|