|
|
tomcat主要由两大核心组件,一个是connector,一个是container。connector负责的是底层的网络通信的实现,而container负责的是上层servlet业务的实现。一个应用服务器的性能很大程度上取决于网络通信模块的实现,因此connector对于tomcat而言是重中之重。
从采用的网络通信技术来看,connector可分为:
- JIoEndpoint,基于java bio实现,特点是每建立一个连接分配一个线程,读数据阻塞。
- NioEndpoint,使用java nio实现,使用反应器模式,线程和连接解绑,多路复用。
AprEndpoint,使用Apache Portable Runtime实现,直接调用native方法,有更高的效率,但是实现依赖具体平台。
1 JIoEndpoint的实现
启动一个org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.Acceptor线程,用于接收用户的连接请求,当连接成功后,会把创建的socket传递给org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.SocketProcessor,由线程池去执行SocketProcessor。Acceptor还具有管理连接数的功能,当连接数达到上限时,会阻塞当前的请求。这里提到的连接数和线程池的容量都是在tomcat_home\conf\server.xml里面配置的。
Acceptor核心代码片段如下
int errorDelay = 0;
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && running) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (!running) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
Socket socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = serverSocketFactory.acceptSocket(serverSocket);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (running && !paused && setSocketOptions(socket)) {
// Hand this socket off to an appropriate processor
if (!processSocket(socket)) {
// Close socket right away
closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
// Close socket right away
closeSocket(socket);
}
} catch (IOException x) {
if (running) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), x);
}
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
if (running) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), npe);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
}
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
processSocket
// Process the request from this socket
try {
SocketWrapper<Socket> wrapper = new SocketWrapper<Socket>(socket);
wrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
// During shutdown, executor may be null - avoid NPE
if (!running) {
return false;
}
getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(wrapper));
} catch (RejectedExecutionException x) {
log.warn("Socket processing request was rejected for:"+socket,x);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.SocketProcessor的职责是把具体的请求处理过程委派给org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.Handler,然后根据handler返回的不同SocketState,来决定是否关闭连接或者进行下一轮处理。
boolean launch = false;
synchronized (socket) {
try {
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
try {
// SSL handshake
serverSocketFactory.handshake(socket.getSocket());
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.handshake"), t);
}
// Tell to close the socket
state = SocketState.CLOSED;
}
if ((state != SocketState.CLOSED)) {
if (status == null) {
state = handler.process(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN);
} else {
state = handler.process(socket,status);
}
}
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
// Close socket
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Closing socket:"+socket);
}
countDownConnection();
try {
socket.getSocket().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADING ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADED){
socket.setKeptAlive(true);
socket.access();
launch = true;
} else if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
socket.access();
waitingRequests.add(socket);
}
} finally {
if (launch) {
try {
getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN));
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
if (running) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.launch.fail"),
npe);
}
}
}
}
}
socket = null;
// Finish up this request
其中handler根据所采用协议的不同,可以分为:
- AjpConnectionHandler,当我们的服务器架构是前端服务器(apache or nginx)+tomcat服务器的时候。用户的请求先到前端服务器,再由前端服务器通过ajp协议和tomcat通信,由tomcat去执行应用的逻辑。使用这种架构的好处是提高性能,前端服务器在管理连接、解析http请求、压缩响应http请求方面性能优于tomcat。
- Http11ConnectionHandler,当应用服务器直接暴露给用户访问时,就会使用这个handler,由tomcat直接负责解析、处理、响应http请求。
下面我们以Http11ConnectionHandler为例来看之后的请求处理过程。

首先在Http11Processor的process方法里,会先从socket里读取http请求数据,并解析请求头,构造httprequest对象,然后调用Adapter.service()。Adapter.service()是connector和container的桥梁,经过这一步,请求就从connector传递到container里了,Adapter.service之后便是filter和servlet的执行逻辑了。对于普通的servlet来说,最后Http11ConnectionHandler会返回SocketState.CLOSED的状态,然后SocketProcessor关闭连接,容器线程回收。
2 NioEndpoint的实现
NioEndpoint是基于java nio机制的,它的特点是采用了异步io经典的reactor模式,无阻塞解析http请求,大大提高了性能。和JioEndpoint一样,它也有一个线程专门负责接收用户连接请求org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Acceptor。实现上也和Jio的类似,在一个线程里循环调用java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel.accept()接收连接,并维护容器连接数。当接收到一个连接后,就把SocketChannel注册到reactor里面,这里的reactor称为Poller。
Acceptor的核心逻辑
int errorDelay = 0;
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && running) {
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (!running) {
break;
}
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = serverSock.accept();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
}
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// setSocketOptions() will add channel to the poller
// if successful
if (running && !paused) {
if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
closeSocket(socket);
}
} catch (SocketTimeoutException sx) {
// Ignore: Normal condition
} catch (IOException x) {
if (running) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), x);
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError oom) {
try {
oomParachuteData = null;
releaseCaches();
log.error("", oom);
}catch ( Throwable oomt ) {
try {
try {
System.err.println(oomParachuteMsg);
oomt.printStackTrace();
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(letsHopeWeDontGetHere);
}
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(letsHopeWeDontGetHere);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
}
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
// Process the connection
try {
//disable blocking, APR style, we are gonna be polling it
socket.configureBlocking(false);
Socket sock = socket.socket();
socketProperties.setProperties(sock);
NioChannel channel = nioChannels.poll();
if ( channel == null ) {
// SSL setup
if (sslContext != null) {
SSLEngine engine = createSSLEngine();
int appbufsize = engine.getSession().getApplicationBufferSize();
NioBufferHandler bufhandler = new NioBufferHandler(Math.max(appbufsize,socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize()),
Math.max(appbufsize,socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize()),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
channel = new SecureNioChannel(socket, engine, bufhandler, selectorPool);
} else {
// normal tcp setup
NioBufferHandler bufhandler = new NioBufferHandler(socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),
socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
channel = new NioChannel(socket, bufhandler);
}
} else {
channel.setIOChannel(socket);
if ( channel instanceof SecureNioChannel ) {
SSLEngine engine = createSSLEngine();
((SecureNioChannel)channel).reset(engine);
} else {
channel.reset();
}
}
getPoller0().register(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error("",t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
// Tell to close the socket
return false;
}
return true;
}
在NioEndpoint启动时,会实例化N个org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller(N为cpu核数)。这是因为在Poller里面无IO等待,所以最优吞吐量的Poller线程个数等于cpu核数。
Poller封装了java nio的就绪选择器java.nio.channels.Selector,实现了一个经典的反应器模式。
Acceptor建立好的socket连接会在Poller注册一个读就绪事件。Poller在一个while里,循环调用java.nio.channels.Selector.select(long),当有读事件就绪时,即http请求数据到达时,则从返回的selectedKeys里拿到socket进行后续处理。
Poller的核心代码
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
try {
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && (!close) ) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
boolean hasEvents = false;
// Time to terminate?
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
} else {
hasEvents = events();
}
try {
if ( !close ) {
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
//if we are here, means we have other stuff to do
//do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
}
} catch ( NullPointerException x ) {
//sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5
if ( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Possibly encountered sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5",x);
if ( wakeupCounter == null || selector == null ) throw x;
continue;
} catch ( CancelledKeyException x ) {
//sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5
if ( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Possibly encountered sun bug 5076772 on windows JDK 1.5",x);
if ( wakeupCounter == null || selector == null ) throw x;
continue;
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error("",x);
continue;
}
//either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// any active event.
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
KeyAttachment attachment = (KeyAttachment)sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (attachment == null) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
attachment.access();
iterator.remove();
processKey(sk, attachment);
}
}//while
//process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
if ( oomParachute > 0 && oomParachuteData == null ) checkParachute();
} catch (OutOfMemoryError oom) {
try {
oomParachuteData = null;
releaseCaches();
log.error("", oom);
}catch ( Throwable oomt ) {
try {
System.err.println(oomParachuteMsg);
oomt.printStackTrace();
}catch (Throwable letsHopeWeDontGetHere){
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(letsHopeWeDontGetHere);
}
}
}
}//while
synchronized (this) {
this.notifyAll();
}
stopLatch.countDown();
public boolean processSocket(NioChannel socket, SocketStatus status, boolean dispatch) {
try {
KeyAttachment attachment = (KeyAttachment)socket.getAttachment(false);
if (attachment == null) {
return false;
}
attachment.setCometNotify(false); //will get reset upon next reg
SocketProcessor sc = processorCache.poll();
if ( sc == null ) sc = new SocketProcessor(socket,status);
else sc.reset(socket,status);
if ( dispatch && getExecutor()!=null ) getExecutor().execute(sc);
else sc.run();
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {
log.warn("Socket processing request was rejected for:"+socket,rx);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
对socket处理在processSocket方法里进行,可以在当前线程中处理,也可以分发到线程池里处理。具体处理逻辑在org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.SocketProcessor里面。对于普通的servlet请求来说,处理完成后,会返回SocketState.CLOSED。然后在SocketProcessor调用org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller.cancelledKey(SelectionKey, SocketStatus, boolean)关闭socket连接,时序图如下。
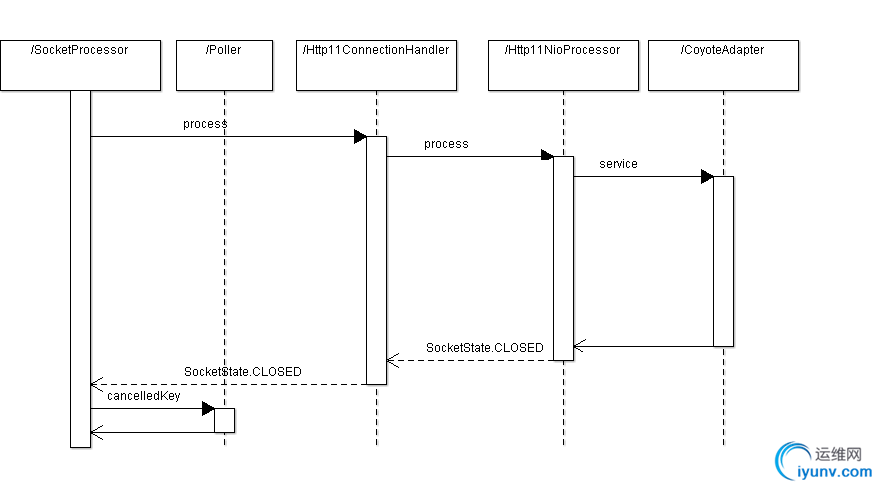
从NioEndpoint的实现原理可以看出,非阻塞读写和反应器模式,可以让NioEndpoint在以少量线程的条件下,并发处理大量的请求。特别是在使用长连接的场景下,反应器模式的多路复用方式,使得不需要给每个连接分配一个线程,这样就不会因为容器同时维护大量长连接而耗尽线程资源。这也就是为什么tomcat采用了NioEndpoint来实现servlet3中的Async servlet和comet。
我们先来看看Async servlet的实现,当需要在响应数据之前回收容器线程时就可以使用Async servlet。使用Async servlet需要把servlet配置为支持异步,例如
<servlet>
<servlet-name>asyncServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.longji.web.AsyncServlet</servlet-class>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
另外在在servlet的处理逻辑里,需要调用javax.servlet.ServletRequest.startAsync(ServletRequest, ServletResponse),这样一来这个连接就被标记为Async。示例代码
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "private");
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
response.setHeader("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
response.setHeader("Proxy-Connection", "Keep-Alive");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("Start ...");
out.flush();
if (!request.isAsyncSupported()) {
log.info("the servlet is not supported Async");
return;
}
request.startAsync(request, response);
if (request.isAsyncStarted()) {
AsyncContext asyncContext = request.getAsyncContext();
asyncContext.setTimeout(1L * 100000L * 1000L);// 60sec
new CounterThread(asyncContext).start();
} else {
log.error("the ruquest is not AsyncStarted !");
}
}
可以看到,在servlet里面另起一个线程处理请求,这个线程持有一个AsyncContext asyncContext = request.getAsyncContext(),通过AsyncContext ,CounterThread异步线程可以拿到ServletRequest和ServletResponse,在完成业务处理之后,可以向客户端响应数据。
Async servlet的处理过程可以分为两个阶段,第一个阶段和普通servlet类似,直至调用了ServletRequest.startAsync,这个连接将被标记为Async的,并且在NioProcessor中返回SocketState.LONG,这样当容器线程回收的时候就不会关闭socket连接。
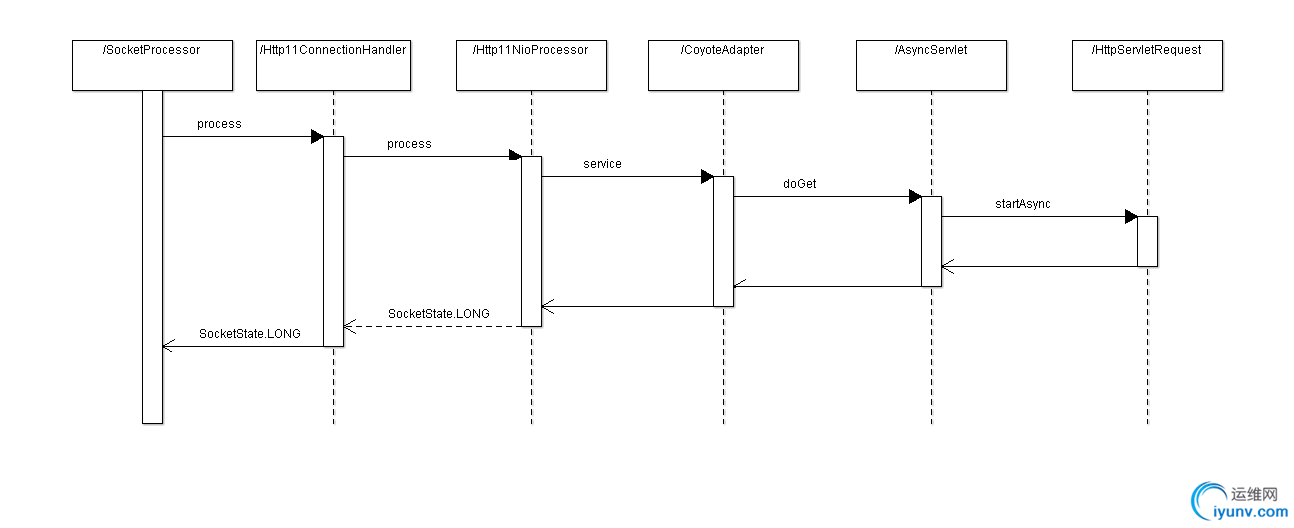
另外一个阶段是在业务处理结束后调用javax.servlet.AsyncContext.complete()的时候触发的。最终调用org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.processSocket(NioChannel, SocketStatus, boolean)。
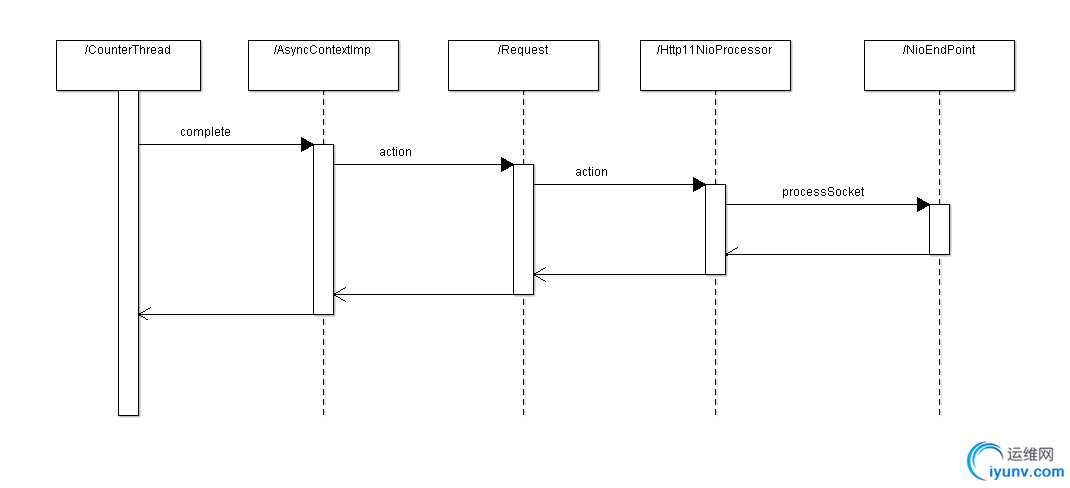
org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.processSocket(NioChannel, SocketStatus, boolean)处理流程如下图。
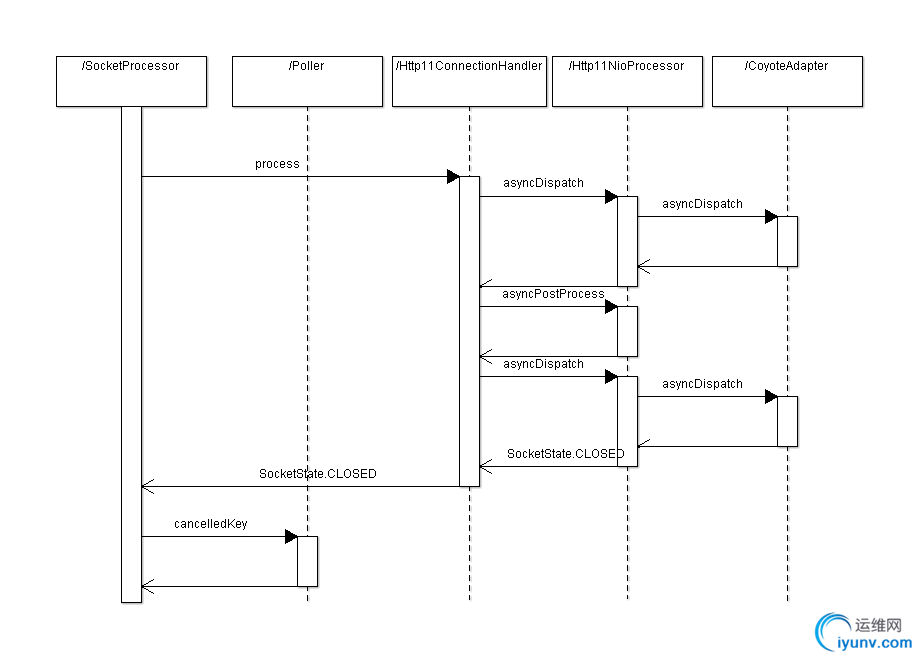
从时序图可以看出,请求又重新进入了SocketProcessor的处理流程,async请求经过几番状态变迁后,最后返回SocketState.CLOSED状态,由Poller关闭连接。
如果是使用comet servlet,需要在servlet里面实现CometProcessor接口,在com.longji.web.CometProcessor.event(CometEvent)方法里编写对应四种事件的处理逻辑。
示例程序
public void event(CometEvent event)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = event.getHttpServletRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = event.getHttpServletResponse();
if (event.getEventType() == CometEvent.EventType.BEGIN) {
log("Begin for session: " + request.getSession(true).getId());
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("<!doctype html public \"-//w3c//dtd html 4.0 transitional//en\">");
writer.println("<head><title>JSP Chat</title></head><body bgcolor=\"#FFFFFF\">");
writer.flush();
synchronized(connections) {
connections.add(response);
}
} else if (event.getEventType() == CometEvent.EventType.ERROR) {
log("Error for session: " + request.getSession(true).getId());
synchronized(connections) {
connections.remove(response);
}
event.close();
} else if (event.getEventType() == CometEvent.EventType.END) {
log("End for session: " + request.getSession(true).getId());
synchronized(connections) {
connections.remove(response);
}
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("</body></html>");
event.close();
} else if (event.getEventType() == CometEvent.EventType.READ) {
InputStream is = request.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[512];
do {
int n = is.read(buf); //can throw an IOException
if (n > 0) {
log("Read " + n + " bytes: " + new String(buf, 0, n)
+ " for session: " + request.getSession(true).getId());
} else if (n < 0) {
//error(event, request, response);
return;
}
} while (is.available() > 0);
}
}
comet包含四个事件,Begin、Read、End、Error。
Begin事件的处理过程和普通的servlet无异,由org.apache.coyote.Adapter.service(Request, Response)进入container处理逻辑,构造Begin事件,最后调用com.longji.web.ChatServlet.event(CometEvent),并返回SocketState.LONG至SocketProcessor,保持和客户端连接。
当客户端下一个请求到达时,会触发Poller的读就绪事件,事件会分发给SocketProcessor处理,处理流程如下时序图

在org.apache.coyote.Adapter.event(Request, Response, SocketStatus)会构造读事件,调用com.longji.web.ChatServlet.event(CometEvent)。
当客户端和服务端一次完整的交互结束时,业务代码可以主动调用org.apache.catalina.comet.CometEvent.close(),这个方法会将Http11NioProcessor的comet标记为false,这样一来Http11NioProcessor.event则返回SocketState.CLOSED,SocketProcessor会执行关闭socket操作,如下图

小tip
char 2 byte

如果对于同一个response,先调用getWriter,再调用getOutputStream,会抛非法状态异常
|
|