一、Tomcat的启动流程与架构
Tomcat启动的时候的debug的运行轨迹图,框出来的代表主要容器的执行方法。
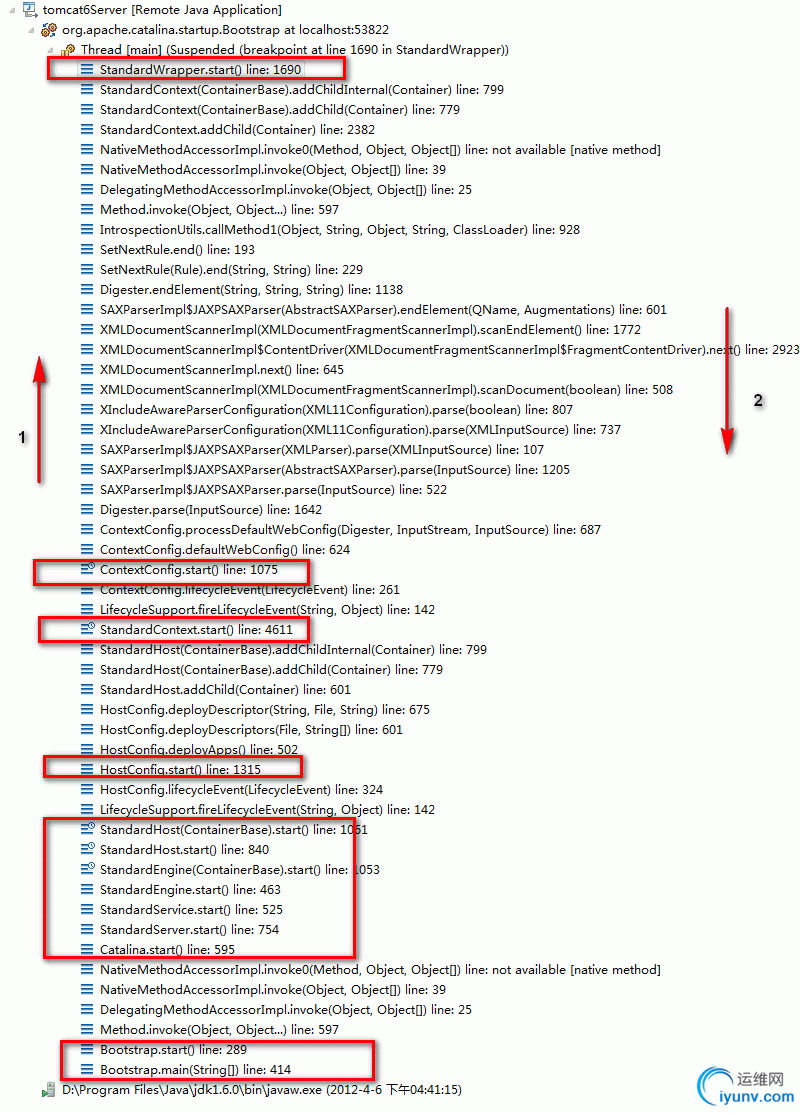
Tomcat执行大致的流程图
整体上看一看Tomcat的概览图

顶层元素:Server,Service
连接器元素:Connector(HTTP,AJP等)
容器元素:Engine(跟Connector结合,处理http请求),Host(对应于多个主机 i.e. mail.test.com,www.test.com,www.test2.com),Context(对应于一个个webapp应用),Wrapper(对应于一个个Servlet)
组件元素:Logger,Value ,Realm,Listener,Cluster等
二、Tomcat启动的步骤:
1. tomcat的启动从Bootstrap.main()开始-->init()-->start()。
Bootstrap
public void start()
throws Exception
{
.........
// Set Catalina path
setCatalinaHome();
setCatalinaBase();
//设置StandardClassLoader,加载${catalina.home}/lib,${catalina.home}/lib/*.jar
initClassLoaders();
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
.........
}
2. Catalina.start().
Catalina
public void start() {
.....
initDirs();
// 初始化JNDI名称
initNaming();
// 创建解析config/server.xml的规则
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
......
//正式解析。至此相关的Server->Service->Enginer->Host,
//也包括LifecycleListence、Connection等的实例和相关属性都组装配置完成
digester.push(this);
digester.parse(inputSource);
...........
// 启动server服务
if (getServer() instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) getServer()).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("Catalina.start: ", e);
}
}
........
if (await) {
//阻塞在默认的8005端口,监听shutdown命令,来关闭tomcat
await(); // -->serverSocket.accept(); 8005端口
stop(); //--> ((Lifecycle) getServer()).stop();
}
.........
}
3. StandardServer.start() ,server启动。
StandardServer
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
.......
// 开启service,一个Server有多个Service,Service互相独立
synchronized (services) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
if (services instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) services).start();
}
}
........
}
4. StandardService.start(),Service启动
StandardService
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
.........
//初始化各种connection,在这里绑定tomcat需要的端口,或者抛出已绑定端口的异常
connectors.initialize();
..........
// 启动Enginer容器
if (container != null) {
synchronized (container) {
if (container instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) container).start();
}
}
}
......
// 但Enginer、Host、Context、Wrapper等容器都启动完成,那么启动connection,接受各种请求。
synchronized (connectors) {
for (int i = 0; i < connectors.length; i++) {
try {
((Lifecycle) connectors).start();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.startFailed",
connectors), e);
}
}
}
.........
}
5. Connector.start(),启动Connector;这步就是建立用户Socket,解析http请求,封装成request。最终request经过Engine->Host->Context->Wrapper等容器的Valve处理,在经过FilterChina的处理,最终由Servlet处理。
Connector
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
........
if( !initialized )
initialize();
//HTTP/1.1或AJP/1.3协议的处理器的启动,听见来自用户的请求Socket
protocolHandler.start();
........
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下面步骤中的组件都是继承ContainerBase容器,看一下简略的关系图

ContainerBase
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate and update our current component state
if (started) {
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info(sm.getString("containerBase.alreadyStarted", logName()));
return;
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null);
started = true;
// 启动各种组件,各种组件由server.xml、web.xml、context.xml等配置文件提供
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
logger = null;
getLogger();
if ((logger != null) && (logger instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) logger).start();
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
if ((resources != null) && (resources instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) resources).start();
// 启动各种子容器Engine->Host->Context->Wrapper
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) children).start();
}
// 启动pipeline组件
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
// 触发事件
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(START_EVENT, null);
// Start our thread
threadStart();
// 触发事件
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(AFTER_START_EVENT, null);
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. StandardEngine.start(),启动Engine;这步开始容器类的start
StandardEngine
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
if( started ) {
return;
}
if( !initialized ) {
init();
}
......
//一个Engine可以有多个Host,Host的启动
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) children).start();
}
.......
//启动各种组件和子容器start()
super.start();
.........
}
7. StandardHost.start(),启动Host,
StandardHost
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
.........
//启动各种组件和子容器start()
super.start(); -->ContainerBase -->HostConfig
..........
// 目录webapps/
File appBase = appBase();
// conf/Catalina/localhost目录
File configBase = configBase();
// 解析conf\Catalina\localhost\*.xml文件,对每个webapp生成一个context
HostConfig --> deployDescriptors(configBase, configBase.list());
// 部署WEBAPPS/目录下的WARs
HostConfig--> deployWARs(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
// Deploy expanded folders
HostConfig--> deployDirectories(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
}
8. StandardContext .start(),启动Context,
StandardContext
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
............
//一个Context对应一个WebappLoader,也就是关联到了WebappClassLoader
//用于每个app下面的WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib类的加载
if (getLoader() == null) {
WebappLoader webappLoader = new WebappLoader(getParentClassLoader());
webappLoader.setDelegate(getDelegate());
setLoader(webappLoader);
}
...........
// 创建work目录,当做临时工作目录
//比如 \work\Catalina\localhost\host-manager
postWorkDirectory();
..............
//初始化classloader
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
..............
//初始化各种组件
if ((logger != null) && (logger instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) logger).start();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
if ((resources != null) && (resources instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) resources).start();
.............
//触发start事件
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(START_EVENT, null);
//解析系统默认的 conf/web.xml文件,完成默认的filterChina、servlet的各种组装
ContextConfig --> defaultWebConfig();
//解析apps下的自定义 /WEB-INF/web.xml 文件,完成filterChina、servlet的各种组装
ContextConfig --> applicationWebConfig();
// 如果设置了 <load-on-startup>,则初始化Servlet,执行init()或servlet为jsp页面,则complile生成servlet文件,再init;
loadOnStartup(findChildren());
..........
}
)
9. StandardWrapper.start(),启动wrapper,standardWrapper就是Servlet的包装类
StandardWrapper
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
..........
//启动各种组件和子容器start()
super.start();
.........
//加载Servlet,此组件也就是Servlet的包装类,跟Servlet的关系通过此类
public synchronized void load() throws ServletException {
instance = loadServlet();
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
三、Tomcat的生命周期关键组件Lifecycle
以上就是整个tomcat的启动过程,tomcat调用一个个组件的start(),父组件调用子组件start(),就这样一步步启动,直至整个tomcat启动完成。
tomcat的启动与关闭的生命周期跟Lifecycle接口息息相关.
图:Lifecycle接口的结构图

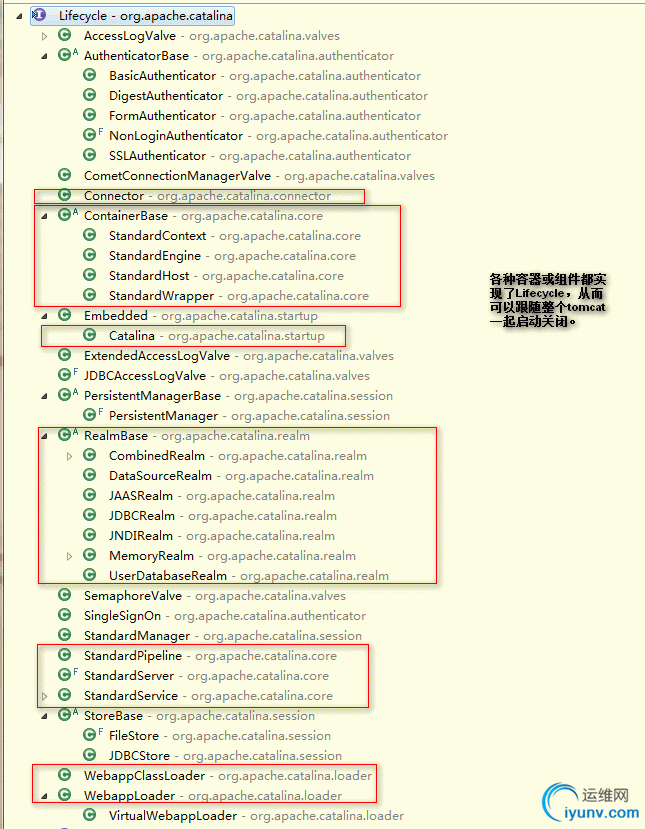
图:Lifecycle的实现类
参考资料:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-tomcat1/(Tomcat 系统架构与设计模式,第 1 部分: 工作原理 )
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-tomcat2/(Tomcat 系统架构与设计模式,第 2 部分: 设计模式分析) |