|
第一部分:PCAP包文件格式
一 基本格式:
文件头 数据包头数据报数据包头数据报......
二、文件头:

文件头结构体
sturct pcap_file_header
{
DWORD magic;
DWORD version_major;
DWORD version_minor;
DWORD thiszone;
DWORD sigfigs;
DWORD snaplen;
DWORD linktype;
}
说明:
1、标识位:32位的,这个标识位的值是16进制的 0xa1b2c3d4。
a 32-bit magic number ,The magic number has the value hex a1b2c3d4.
2、主版本号:16位, 默认值为0x2。
a 16-bit major version number,The major version number should have the value 2.
3、副版本号:16位,默认值为0x04。
a 16-bit minor version number,The minor version number should have the value 4.
4、区域时间:32位,实际上该值并未使用,因此可以将该位设置为0。
a 32-bit time zone offset field that actually not used, so you can (and probablyshould) just make it 0;
5、精确时间戳:32位,实际上该值并未使用,因此可以将该值设置为0。
a 32-bit time stamp accuracy field tha not actually used,so you can (and probablyshould) just make it 0;
6、数据包最大长度:32位,该值设置所抓获的数据包的最大长度,如果所有数据包都要抓获,将该值设置为65535;例如:想获取数据包的前64字节,可将该值设置为64。
a 32-bit snapshot length" field;The snapshot length field should be themaximum number of bytes perpacket that will be captured. If the entire packetis captured, make it 65535; if you only capture, for example, the first 64bytes of the packet, make it 64.
7、链路层类型:32位, 数据包的链路层包头决定了链路层的类型。
a 32-bit link layer type field.The link-layer type depends on the type oflink-layer header that the
packets in the capture file have:
以下是数据值与链路层类型的对应表
0 BSD loopback devices, except for later OpenBSD
1 Ethernet, and Linux loopback devices 以太网类型,大多数的数据包为这种类型。
6 802.5 Token Ring
7 ARCnet
8 SLIP
9 PPP
10 FDDI
100 LLC/SNAP-encapsulated ATM
101 raw IP, with no link
102 BSD/OS SLIP
103 BSD/OS PPP
104 Cisco HDLC
105 802.11
108 later OpenBSD loopback devices (with the AF_value in network byte order)
113 special Linux cooked capture
114 LocalTalk
三 packet数据包头:
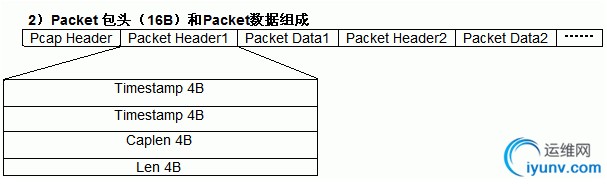
struct pcap_pkthdr
{
struct tim ts;
DWORD caplen;
DWORD len;
}
struct tim
{
DWORD GMTtime;
DWORD microTime
}
说明:
1、时间戳,包括:
秒计时:32位,一个UNIX格式的精确到秒时间值,用来记录数据包抓获的时间,记录方式是记录从格林尼治时间的1970年1月1日 00:00:00 到抓包时经过的秒数;
微秒计时:32位, 抓取数据包时的微秒值。
a time stamp, consisting of:
a UNIX-format time-in-seconds when the packet was captured, i.e. the number ofseconds since January 1,1970, 00:00:00 GMT (that GMT, *NOT* local time!);
the number of microseconds since that second when the packet was captured;
2、数据包长度:32位 ,标识所抓获的数据包保存在pcap文件中的实际长度,以字节为单位。
a 32-bit value giving the number of bytes of packet data that were captured;
3、数据包实际长度: 所抓获的数据包的真实长度,如果文件中保存不是完整的数据包,那么这个值可能要比前面的数据包长度的值大。
a 32-bit value giving the actual length of the packet, in bytes (which may begreater than the previous number, if you are not saving the entire packet).
四:packet数据:
即Packet(通常就是链路层的数据帧)具体内容,长度就是Caplen,这个长度的后面,就是当前PCAP文件中存放的下一个Packet数据包,也就是说:PCAP文件里面并没有规定捕获的Packet数据包之间有什么间隔字符串,下一组数据在文件中的起始位置。我们需要靠第一个Packet包确定。最后,Packet数据部分的格式其实就是标准的网路协议格式了可以任何网络教材上找得到。
五:举例分析
图中最开始的绿色部分就是24 Bytes的Pcap Header,接下来红色的16 Bytes是第一个消息的Pcap Header。后面的红色的16 Bytes是第二个消息的Pcap Header。两块蓝色的部分分别是两个消息从链路层开始的完整内容。在网络上实际传输的数据包在数据链路层上每一个Packet开始都会有7个用于同步的字节和一个用于标识该Packet开始的字节,最后还会有四个CRC校验字节;而PCAP文件中会把前8个字节和最后4个校验自己去掉,因为这些信息对于协议分析是没有用的。
用Wireshark打开一个PCAP数据包,每条消息的所有field会被解析出来并会按照协议层次折叠起来。第一层显示的是FrameXXX,这一级别没有对应某层具体的协议,而是对本条消息的一个概括性总结,描述了一些有用的概括性信息,比如从里面我们可以看到本条消息各种协议的层次关系,展开其它协议层之后对应的是该协议的各个域,如下图所示:
第二部分:PCAP文件解析
1、 pcap解析工具 Xplico
Xplico 是一个从 pcap 文件中解析出IP流量数据的工具,可解析每个邮箱 (POP, IMAP, 和 SMTP 协议), 所有 HTTP 内容, VoIP calls (SIP) 等等
2、 C语言实现PCAP文件分析
实现步骤:
1)用Wireshark软件抓包得到test.pcap文件
2)程序:分析pcap文件头 -> 分析pcap_pkt头 -> 分析帧头 -> 分析ip头 -> 分析tcp头 -> 分析http信息
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<time.h>
#define BUFSIZE 10240
#define STRSIZE 1024
typedef long bpf_int32;
typedef unsigned longbpf_u_int32;
typedef unsigned short u_short;
typedef unsigned longu_int32;
typedef unsigned shortu_int16;
typedef unsigned charu_int8;
//pacp文件头结构体
struct pcap_file_header
{
bpf_u_int32 magic; /* 0xa1b2c3d4 */
u_short version_major; /* magjor Version 2 */
u_short version_minor; /* magjor Version 4 */
bpf_int32 thiszone; /* gmt to local correction */
bpf_u_int32 sigfigs; /* accuracy of timestamps */
bpf_u_int32 snaplen; /* max length saved portion of each pkt */
bpf_u_int32 linktype; /* data link type (LINKTYPE_*) */
};
//时间戳
struct time_val
{
long tv_sec; /* seconds 含义同 time_t 对象的值 */
long tv_usec; /* and microseconds */
};
//pcap数据包头结构体
struct pcap_pkthdr
{
struct time_val ts; /* time stamp */
bpf_u_int32 caplen; /*length of portion present */
bpf_u_int32 len; /* length this packet (off wire) */
};
//数据帧头
typedef struct FramHeader_t
{ //Pcap捕获的数据帧头
u_int8 DstMAC[6]; //目的MAC地址
u_int8 SrcMAC[6]; //源MAC地址
u_short FrameType; //帧类型
} FramHeader_t;
//IP数据报头
typedef structIPHeader_t
{ //IP数据报头
u_int8 Ver_HLen; //版本+报头长度
u_int8 TOS; //服务类型
u_int16 TotalLen; //总长度
u_int16 ID; //标识
u_int16 Flag_Segment; //标志+片偏移
u_int8 TTL; //生存周期
u_int8 Protocol; //协议类型
u_int16 Checksum; //头部校验和
u_int32 SrcIP; //源IP地址
u_int32 DstIP; //目的IP地址
} IPHeader_t;
//TCP数据报头
typedef structTCPHeader_t
{ //TCP数据报头
u_int16 SrcPort; //源端口
u_int16 DstPort; //目的端口
u_int32 SeqNO; //序号
u_int32 AckNO; //确认号
u_int8 HeaderLen; //数据报头的长度(4 bit) + 保留(4 bit)
u_int8 Flags; //标识TCP不同的控制消息
u_int16 Window; //窗口大小
u_int16 Checksum; //校验和
u_int16 UrgentPointer; //紧急指针
}TCPHeader_t;
//
void match_http(FILE*fp, char *head_str, char *tail_str, char *buf, int total_len); //查找 http 信息函数
//
int main()
{
struct pcap_file_header*file_header;
struct pcap_pkthdr*ptk_header;
IPHeader_t *ip_header;
TCPHeader_t*tcp_header;
FILE *fp, *output;
int pkt_offset,i=0;
int ip_len, http_len,ip_proto;
int src_port, dst_port,tcp_flags;
char buf[BUFSIZE],my_time[STRSIZE];
char src_ip[STRSIZE],dst_ip[STRSIZE];
char host[STRSIZE], uri[BUFSIZE];
//初始化
file_header = (structpcap_file_header *)malloc(sizeof(struct pcap_file_header));
ptk_header =(struct pcap_pkthdr *)malloc(sizeof(struct pcap_pkthdr));
ip_header = (IPHeader_t*)malloc(sizeof(IPHeader_t));
tcp_header =(TCPHeader_t *)malloc(sizeof(TCPHeader_t));
memset(buf, 0,sizeof(buf));
//
if((fp =fopen(“test.pcap”,”r”)) == NULL)
{
printf(“error: can notopen pcap file\n”);
exit(0);
}
if((output =fopen(“output.txt”,”w+”)) == NULL)
{
printf(“error: can notopen output file\n”);
exit(0);
}
//开始读数据包
pkt_offset = 24; //pcap文件头结构 24个字节
while(fseek(fp,pkt_offset, SEEK_SET) == 0) //遍历数据包
{
i++;
//pcap_pkt_header 16byte
if(fread(ptk_header,16, 1, fp) != 1) //读pcap数据包头结构
{
printf(“\nread end ofpcap file\n”);
break;
}
pkt_offset += 16 +ptk_header->caplen; //下一个数据包的偏移值
strftime(my_time,sizeof(my_time), “%Y-%m-%d %T”, localtime(&(ptk_header->ts.tv_sec))); //获取时间
// printf(“%d: %s\n”,i, my_time);
//数据帧头 14字节
fseek(fp, 14,SEEK_CUR); //忽略数据帧头
//IP数据报头 20字节
if(fread(ip_header,sizeof(IPHeader_t), 1, fp) != 1)
{
printf(“%d: can notread ip_header\n”, i);
break;
}
inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void *)&(ip_header->SrcIP), src_ip, 16);
inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void *)&(ip_header->DstIP), dst_ip, 16);
ip_proto =ip_header->Protocol;
ip_len =ip_header->TotalLen; //IP数据报总长度
// printf(“%d: src=%s\n”, i, src_ip);
if(ip_proto != 0×06) //判断是否是 TCP 协议
{
continue;
}
//TCP头 20字节
if(fread(tcp_header,sizeof(TCPHeader_t), 1, fp) != 1)
{
printf(“%d: can notread ip_header\n”, i);
break;
}
src_port =ntohs(tcp_header->SrcPort);
dst_port =ntohs(tcp_header->DstPort);
tcp_flags =tcp_header->Flags;
// printf(“%d: src=%x\n”, i, tcp_flags);
if(tcp_flags == 0×18)// (PSH, ACK) 3路握手成功后
{
if(dst_port == 80) //HTTP GET请求
{
http_len = ip_len – 40;//http 报文长度
match_http(fp, “Host:“, “\r\n”, host, http_len); //查找 host 值
match_http(fp, “GET “,“HTTP”, uri, http_len); //查找 uri 值
sprintf(buf, “%d: %s src=%s:%d dst=%s:%d %s%s\r\n”, i, my_time, src_ip,src_port, dst_ip, dst_port, host, uri);
//printf(“%s”, buf);
if(fwrite(buf,strlen(buf), 1, output) != 1)
{
printf(“output file cannot write”);
break;
}
}
}
} // end while
fclose(fp);
fclose(output);
return 0;
}
//查找 HTTP 信息
void match_http(FILE*fp, char *head_str, char *tail_str, char *buf, int total_len)
{
int i;
int http_offset;
int head_len, tail_len,val_len;
char head_tmp[STRSIZE],tail_tmp[STRSIZE];
//初始化
memset(head_tmp, 0,sizeof(head_tmp));
memset(tail_tmp, 0,sizeof(tail_tmp));
head_len =strlen(head_str);
tail_len =strlen(tail_str);
//查找 head_str
http_offset =ftell(fp); //记录下HTTP报文初始文件偏移
while((head_tmp[0] =fgetc(fp)) != EOF) //逐个字节遍历
{
if((ftell(fp) –http_offset) > total_len) //遍历完成
{
sprintf(buf, “can notfind %s \r\n”, head_str);
exit(0);
}
if(head_tmp[0] ==*head_str) //匹配到第一个字符
{
for(i=1; i<head_len;i++) //匹配head_str 的其他字符
{
head_tmp=fgetc(fp);
if(head_tmp !=*(head_str+i))
break;
}
if(i == head_len) //匹配 head_str 成功,停止遍历
break;
}
}
// printf(“head_tmp=%s\n”, head_tmp);
//查找 tail_str
val_len = 0;
while((tail_tmp[0] =fgetc(fp)) != EOF) //遍历
{
if((ftell(fp) –http_offset) > total_len) //遍历完成
{
sprintf(buf, “can notfind %s \r\n”, tail_str);
exit(0);
}
buf[val_len++] =tail_tmp[0]; //用buf 存储 value 直到查找到 tail_str
if(tail_tmp[0] ==*tail_str) //匹配到第一个字符
{
for(i=1; i<tail_len;i++) //匹配head_str 的其他字符
{
tail_tmp=fgetc(fp);
if(tail_tmp !=*(tail_str+i))
break;
}
if(i == tail_len) //匹配 head_str 成功,停止遍历
{
buf[val_len-1] = 0; //清除多余的一个字符
break;
}
}
}
// printf(“val=%s\n”,buf);
fseek(fp, http_offset,SEEK_SET); //将文件指针 回到初始偏移
} |