|
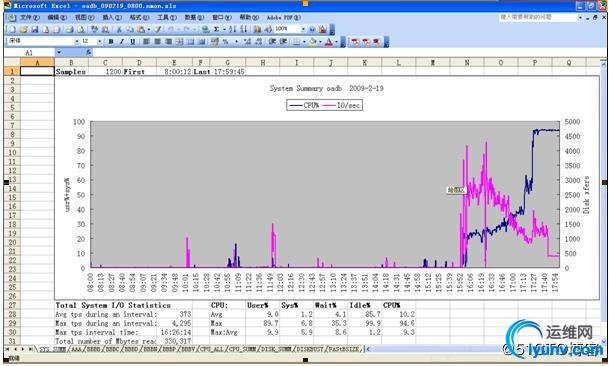
AIX下用nmon进行监控和分析实战 nmon从这里下载: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/wikis/display/Wikiptype/nmonanalyser 1、准备: 1)用root用户登录到系统中 2)建目录:#mkdir /nmon/script 3)确定版本:#oslevel,以便确定用哪个脚本,我是用530 # oslevel -s 5300-09-01-0847 4)把nmon12e_aix530用ftp上传到/nmon/script 5)执行授权命令:#chmod +x nmon12e_aix530 2、使用: 1)直接使用: ./nmon/nmon12e_aix536 -f -N -m /nmon/log -s 30 -c 2880 表示: -f 按标准格式输出文件:_YYYYMMDD_HHMM.nmon -N include NFS sections -m 切换到路径去保存日志文件 -s 每隔n秒抽样一次,这里为30 -c 取出多少个抽样数量,这里为2880,即监控=2880*(30/60/60)=24小时 根据小时计算这个数字的公式为:c=h*3600/s,比如要监控10小时,每隔30秒采样一次,则c=10*3600/30=1200 2)用crontab定期使用: A、执行命令:#crontab -e B、在最后一行添加如下命令: 0 8 * * 1,2,3,4,5 /nmon/script/nmon12e_aix530 -f -N -m /nmon/log -s 30 -c 1200 表示: 周一到周五,从早上08点开始,监控10个小时(到18:00整为止),输出到/nmon/log 3、分析 1)会在/tmp/nmon生成*.nmon的文件把它下载到你的电脑上 2)打开nmon analyser v339.xls,把宏的安全性设成最低,打开下载好的*.nmon文件。 并且保存为一个文件,生成的是视图模式的,非常直观!
参考: 附录一:crontab参数: 参考:http://tech.ddvip.com/2008-11/122629526990895.html f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 program minute hour day_of_month month weekday command这些字段接收以下值: minute 0 到 59 hour 0 到 23 day_of_month 1 到 31 month 1 到 12 weekday 0 到 6(星期天到星期六) 其中f1 是表示分钟,f2 表示小时,f3 表示一个月份中的第几日,f4 表示月份,f5 表示一个星期中的第几天。program 表示要执行的程序。 当 f1 为 * 时表示每分钟都要执行 program,f2 为 * 时表示每小时都要执行程序,其馀类推 当 f1 为 a-b 时表示从第 a 分钟到第 b 分钟这段时间内要执行,f2 为 a-b 时表示从第 a 到第 b 小时都要执行,其馀类推 当 f1 为 */n 时表示每 n 分钟个时间间隔执行一次,f2 为 */n 表示每 n 小时个时间间隔执行一次,其馀类推 当 f1 为 a, b, c,... 时表示第 a, b, c,... 分钟要执行,f2 为 a, b, c,... 时表示第 a, b, c...个小时要执行,其馀类推 附录二:nmon参数: 参考http://www.ibm.com/developerwork ... iptype/nmonanalyser nmon: -f spreadsheet output format [note: default -s300 -c288] Output file is _YYYYMMDD_HHMM.nmon -F same as -f but user supplied filename -c number of snapshots -d requests disk service and wait times (DISKSERV and DISKWAIT) -i Ignore processes using less than this amount of CPU when generating TOP section – useful for reducing data volumes -g file containing disk group definitions -l number of hdisks per sheet - defaults to 150, maximum 250. See notes -m NMON changes to this directory before saving the file
-r goes into spreadsheet file [default hostname] -s interval between snap shots -x capacity planning (15 mins for 1 day = -fdt -s900 -c96) -t include top processes in the output -T as –t plus saves command line arguments in UARG section -A include data for async I/O (PROCAIO) sections -D prevents DISK sections being produced (useful when Disk Groups are being used because there are too many hdisks to process) -E stops ESS sections being produced (necessary when Disk Groups are being used because there are too many vpaths to process) -J prevents JFS sections being produced (prevents Excel errors when you have more than 255 filesystems) -L includes LARGEPAGE section -N include NFS sections -S include WLM sections with subclasses -W include WLM sections without subclasses -Y include SUMMARY section (very efficient alternative to –t if PID level data is not required) example: nmon_aix51 -F asterix.nmon -r Test1 -s6 -c12 posted on 2009-02-19 20:24 IT进行时 阅读(4975) 评论(4) 编辑 收藏 
评论 # re: AIX下用nmon进行监控和分析实战 2009-03-25 15:46 无名网 写得不错,很多的文章一样的问题那就是没有说当nmon收到参数以的都是以daemon的形式运行的。开始的时候我就认为他没有工作,后来对产生的文件进行监控才发一它是以daemon的形式运行的。 回复 更多评论 下面是cronatab 服务的man : Examples 1 To copy a file called mycronjobs into the /var/spool/cron/crontabs directory, enter the following: crontab mycronjobs The file will be copied as: /var/spool/cron/crontabs/ where is your current user name. 2 To write the time to the console every hour on the hour, enter: 0 * * * * echo The hour is `date` . >/dev/console 3 To run the calendar command at 6:30 a.m. every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday, enter: 30 6 * * 1,3,5 /usr/bin/calendar 4 To run the calendar command every day of the year at 6:30, enter the following: 30 6 * * * /usr/bin/calendar 5 To run a script called maintenance every day at midnight in August, enter the following: 0 0 * 8 * /u/harry/bin/maintenance 6 To define text for the standard input to a command, enter: 0 16 * 12 5 /usr/sbin/wall%HAPPY HOLIDAY!%Remember to turn in your time card. The text following the % (percent sign) defines the standard input to the wall command as: HAPPY HOLIDAY! Remember to turn in your time card. http://tech.ddvip.com/2008-11/122629526990895.html 名称 : crontab 使用权限 : 所有使用者 使用方式 : crontab [ -u user ] file crontab [ -u user ] { -l | -r | -e } 说明 : crontab 是用来让使用者在固定时间或固定间隔执行程序之用,换句话说,也就是类似使用者的时程表。-u user 是指设定指定 user 的时程表,这个前提是你必须要有其权限(比如说是 root)才能够指定他人的时程表。如果不使用 -u user 的话,就是表示设定自己的时程表。 参数 : crontab -e : 执行文字编辑器来设定时程表,内定的文字编辑器是 VI,如果你想用别的文字编辑器,则请先设定 VISUAL 环境变数来指定使用那个文字编辑器(比如说 setenv VISUAL joe) crontab -r : 删除目前的时程表 crontab -l : 列出目前的时程表 crontab file [-u user]-用指定的文件替代目前的crontab。 时程表的格式如下 : f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 program 其中 f1 是表示分钟,f2 表示小时,f3 表示一个月份中的第几日,f4 表示月份,f5 表示一个星期中的第几天。program 表示要执行的程序。 当 f1 为 * 时表示每分钟都要执行 program,f2 为 * 时表示每小时都要执行程序,其馀类推 当 f1 为 a-b 时表示从第 a 分钟到第 b 分钟这段时间内要执行,f2 为 a-b 时表示从第 a 到第 b 小时都要执行,其馀类推 当 f1 为 */n 时表示每 n 分钟个时间间隔执行一次,f2 为 */n 表示每 n 小时个时间间隔执行一次,其馀类推 当 f1 为 a, b, c,... 时表示第 a, b, c,... 分钟要执行,f2 为 a, b, c,... 时表示第 a, b, c...个小时要执行,其馀类推 使用者也可以将所有的设定先存放在档案 file 中,用 crontab file 的方式来设定时程表。 例子1 : Quote:#每天早上7点执行一次 /bin/ls : 0 7 * * * /bin/ls 在 12 月内, 每天的早上 6 点到 12 点中,每隔3个小时执行一次 /usr/bin/backup : 0 6-12/3 * 12 * /usr/bin/backup 周一到周五每天下午 5:00 寄一封信给 alex@domain.name : 0 17 * * 1-5 mail -s "hi" alex@domain.name < /tmp/maildata 每月每天的午夜 0 点 20 分, 2 点 20 分, 4 点 20 分....执行 echo "haha" 20 0-23/2 * * * echo "haha" 注意 : 当程序在你所指定的时间执行后,系统会寄一封信给你,显示该程序执行的内容,若是你不希望收到这样的信,请在每一行空一格之后加上 > /dev/null 2>&1 即可 例子2 : Quote:#每天早上6点10分 10 6 * * * date #每两个小时 0 */2 * * * date #晚上11点到早上8点之间每两个小时,早上8点 0 23-7/2,8 * * * date #每个月的4号和每个礼拜的礼拜一到礼拜三的早上11点 0 11 4 * mon-wed date #1月份日早上4点 0 4 1 jan * date 执行步骤如下: Quote:crontab -e 添加如下内容 0 0 * * * /nmon/nmon.ksh 在nmon目录下创建nmon.ksh文件,用vi编辑器编辑 Quote:cd /nmon/ /nmon/nmon_aix53 -fdt -s 90 -c 960
|