|
|
Bootstrapping Tomcat
The bootstrapping process is actually rather simple. All we have to do is:
1、Set up the environment variables required by this Tomcat instance
2、Instantiate the general class loaders that will be used for our running Tomcat instance
3、Initialize this Tomcat instance
4、Parse the main configuration file for a Tomcat instance, server.xml, converting each configuration element into the appropriate Tomcat component
5、Start up our outermost Top Level Element—the Server instance
6、Set up a shutdown hook
分别看看如何执行:
1、执行startup.bat,调用catalina.bat进行环境变量的设置,否则通过
Bootstrap的ini()
// Set Catalina path
setCatalinaHome();
setCatalinaBase();
2、classloader
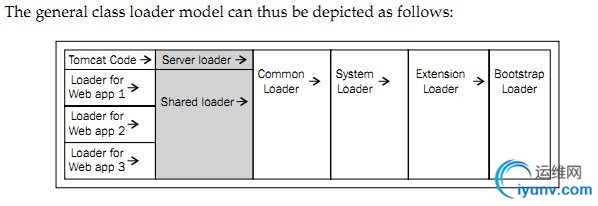
Our Bootstrap instance holds references to the following three class loaders:
1、commonLoader, which loads classes that are common across Tomcat, as well
as all the web applications.
2、catalinaLoader, or serverLoader, which loads classes that are used just
by Tomcat.
3、sharedLoader, which loads classes that are common just across all the web
applications within a Tomcat instance.
其中:org.apache.catalina.startup.CatalinaProperties类解析catalina.properties文件,
org.apache.catalina.startup.ClassLoaderFactory 的createClassLoader()方法将.jar文件url放入set,并返回StandardClassLoader
在ini方法中会
initClassLoaders();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
Class startupClass =
catalinaLoader.loadClass
("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();
而其中的initClassLoaders()方法会初始化loaders,如下:
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if( commonLoader == null ) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader=this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}}
上面代码
Class startupClass =catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();
实例化了startup实例。
4、解析Server.xml,使用了 Apache Commons Digester
It takes an XML document and a RuleSet document as inputs, and generates a graph of Java objects that
represents the structure that is defined in the XML instance document

The pattern:sax方式,例如:Server/Service/Connector
The rule:普通有4种
1、Creational actions (create an instance of a given class to represent this XML element)
创建行为
2、Property setting actions (call setters on the Java object representing this XML element, passing in the value of either a child element or an attribute)
属性设置
3、Method invocation actions (call the specified method on the Java object representing this element, passing in the specified parameters)
激活方法
4、Object linking actions (set an object reference by calling a setter on one object while passing in the other as an argument)
对象引用
Server.xml的Digester
通过Catalina.java中的createStartDigester ()方法创建,并设置规则
5、 在 Catalina.java中调用start()方法中调用getServer().initialize();
接着:services.initialize();
接着:connectors.initialize();
。。。(详见最后的代码跟踪)
6、shutdown hook
A shutdown hook is a standard Thread that encapsulates cleanup actions that should be taken before the Java runtime exits. All shutdown hooks are called by the runtime when the JVM is shutting down.
Therefore, the last task that we perform is to install a shutdown hook, as implemented by CatalinaShutdownHook. This hook is registered with the Java Runtime by invoking its addShutdownHook() method:
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(),
CatalinaShutdownHook is an inner class of Catalina and so has access to all the data members of Catalina. Its run() method is very simple. It just ensures that stop() is called on this instance of Catalina. This method invokes stop() on the StandardServer instance, which in turn performs a cascaded invocation of stop() on all its child components. Each child does the same for its children, until the entire server has been cleanly stopped.
使用类CatalinaShutdownHook实现,它继承Thread,run中进行清理
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}}
启动tomat代码跟踪

 View Code
View Code
1、Bootstrap.java中的main方法,启动tomcat;
调用init()方法初始化,并用Catalina.load(),获取server对象,并调用ini方法
// Start the new server
if (getServer() instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
getServer().initialize();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"))
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
else
log.error("Catalina.start", e);
}
}
但是server对象是怎么来的 ?
往回看,在load方法中,
// Create and execute our Digester
Digester digester = createStartDigester(); 中创建了规则,如下:
// Configure the actions we will be using
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
经过反射,到类ObjectCreateRule类的begin方法中
// Instantiate the new object and push it on the context stack
Class clazz = digester.getClassLoader().loadClass(realClassName);
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
利用反射创建对象,其中:realClassName =org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer
在类org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer构造方法中调用ServerFactory.setServer(this);
实现单例Server对象创建。
2、
getServer().initialize();方法中调用service的ini方法:其中services为解析server.xml
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services.initialize();
}
在 initialize
执行connector的ini方法
for (int i = 0; i < connectors.length; i++) {
try {
connectors.initialize();
connectors的来源也是server.xml配置文件,默认配置:
3、接下来分析connector,默认使用protocol="HTTP/1.1"协议
// Initializa adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
生成CoyoteAdapter,并设置,调用ini方法
protocolHandler.init();
4、接下来调用
endpoint.init();
我们了看看JIoEndpoint 类是做神马的?
* Handle incoming TCP connections.
*
* This class implement a simple server model: one listener thread accepts on a socket and
* creates a new worker thread for each incoming connection.
此类实现了简单的server模型:一个监听线程,接受socket并且为每一个到来的连接创建一个worker线程
真正干活的是这个!后面我们会分析它的start方法
接下来初始化其他conector
5、当以上初始化完成后,调用Catalina.start()方法,接着启动server.start()方法:
((Lifecycle) getServer()).start();
接着调用service.start()方法
接下来是一系列的container的start,后续在分析(会部署所有的项目)
在service.start()中,调用executors,connectors的start方法,我们直接往下看
synchronized (executors) {
for ( int i=0; i 0 && maxThreads > 0) {
// Only auto-disable keep-alive if the current thread usage % can be
// calculated correctly
if ((curThreads*100)/maxThreads > 75) {
keepAliveLeft = 1;
}
}
//以下设置了超时,如果没有超时,那依然使用同一个socket请求资源,此时不用重建socket,效率高
try {
socket.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.socket.timeout"), t);
error = true;
}
boolean keptAlive = false;
while (started && !error && keepAlive && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// Parsing the request header
try {
if (keptAlive) {
if (keepAliveTimeout > 0) {
socket.setSoTimeout(keepAliveTimeout);
}
else if (soTimeout > 0) {
socket.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);
}
}
inputBuffer.parseRequestLine();
request.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
keptAlive = true;
if (disableUploadTimeout) {
socket.setSoTimeout(soTimeout);
} else {
socket.setSoTimeout(timeout);
}
inputBuffer.parseHeaders();
} catch (IOException e) {
error = true;
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), t);
}
// 400 - Bad Request
response.setStatus(400);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
if (!error) {
// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
try {
prepareRequest();
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
}
// 400 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(400);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
}
if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && --keepAliveLeft == 0)
keepAlive = false;
// Process the request in the adapter
if (!error) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
adapter.service(request, response);
// Handle when the response was committed before a serious
// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both
// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.
// If we fail here, then the response is likely already
// committed, so we can't try and set headers.
if(keepAlive && !error) { // Avoid checking twice.
error = response.getErrorException() != null ||
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus());
}
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
error = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
// If we know we are closing the connection, don't drain input.
// This way uploading a 100GB file doesn't tie up the thread
// if the servlet has rejected it.
if(error)
inputBuffer.setSwallowInput(false);
inputBuffer.endRequest();
} catch (IOException e) {
error = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.finish"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
outputBuffer.endRequest();
} catch (IOException e) {
error = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.response.finish"), t);
error = true;
}
// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
// and error, and update the statistics counter
if (error) {
response.setStatus(500);
}
request.updateCounters();
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
// Don't reset the param - we'll see it as ended. Next request
// will reset it
// thrA.setParam(null);
// Next request
inputBuffer.nextRequest();
outputBuffer.nextRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
// Recycle
inputBuffer.recycle();
outputBuffer.recycle();
this.socket = null;
// Recycle ssl info
sslSupport = null;
} |
|